Ghazale Ghorbanzade
Selection of Proper EEG Channels for Subject Intention Classification Using Deep Learning
Jul 24, 2020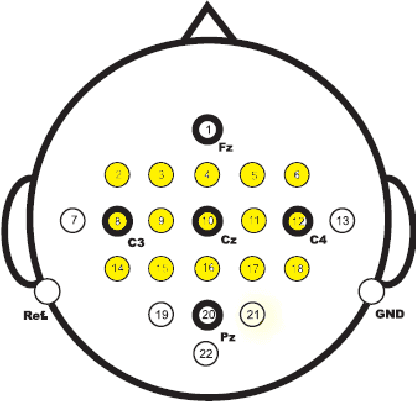
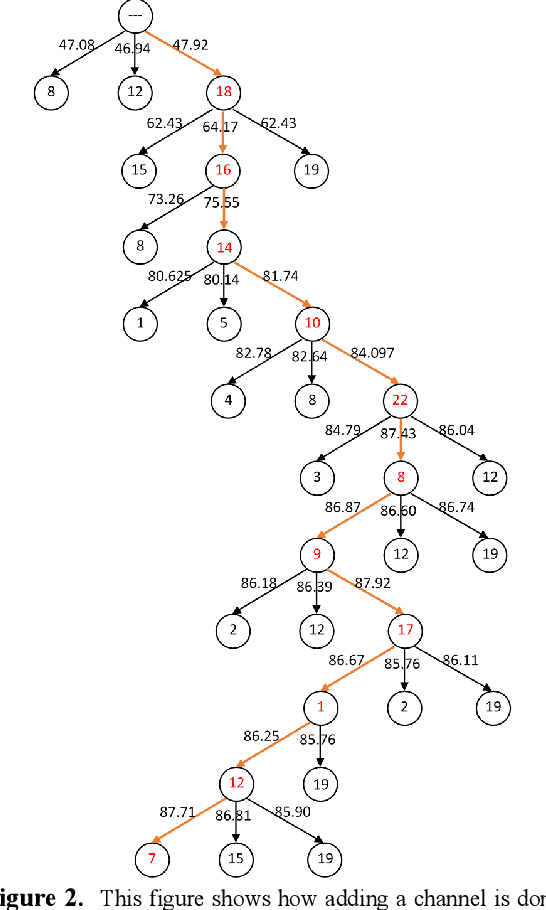
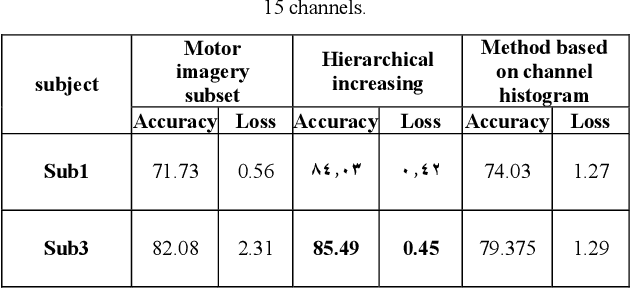
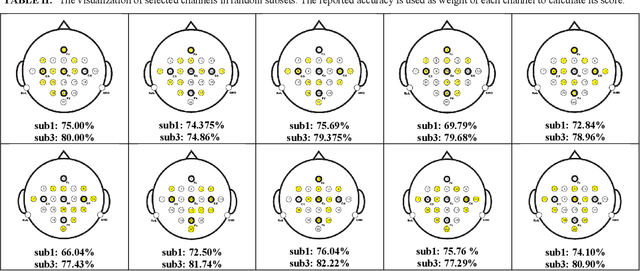
Abstract:Brain signals could be used to control devices to assist individuals with disabilities. Signals such as electroencephalograms are complicated and hard to interpret. A set of signals are collected and should be classified to identify the intention of the subject. Different approaches have tried to reduce the number of channels before sending them to a classifier. We are proposing a deep learning-based method for selecting an informative subset of channels that produce high classification accuracy. The proposed network could be trained for an individual subject for the selection of an appropriate set of channels. Reduction of the number of channels could reduce the complexity of brain-computer-interface devices. Our method could find a subset of channels. The accuracy of our approach is comparable with a model trained on all channels. Hence, our model's temporal and power costs are low, while its accuracy is kept high.
Image Inpainting by Multiscale Spline Interpolation
Jan 10, 2020
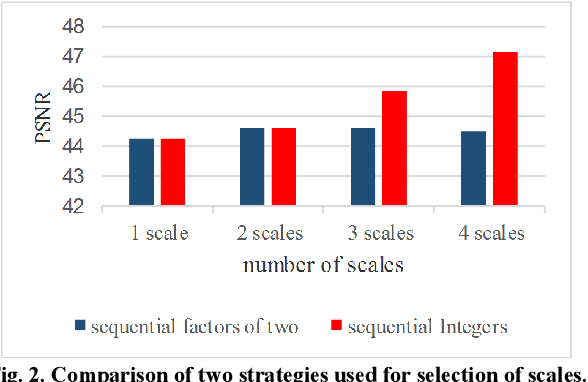


Abstract:Recovering the missing regions of an image is a task that is called image inpainting. Depending on the shape of missing areas, different methods are presented in the literature. One of the challenges of this problem is extracting features that lead to better results. Experimental results show that both global and local features are useful for this purpose. In this paper, we propose a multi-scale image inpainting method that utilizes both local and global features. The first step of this method is to determine how many scales we need to use, which depends on the width of the lines in the map of the missing region. Then we apply adaptive image inpainting to the damaged areas of the image, and the lost pixels are predicted. Each scale is inpainted and the result is resized to the original size. Then a voting process produces the final result. The proposed method is tested on damaged images with scratches and creases. The metric that we use to evaluate our approach is PSNR. On average, we achieved 1.2 dB improvement over some existing inpainting approaches.
Image Inpainting by Adaptive Fusion of Variable Spline Interpolations
Nov 03, 2019


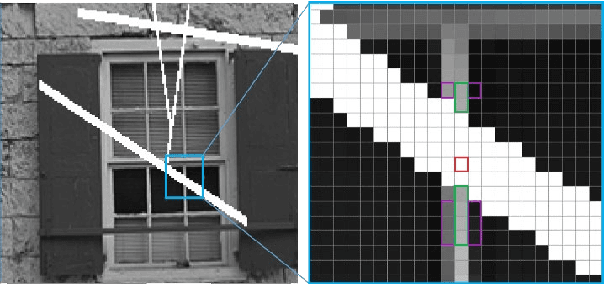
Abstract:There are many methods for image enhancement. Image inpainting is one of them which could be used in reconstruction and restoration of scratch images or editing images by adding or removing objects. According to its application, different algorithmic and learning methods are proposed. In this paper, the focus is on applications, which enhance the old and historical scratched images. For this purpose, we proposed an adaptive spline interpolation. In this method, a different number of neighbors in four directions are considered for each pixel in the lost block. In the previous methods, predicting the lost pixels that are on edges is the problem. To address this problem, we consider horizontal and vertical edge information. If the pixel is located on an edge, then we use the predicted value in that direction. In other situations, irrelevant predicted values are omitted, and the average of rest values is used as the value of the missing pixel. The method evaluates by PSNR and SSIM metrics on the Kodak dataset. The results show improvement in PSNR and SSIM compared to similar procedures. Also, the run time of the proposed method outperforms others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge