Gwanjun Shin
NeuroFlow: Development of lightweight and efficient model integration scheduling strategy for autonomous driving system
Dec 15, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a specialized autonomous driving system that takes into account the unique constraints and characteristics of automotive systems, aiming for innovative advancements in autonomous driving technology. The proposed system systematically analyzes the intricate data flow in autonomous driving and provides functionality to dynamically adjust various factors that influence deep learning models. Additionally, for algorithms that do not rely on deep learning models, the system analyzes the flow to determine resource allocation priorities. In essence, the system optimizes data flow and schedules efficiently to ensure real-time performance and safety. The proposed system was implemented in actual autonomous vehicles and experimentally validated across various driving scenarios. The experimental results provide evidence of the system's stable inference and effective control of autonomous vehicles, marking a significant turning point in the development of autonomous driving systems.
Hybrid tracker based optimal path tracking system for complex road environments for autonomous driving
Apr 29, 2021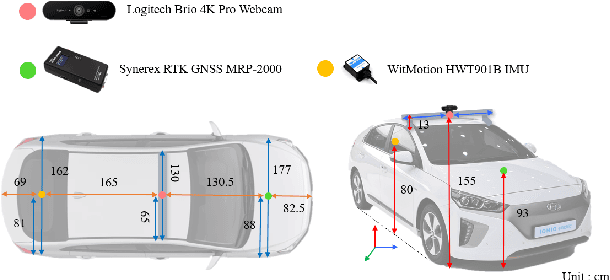
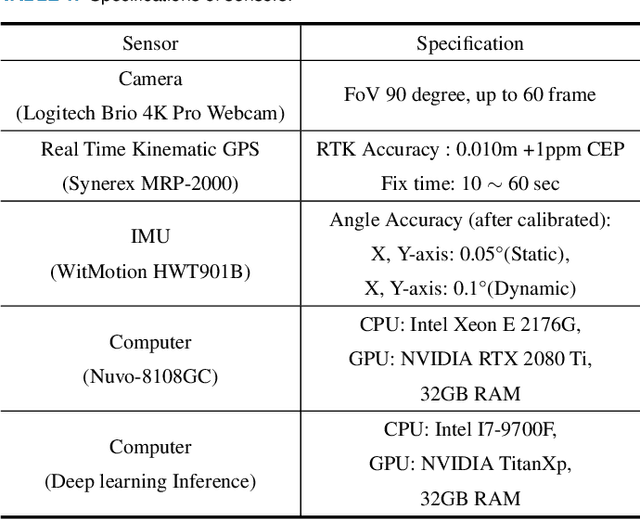
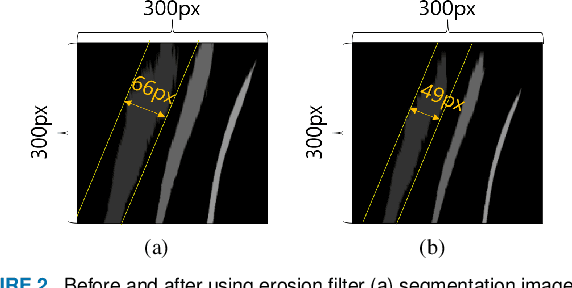
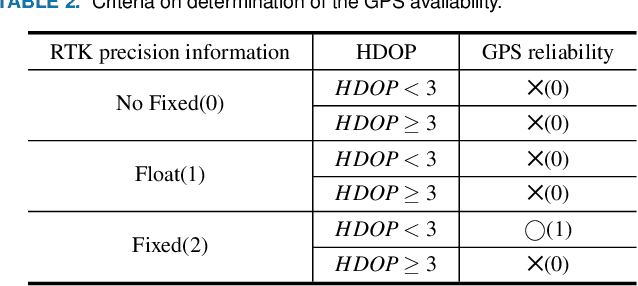
Abstract:Path tracking system plays a key technology in autonomous driving. The system should be driven accurately along the lane and be careful not to cause any inconvenience to passengers. To address such tasks, this paper proposes hybrid tracker based optimal path tracking system. By applying a deep learning based lane detection algorithm and a designated fast lane fitting algorithm, this paper developed a lane processing algorithm that shows a match rate with actual lanes with minimal computational cost. In addition, three modified path tracking algorithms were designed using the GPS based path or the vision based path. In the driving system, a match rate for the correct ideal path does not necessarily represent driving stability. This paper proposes hybrid tracker based optimal path tracking system by applying the concept of an observer that selects the optimal tracker appropriately in complex road environments. The driving stability has been studied in complex road environments such as straight road with multiple 3-way junctions, roundabouts, intersections, and tunnels. Consequently, the proposed system experimentally showed the high performance with consistent driving comfort by maintaining the vehicle within the lanes accurately even in the presence of high complexity of road conditions. Code will be available in https://github.com/DGIST-ARTIV.
Estimation of Closest In-Path Vehicle by Low-Channel LiDAR and Camera Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Vehicle
Mar 25, 2021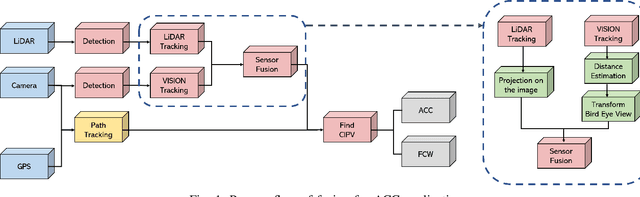
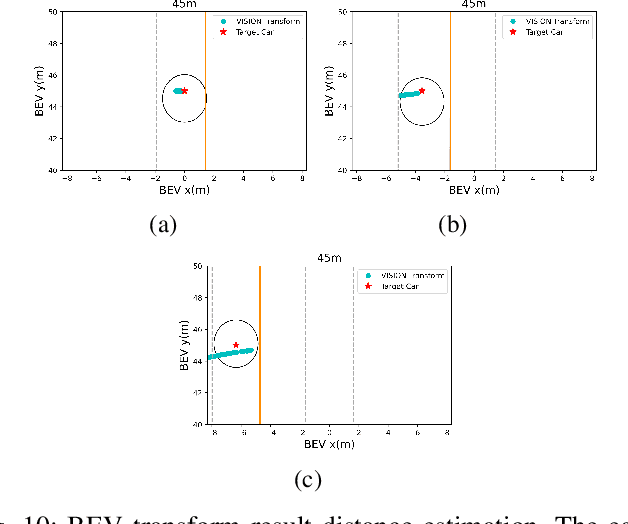
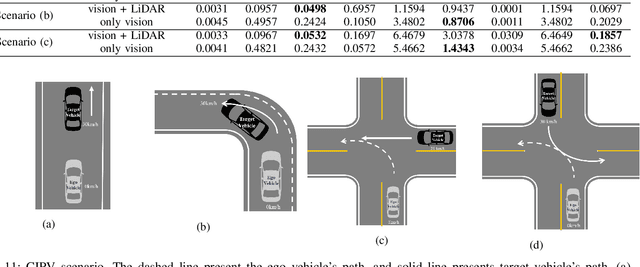
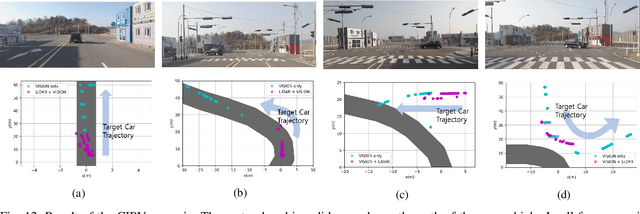
Abstract:In autonomous driving, using a variety of sensors to recognize preceding vehicles in middle and long distance is helpful for improving driving performance and developing various functions. However, if only LiDAR or camera is used in the recognition stage, it is difficult to obtain necessary data due to the limitations of each sensor. In this paper, we proposed a method of converting the tracking data of vision into bird's eye view (BEV) coordinates using an equation that projects LiDAR points onto an image, and a method of fusion between LiDAR and vision tracked data. Thus, the newly proposed method was effective through the results of detecting closest in-path vehicle (CIPV) in various situations. In addition, even when experimenting with the EuroNCAP autonomous emergency braking (AEB) test protocol using the result of fusion, AEB performance is improved through improved cognitive performance than when using only LiDAR. In experimental results, the performance of the proposed method was proved through actual vehicle tests in various scenarios. Consequently, it is convincing that the newly proposed sensor fusion method significantly improves the ACC function in autonomous maneuvering. We expect that this improvement in perception performance will contribute to improving the overall stability of ACC.
Real-Time Navigation System for a Low-Cost Mobile Robot with an RGB-D Camera
Mar 04, 2021



Abstract:Currently, mobile robots are developing rapidly and are finding numerous applications in industry. However, there remain a number of problems related to their practical use, such as the need for expensive hardware and their high power consumption levels. In this study, we propose a navigation system that is operable on a low-end computer with an RGB-D camera and a mobile robot platform for the operation of an integrated autonomous driving system. The proposed system does not require LiDARs or a GPU. Our raw depth image ground segmentation approach extracts a traversability map for the safe driving of low-body mobile robots. It is designed to guarantee real-time performance on a low-cost commercial single board computer with integrated SLAM, global path planning, and motion planning. Running sensor data processing and other autonomous driving functions simultaneously, our navigation method performs rapidly at a refresh rate of 18Hz for control command, whereas other systems have slower refresh rates. Our method outperforms current state-of-the-art navigation approaches as shown in 3D simulation tests. In addition, we demonstrate the applicability of our mobile robot system through successful autonomous driving in a residential lobby.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge