Guoyuan Liang
Trunk-branch Contrastive Network with Multi-view Deformable Aggregation for Multi-view Action Recognition
Feb 23, 2025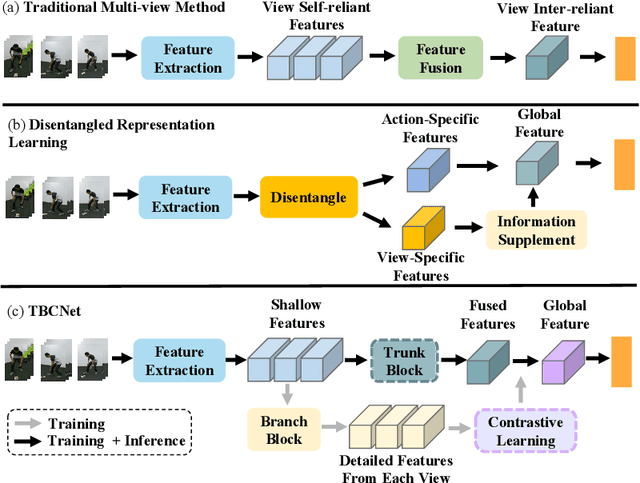
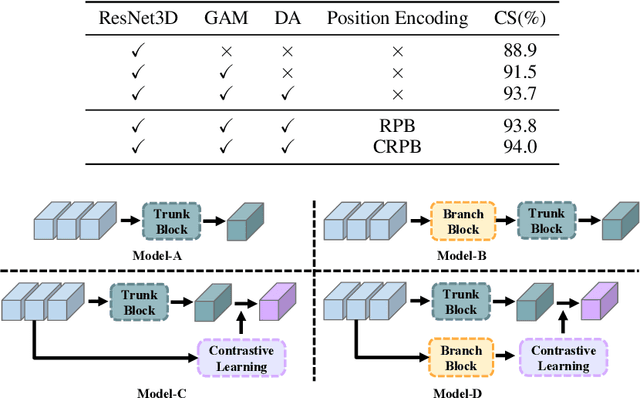
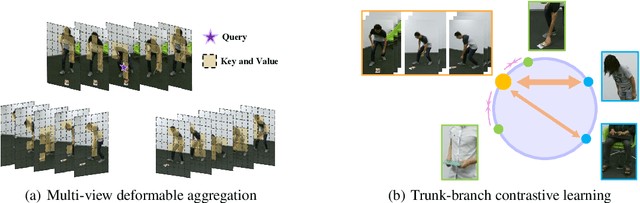
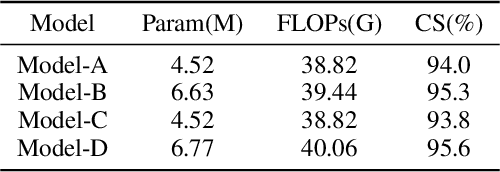
Abstract:Multi-view action recognition aims to identify actions in a given multi-view scene. Traditional studies initially extracted refined features from each view, followed by implemented paired interaction and integration, but they potentially overlooked the critical local features in each view. When observing objects from multiple perspectives, individuals typically form a comprehensive impression and subsequently fill in specific details. Drawing inspiration from this cognitive process, we propose a novel trunk-branch contrastive network (TBCNet) for RGB-based multi-view action recognition. Distinctively, TBCNet first obtains fused features in the trunk block and then implicitly supplements vital details provided by the branch block via contrastive learning, generating a more informative and comprehensive action representation. Within this framework, we construct two core components: the multi-view deformable aggregation and the trunk-branch contrastive learning. MVDA employed in the trunk block effectively facilitates multi-view feature fusion and adaptive cross-view spatio-temporal correlation, where a global aggregation module is utilized to emphasize significant spatial information and a composite relative position bias is designed to capture the intra- and cross-view relative positions. Moreover, a trunk-branch contrastive loss is constructed between aggregated features and refined details from each view. By incorporating two distinct weights for positive and negative samples, a weighted trunk-branch contrastive loss is proposed to extract valuable information and emphasize subtle inter-class differences. The effectiveness of TBCNet is verified by extensive experiments on four datasets including NTU-RGB+D 60, NTU-RGB+D 120, PKU-MMD, and N-UCLA dataset. Compared to other RGB-based methods, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in cross-subject and cross-setting protocols.
Subpixel Edge Localization Based on Converted Intensity Summation under Stable Edge Region
Feb 23, 2025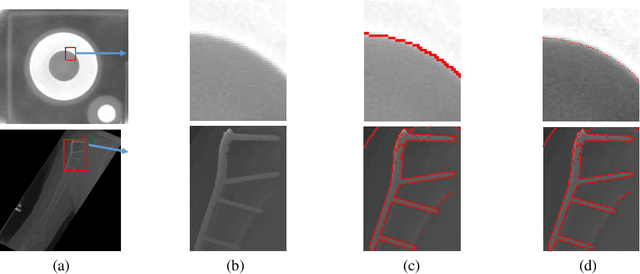

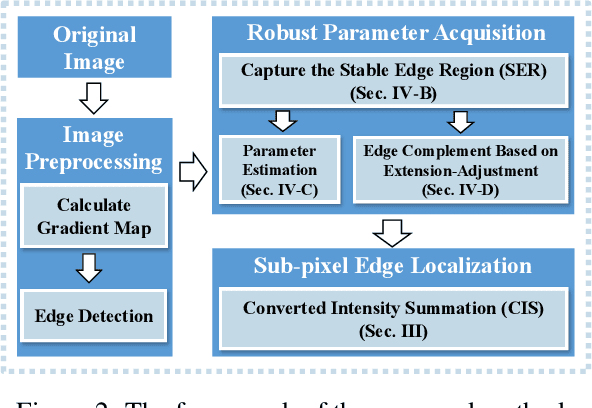
Abstract:To satisfy the rigorous requirements of precise edge detection in critical high-accuracy measurements, this article proposes a series of efficient approaches for localizing subpixel edge. In contrast to the fitting based methods, which consider pixel intensity as a sample value derived from a specific model. We take an innovative perspective by assuming that the intensity at the pixel level can be interpreted as a local integral mapping in the intensity model for subpixel localization. Consequently, we propose a straightforward subpixel edge localization method called Converted Intensity Summation (CIS). To address the limited robustness associated with focusing solely on the localization of individual edge points, a Stable Edge Region (SER) based algorithm is presented to alleviate local interference near edges. Given the observation that the consistency of edge statistics exists in the local region, the algorithm seeks correlated stable regions in the vicinity of edges to facilitate the acquisition of robust parameters and achieve higher precision positioning. In addition, an edge complement method based on extension-adjustment is also introduced to rectify the irregular edges through the efficient migration of SERs. A large number of experiments are conducted on both synthetic and real image datasets which cover common edge patterns as well as various real scenarios such as industrial PCB images, remote sensing and medical images. It is verified that CIS can achieve higher accuracy than the state-of-the-art method, while requiring less execution time. Moreover, by integrating SER into CIS, the proposed algorithm demonstrates excellent performance in further improving the anti-interference capability and positioning accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge