Guangzhi Chen
Subspace Prototype Guidance for Mitigating Class Imbalance in Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Aug 20, 2024
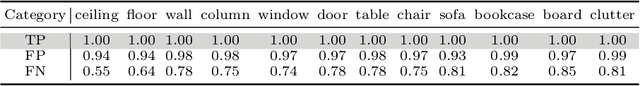
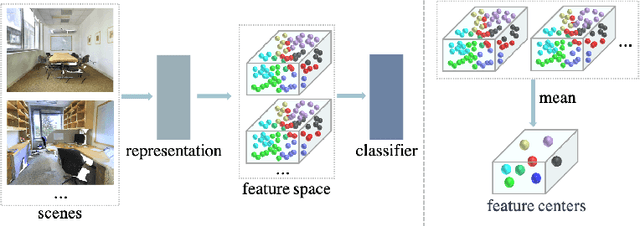
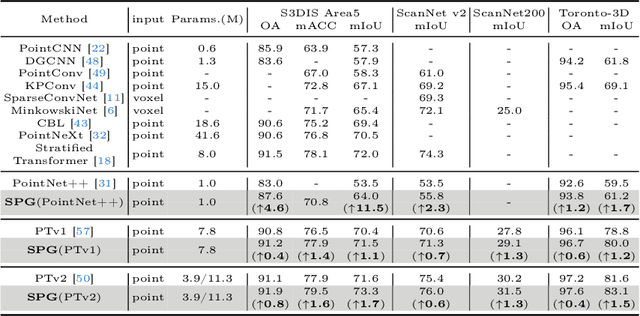
Abstract:Point cloud semantic segmentation can significantly enhance the perception of an intelligent agent. Nevertheless, the discriminative capability of the segmentation network is influenced by the quantity of samples available for different categories. To mitigate the cognitive bias induced by class imbalance, this paper introduces a novel method, namely subspace prototype guidance (\textbf{SPG}), to guide the training of segmentation network. Specifically, the point cloud is initially separated into independent point sets by category to provide initial conditions for the generation of feature subspaces. The auxiliary branch which consists of an encoder and a projection head maps these point sets into separate feature subspaces. Subsequently, the feature prototypes which are extracted from the current separate subspaces and then combined with prototypes of historical subspaces guide the feature space of main branch to enhance the discriminability of features of minority categories. The prototypes derived from the feature space of main branch are also employed to guide the training of the auxiliary branch, forming a supervisory loop to maintain consistent convergence of the entire network. The experiments conducted on the large public benchmarks (i.e. S3DIS, ScanNet v2, ScanNet200, Toronto-3D) and collected real-world data illustrate that the proposed method significantly improves the segmentation performance and surpasses the state-of-the-art method. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/Javion11/PointLiBR.git}.
RIMformer: An End-to-End Transformer for FMCW Radar Interference Mitigation
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) radar plays a pivotal role in the field of remote sensing. The increasing degree of FMCW radar deployment has increased the mutual interference, which weakens the detection capabilities of radars and threatens reliability and safety of systems. In this paper, a novel FMCW radar interference mitigation (RIM) method, termed as RIMformer, is proposed by using an end-to-end Transformer-based structure. In the RIMformer, a dual multi-head self-attention mechanism is proposed to capture the correlations among the distinct distance elements of intermediate frequency (IF) signals. Additionally, an improved convolutional block is integrated to harness the power of convolution for extracting local features. The architecture is designed to process time-domain IF signals in an end-to-end manner, thereby avoiding the need for additional manual data processing steps. The improved decoder structure ensures the parallelization of the network to increase its computational efficiency. Simulation and measurement experiments are carried out to validate the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that the proposed RIMformer can effectively mitigate interference and restore the target signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge