Graham Thomas
Automatic Recognition of Food Ingestion Environment from the AIM-2 Wearable Sensor
May 13, 2024


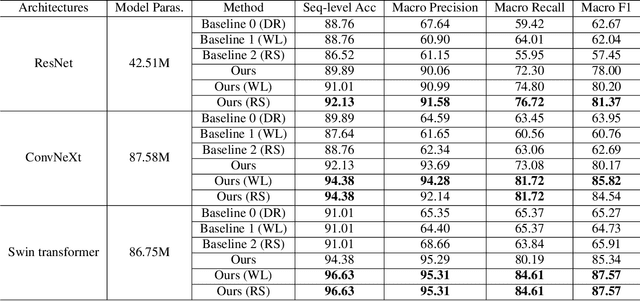
Abstract:Detecting an ingestion environment is an important aspect of monitoring dietary intake. It provides insightful information for dietary assessment. However, it is a challenging problem where human-based reviewing can be tedious, and algorithm-based review suffers from data imbalance and perceptual aliasing problems. To address these issues, we propose a neural network-based method with a two-stage training framework that tactfully combines fine-tuning and transfer learning techniques. Our method is evaluated on a newly collected dataset called ``UA Free Living Study", which uses an egocentric wearable camera, AIM-2 sensor, to simulate food consumption in free-living conditions. The proposed training framework is applied to common neural network backbones, combined with approaches in the general imbalanced classification field. Experimental results on the collected dataset show that our proposed method for automatic ingestion environment recognition successfully addresses the challenging data imbalance problem in the dataset and achieves a promising overall classification accuracy of 96.63%.
CAD -- Contextual Multi-modal Alignment for Dynamic AVQA
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:In the context of Audio Visual Question Answering (AVQA) tasks, the audio visual modalities could be learnt on three levels: 1) Spatial, 2) Temporal, and 3) Semantic. Existing AVQA methods suffer from two major shortcomings; the audio-visual (AV) information passing through the network isn't aligned on Spatial and Temporal levels; and, inter-modal (audio and visual) Semantic information is often not balanced within a context; this results in poor performance. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end Contextual Multi-modal Alignment (CAD) network that addresses the challenges in AVQA methods by i) introducing a parameter-free stochastic Contextual block that ensures robust audio and visual alignment on the Spatial level; ii) proposing a pre-training technique for dynamic audio and visual alignment on Temporal level in a self-supervised setting, and iii) introducing a cross-attention mechanism to balance audio and visual information on Semantic level. The proposed novel CAD network improves the overall performance over the state-of-the-art methods on average by 9.4% on the MUSIC-AVQA dataset. We also demonstrate that our proposed contributions to AVQA can be added to the existing methods to improve their performance without additional complexity requirements.
SEM-POS: Grammatically and Semantically Correct Video Captioning
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:Generating grammatically and semantically correct captions in video captioning is a challenging task. The captions generated from the existing methods are either word-by-word that do not align with grammatical structure or miss key information from the input videos. To address these issues, we introduce a novel global-local fusion network, with a Global-Local Fusion Block (GLFB) that encodes and fuses features from different parts of speech (POS) components with visual-spatial features. We use novel combinations of different POS components - 'determinant + subject', 'auxiliary verb', 'verb', and 'determinant + object' for supervision of the POS blocks - Det + Subject, Aux Verb, Verb, and Det + Object respectively. The novel global-local fusion network together with POS blocks helps align the visual features with language description to generate grammatically and semantically correct captions. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on benchmark MSVD and MSRVTT datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach generates more grammatically and semantically correct captions compared to the existing methods, achieving the new state-of-the-art. Ablations on the POS blocks and the GLFB demonstrate the impact of the contributions on the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge