Gina R. Bai
Fair Enough: Searching for Sufficient Measures of Fairness
Oct 25, 2021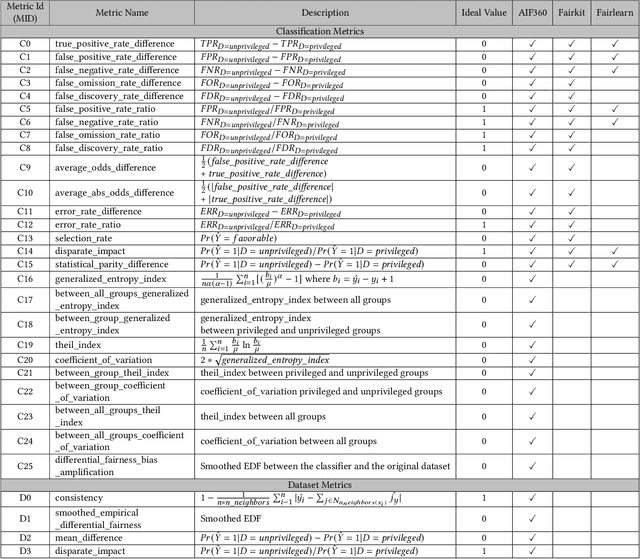
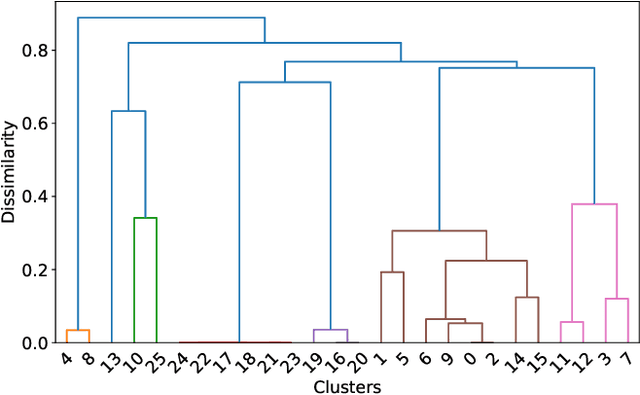
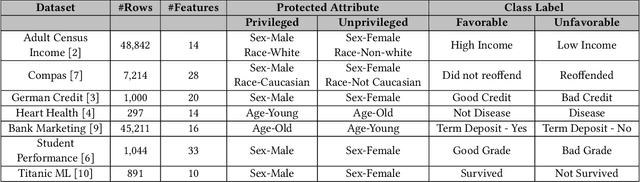
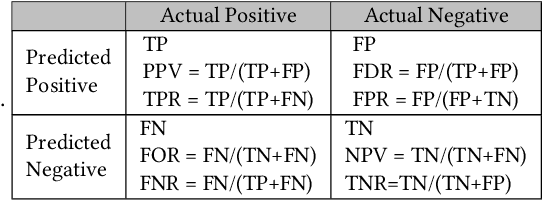
Abstract:Testing machine learning software for ethical bias has become a pressing current concern. In response, recent research has proposed a plethora of new fairness metrics, for example, the dozens of fairness metrics in the IBM AIF360 toolkit. This raises the question: How can any fairness tool satisfy such a diverse range of goals? While we cannot completely simplify the task of fairness testing, we can certainly reduce the problem. This paper shows that many of those fairness metrics effectively measure the same thing. Based on experiments using seven real-world datasets, we find that (a) 26 classification metrics can be clustered into seven groups, and (b) four dataset metrics can be clustered into three groups. Further, each reduced set may actually predict different things. Hence, it is no longer necessary (or even possible) to satisfy all fairness metrics. In summary, to simplify the fairness testing problem, we recommend the following steps: (1) determine what type of fairness is desirable (and we offer a handful of such types); then (2) lookup those types in our clusters; then (3) just test for one item per cluster. To support that processing, all our scripts (and example datasets) are available at https://github.com/Repoanonymous/Fairness\_Metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge