George Alexandru Adam
Extracting Clinician's Goals by What-if Interpretable Modeling
Oct 28, 2021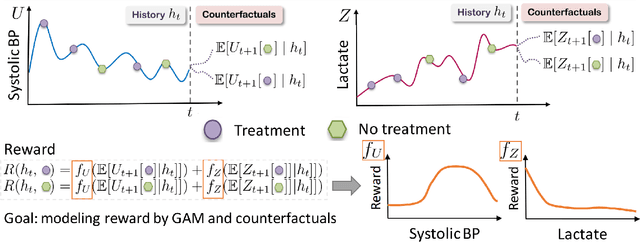
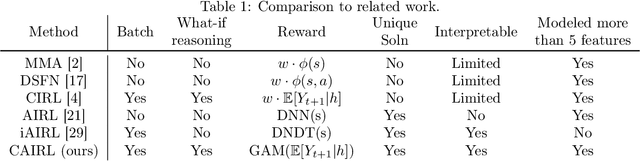
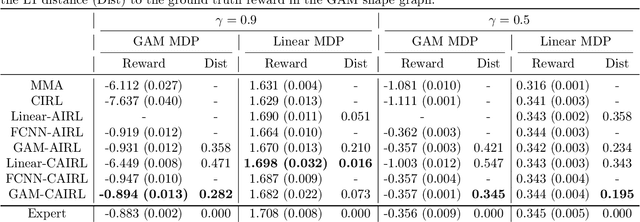
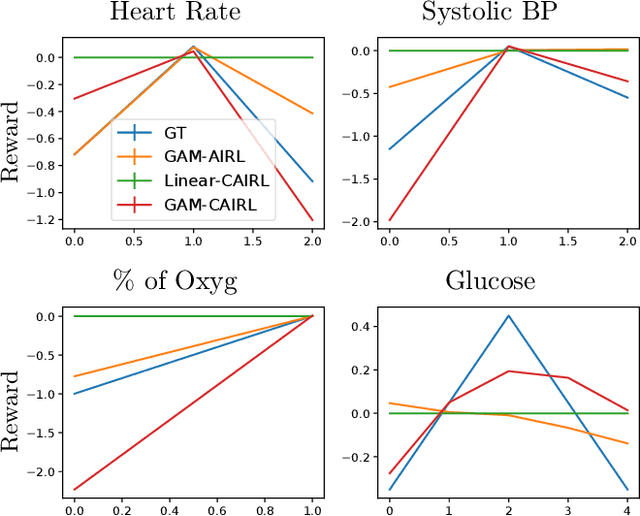
Abstract:Although reinforcement learning (RL) has tremendous success in many fields, applying RL to real-world settings such as healthcare is challenging when the reward is hard to specify and no exploration is allowed. In this work, we focus on recovering clinicians' rewards in treating patients. We incorporate the what-if reasoning to explain clinician's actions based on future outcomes. We use generalized additive models (GAMs) - a class of accurate, interpretable models - to recover the reward. In both simulation and a real-world hospital dataset, we show our model outperforms baselines. Finally, our model's explanations match several clinical guidelines when treating patients while we found the previously-used linear model often contradicts them.
Towards Robust Classification Model by Counterfactual and Invariant Data Generation
Jun 03, 2021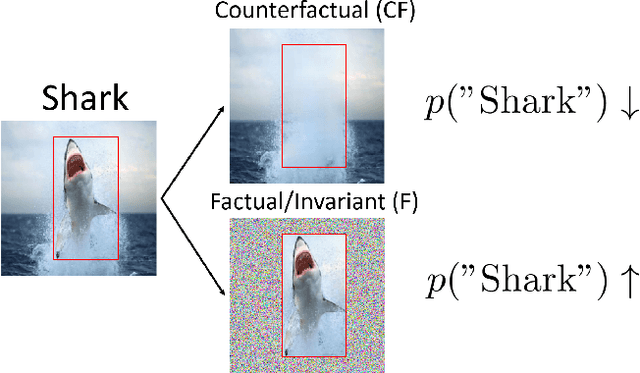
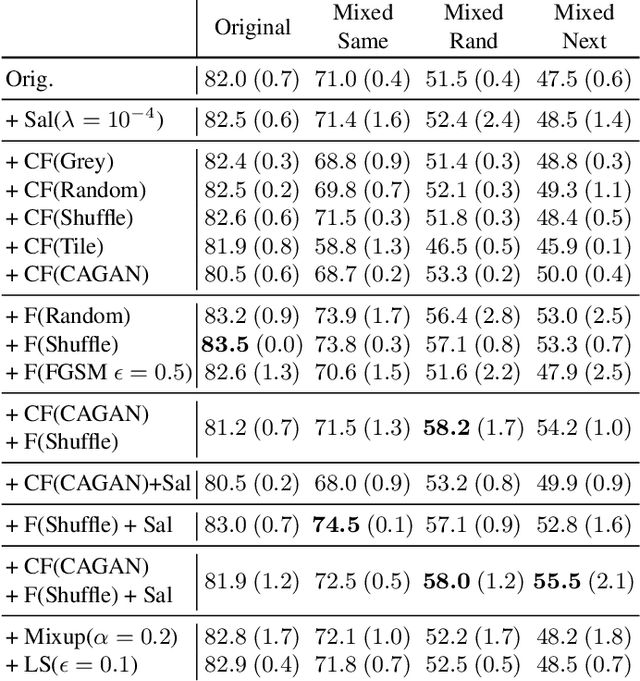

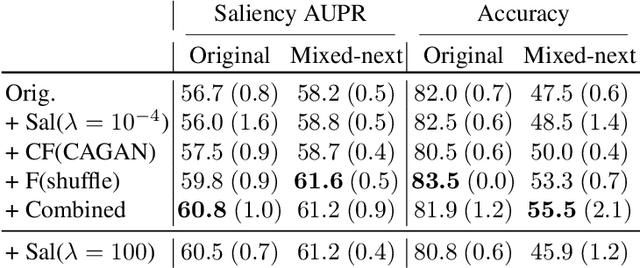
Abstract:Despite the success of machine learning applications in science, industry, and society in general, many approaches are known to be non-robust, often relying on spurious correlations to make predictions. Spuriousness occurs when some features correlate with labels but are not causal; relying on such features prevents models from generalizing to unseen environments where such correlations break. In this work, we focus on image classification and propose two data generation processes to reduce spuriousness. Given human annotations of the subset of the features responsible (causal) for the labels (e.g. bounding boxes), we modify this causal set to generate a surrogate image that no longer has the same label (i.e. a counterfactual image). We also alter non-causal features to generate images still recognized as the original labels, which helps to learn a model invariant to these features. In several challenging datasets, our data generations outperform state-of-the-art methods in accuracy when spurious correlations break, and increase the saliency focus on causal features providing better explanations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge