Graziano Pravadelli
A Comprehensive Review of Automated Data Annotation Techniques in Human Activity Recognition
Jul 12, 2023Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) has become one of the leading research topics of the last decade. As sensing technologies have matured and their economic costs have declined, a host of novel applications, e.g., in healthcare, industry, sports, and daily life activities have become popular. The design of HAR systems requires different time-consuming processing steps, such as data collection, annotation, and model training and optimization. In particular, data annotation represents the most labor-intensive and cumbersome step in HAR, since it requires extensive and detailed manual work from human annotators. Therefore, different methodologies concerning the automation of the annotation procedure in HAR have been proposed. The annotation problem occurs in different notions and scenarios, which all require individual solutions. In this paper, we provide the first systematic review on data annotation techniques for HAR. By grouping existing approaches into classes and providing a taxonomy, our goal is to support the decision on which techniques can be beneficially used in a given scenario.
WiFiEye -- Seeing over WiFi Made Accessible
Apr 06, 2022
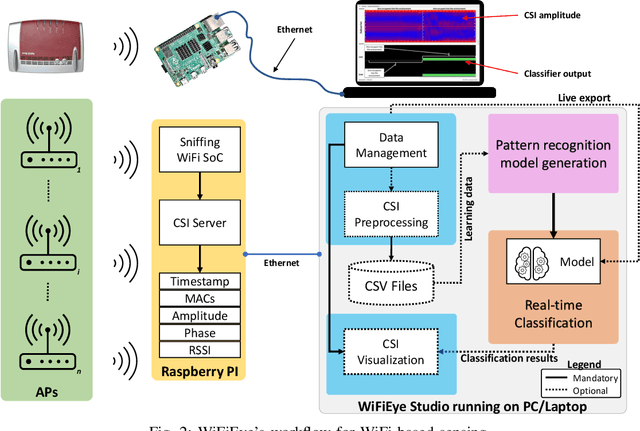


Abstract:While commonly used for communication purposes, an increasing number of recent studies consider WiFi for sensing. In particular, wireless signals are altered (e.g., reflected and attenuated) by the human body and objects in the environment. This can be perceived by an observer to infer information on human activities or changes in the environment and, hence, to "see" over WiFi. Until now, works on WiFi-based sensing have resulted in a set of custom software tools - each designed for a specific purpose. Moreover, given how scattered the literature is, it is difficult to even identify all steps/functions necessary to build a basic system for WiFi-based sensing. This has led to a high entry barrier, hindering further research in this area. There has been no effort to integrate these tools or to build a general software framework that can serve as the basis for further research, e.g., on using machine learning to interpret the altered WiFi signals. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose WiFiEye - a generic software framework that makes all necessary steps/functions available "out of the box". This way, WiFiEye allows researchers to easily bootstrap new WiFi-based sensing applications, thereby, focusing on research rather than on implementation aspects. To illustrate WiFiEye's workflow, we present a case study on WiFi-based human activity recognition.
Estimating indoor occupancy through low-cost BLE devices
Jan 30, 2021



Abstract:Detecting the presence and estimating the number of subjects in an indoor environment has grown in importance recently. For example, the information if a room is unoccupied can be used for automatically switching off the light, air conditioning, and ventilation, thereby saving significant amounts of energy in public buildings. Most existing solutions rely on dedicated hardware installations, which involve presence sensors, video cameras, and carbon dioxide sensors. Unfortunately, such approaches are costly, subject to privacy concerns, have high computational requirements, and lack ubiquitousness. The work presented in this article addresses these limitations by proposing a low-cost system for occupancy detection. Our approach builds upon detecting variations in Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) signals related to the presence of humans. The effectiveness of this approach is evaluated by performing comprehensive tests on 5 different datasets. We apply different pattern recognition models and compare our methodology with systems building upon IEEE 802.11 (WiFi). On average, in different environments, we can correctly classify the occupancy with an accuracy of 97.97\%. When estimating the number of people in a room, on average, the estimated number of subjects differs from the actual one by 0.32 persons. We conclude that the performance of our system is comparable to existing ones based on WiFi, while leading to a significantly reduced cost and installation effort. Hence, our approach makes occupancy detection practical for real-world deployments.
B-HAR: an open-source baseline framework for in depth study of human activity recognition datasets and workflows
Jan 23, 2021



Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR), based on machine and deep learning algorithms is considered one of the most promising technologies to monitor professional and daily life activities for different categories of people (e.g., athletes, elderly, kids, employers) in order to provide a variety of services related, for example to well-being, empowering of technical performances, prevention of risky situation, and educational purposes. However, the analysis of the effectiveness and the efficiency of HAR methodologies suffers from the lack of a standard workflow, which might represent the baseline for the estimation of the quality of the developed pattern recognition models. This makes the comparison among different approaches a challenging task. In addition, researchers can make mistakes that, when not detected, definitely affect the achieved results. To mitigate such issues, this paper proposes an open-source automatic and highly configurable framework, named B-HAR, for the definition, standardization, and development of a baseline framework in order to evaluate and compare HAR methodologies. It implements the most popular data processing methods for data preparation and the most commonly used machine and deep learning pattern recognition models.
Joint Distribution and Transitions of Pain and Activity in Critically Ill Patients
Apr 20, 2020



Abstract:Pain and physical function are both essential indices of recovery in critically ill patients in the Intensive Care Units (ICU). Simultaneous monitoring of pain intensity and patient activity can be important for determining which analgesic interventions can optimize mobility and function, while minimizing opioid harm. Nonetheless, so far, our knowledge of the relation between pain and activity has been limited to manual and sporadic activity assessments. In recent years, wearable devices equipped with 3-axis accelerometers have been used in many domains to provide a continuous and automated measure of mobility and physical activity. In this study, we collected activity intensity data from 57 ICU patients, using the Actigraph GT3X device. We also collected relevant clinical information, including nurse assessments of pain intensity, recorded every 1-4 hours. Our results show the joint distribution and state transition of joint activity and pain states in critically ill patients.
Human Activity Recognition using Inertial, Physiological and Environmental Sensors: a Comprehensive Survey
Apr 19, 2020



Abstract:In the last decade, Human Activity Recognition (HAR) has become a very important research area, especially due to the spread of electronic devices such as smartphones, smartwatches and video cameras present in our daily lives. In addition, the advance of Deep Learning (DL) has led researchers to use HAR in various domains including health and well-being applications. HAR is one of the most promising assistive technology tools to support elderly's daily life. However, this class of algorithms requires large amounts of data. Furthermore, not all the HAR application fields generate a significant amount of data and not all of them provide the computational power that DL models in HAR require. This survey focuses on critical applications of Machine Learning (ML) in the fields of HAR, largely oriented to Daily Life Activities by presenting an overview of the publications on HAR based on ML and inertial, physiological and environmental sensors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge