Giuseppe Di Fabbrizio
ATT Labs Research
Active Annotation: bootstrapping annotation lexicon and guidelines for supervised NLU learning
Aug 12, 2019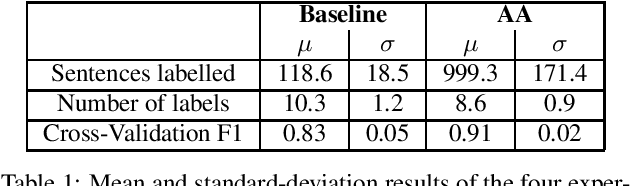
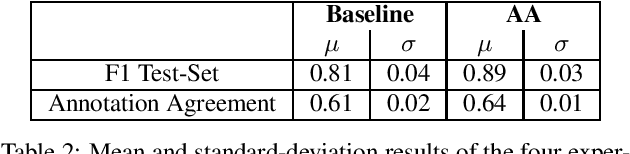
Abstract:Natural Language Understanding (NLU) models are typically trained in a supervised learning framework. In the case of intent classification, the predicted labels are predefined and based on the designed annotation schema while the labelling process is based on a laborious task where annotators manually inspect each utterance and assign the corresponding label. We propose an Active Annotation (AA) approach where we combine an unsupervised learning method in the embedding space, a human-in-the-loop verification process, and linguistic insights to create lexicons that can be open categories and adapted over time. In particular, annotators define the y-label space on-the-fly during the annotation using an iterative process and without the need for prior knowledge about the input data. We evaluate the proposed annotation paradigm in a real use-case NLU scenario. Results show that our Active Annotation paradigm achieves accurate and higher quality training data, with an annotation speed of an order of magnitude higher with respect to the traditional human-only driven baseline annotation methodology.
* 4 pages
Evaluating Competing Agent Strategies for a Voice Email Agent
Jun 13, 1997
Abstract:This paper reports experimental results comparing a mixed-initiative to a system-initiative dialog strategy in the context of a personal voice email agent. To independently test the effects of dialog strategy and user expertise, users interact with either the system-initiative or the mixed-initiative agent to perform three successive tasks which are identical for both agents. We report performance comparisons across agent strategies as well as over tasks. This evaluation utilizes and tests the PARADISE evaluation framework, and discusses the performance function derivable from the experimental data.
* 6 pages latex, uses icassp91.sty, psfig
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge