Giuseppe Pisano
Large Language Models and Explainable Law: a Hybrid Methodology
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:The paper advocates for LLMs to enhance the accessibility, usage and explainability of rule-based legal systems, contributing to a democratic and stakeholder-oriented view of legal technology. A methodology is developed to explore the potential use of LLMs for translating the explanations produced by rule-based systems, from high-level programming languages to natural language, allowing all users a fast, clear, and accessible interaction with such technologies. The study continues by building upon these explanations to empower laypeople with the ability to execute complex juridical tasks on their own, using a Chain of Prompts for the autonomous legal comparison of different rule-based inferences, applied to the same factual case.
Legal Summarisation through LLMs: The PRODIGIT Project
Aug 04, 2023


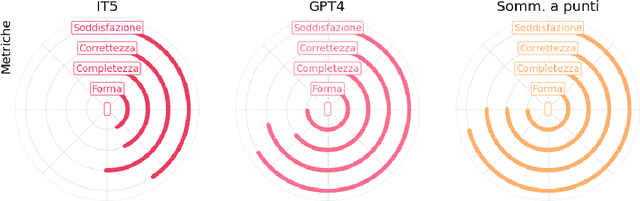
Abstract:We present some initial results of a large-scale Italian project called PRODIGIT which aims to support tax judges and lawyers through digital technology, focusing on AI. We have focused on generation of summaries of judicial decisions and on the extraction of related information, such as the identification of legal issues and decision-making criteria, and the specification of keywords. To this end, we have deployed and evaluated different tools and approaches to extractive and abstractive summarisation. We have applied LLMs, and particularly on GPT4, which has enabled us to obtain results that proved satisfactory, according to an evaluation by expert tax judges and lawyers. On this basis, a prototype application is being built which will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge