Geunho Lee
Siamese Meets Diffusion Network: SMDNet for Enhanced Change Detection in High-Resolution RS Imagery
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Recently, the application of deep learning to change detection (CD) has significantly progressed in remote sensing images. In recent years, CD tasks have mostly used architectures such as CNN and Transformer to identify these changes. However, these architectures have shortcomings in representing boundary details and are prone to false alarms and missed detections under complex lighting and weather conditions. For that, we propose a new network, Siamese Meets Diffusion Network (SMDNet). This network combines the Siam-U2Net Feature Differential Encoder (SU-FDE) and the denoising diffusion implicit model to improve the accuracy of image edge change detection and enhance the model's robustness under environmental changes. First, we propose an innovative SU-FDE module that utilizes shared weight features to capture differences between time series images and identify similarities between features to enhance edge detail detection. Furthermore, we add an attention mechanism to identify key coarse features to improve the model's sensitivity and accuracy. Finally, the diffusion model of progressive sampling is used to fuse key coarse features, and the noise reduction ability of the diffusion model and the advantages of capturing the probability distribution of image data are used to enhance the adaptability of the model in different environments. Our method's combination of feature extraction and diffusion models demonstrates effectiveness in change detection in remote sensing images. The performance evaluation of SMDNet on LEVIR-CD, DSIFN-CD, and CDD datasets yields validated F1 scores of 90.99%, 88.40%, and 88.47%, respectively. This substantiates the advanced capabilities of our model in accurately identifying variations and intricate details.
Deep neural network Grad-Shafranov solver constrained with measured magnetic signals
Nov 07, 2019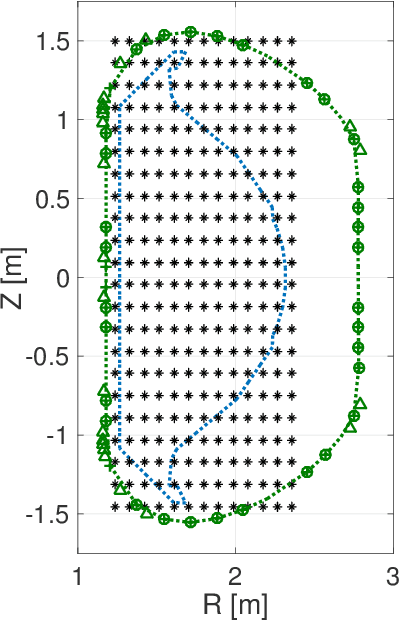
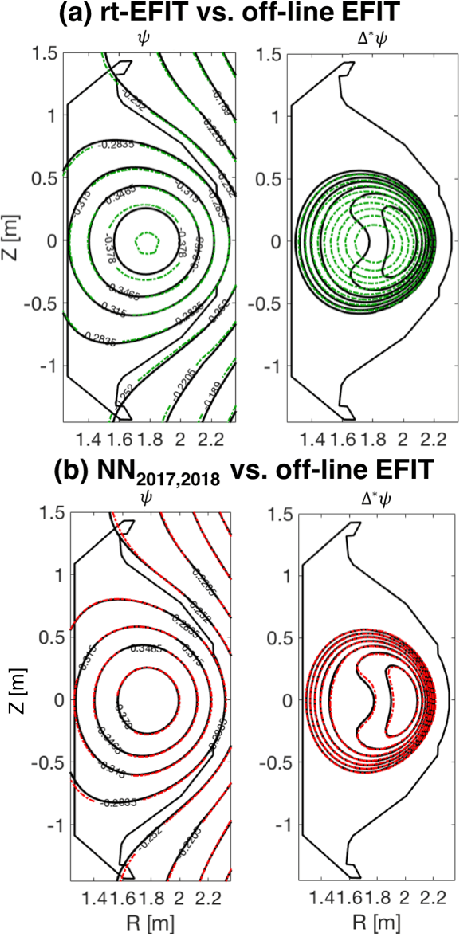
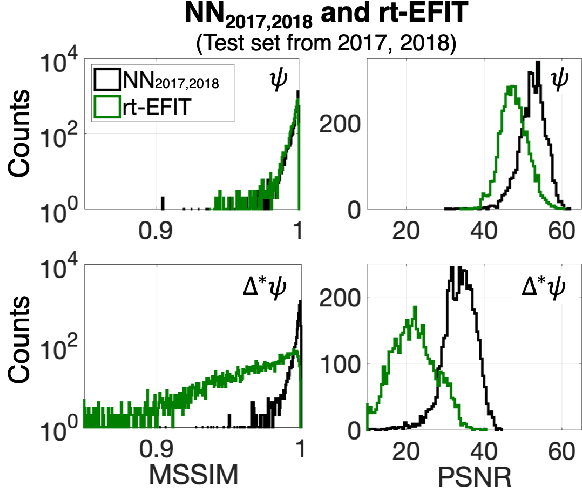
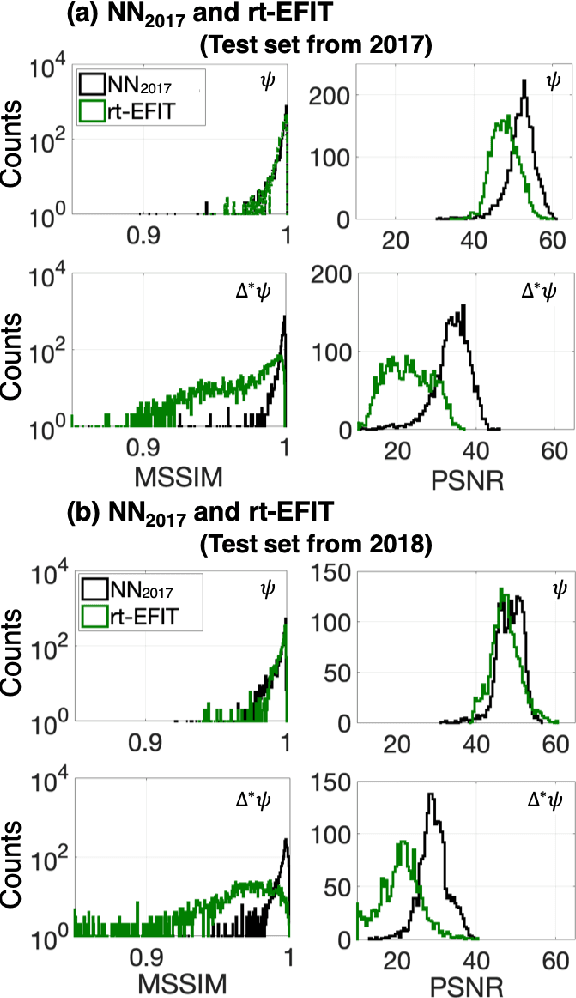
Abstract:A neural network solving Grad-Shafranov equation constrained with measured magnetic signals to reconstruct magnetic equilibria in real time is developed. Database created to optimize the neural network's free parameters contain off-line EFIT results as the output of the network from $1,118$ KSTAR experimental discharges of two different campaigns. Input data to the network constitute magnetic signals measured by a Rogowski coil (plasma current), magnetic pick-up coils (normal and tangential components of magnetic fields) and flux loops (poloidal magnetic fluxes). The developed neural networks fully reconstruct not only the poloidal flux function $\psi\left( R, Z\right)$ but also the toroidal current density function $j_\phi\left( R, Z\right)$ with the off-line EFIT quality. To preserve robustness of the networks against a few missing input data, an imputation scheme is utilized to eliminate the required additional training sets with large number of possible combinations of the missing inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge