Geoff S. Baldwin
Active learning of digenic functions with boolean matrix logic programming
Aug 19, 2024Abstract:We apply logic-based machine learning techniques to facilitate cellular engineering and drive biological discovery, based on comprehensive databases of metabolic processes called genome-scale metabolic network models (GEMs). Predicted host behaviours are not always correctly described by GEMs. Learning the intricate genetic interactions within GEMs presents computational and empirical challenges. To address these, we describe a novel approach called Boolean Matrix Logic Programming (BMLP) by leveraging boolean matrices to evaluate large logic programs. We introduce a new system, $BMLP_{active}$, which efficiently explores the genomic hypothesis space by guiding informative experimentation through active learning. In contrast to sub-symbolic methods, $BMLP_{active}$ encodes a state-of-the-art GEM of a widely accepted bacterial host in an interpretable and logical representation using datalog logic programs. Notably, $BMLP_{active}$ can successfully learn the interaction between a gene pair with fewer training examples than random experimentation, overcoming the increase in experimental design space. $BMLP_{active}$ enables rapid optimisation of metabolic models and offers a realistic approach to a self-driving lab for microbial engineering.
Simulating Petri nets with Boolean Matrix Logic Programming
May 18, 2024Abstract:Recent attention to relational knowledge bases has sparked a demand for understanding how relations change between entities. Petri nets can represent knowledge structure and dynamically simulate interactions between entities, and thus they are well suited for achieving this goal. However, logic programs struggle to deal with extensive Petri nets due to the limitations of high-level symbol manipulations. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel approach called Boolean Matrix Logic Programming (BMLP), utilising boolean matrices as an alternative computation mechanism for Prolog to evaluate logic programs. Within this framework, we propose two novel BMLP algorithms for simulating a class of Petri nets known as elementary nets. This is done by transforming elementary nets into logically equivalent datalog programs. We demonstrate empirically that BMLP algorithms can evaluate these programs 40 times faster than tabled B-Prolog, SWI-Prolog, XSB-Prolog and Clingo. Our work enables the efficient simulation of elementary nets using Prolog, expanding the scope of analysis, learning and verification of complex systems with logic programming techniques.
Boolean matrix logic programming for active learning of gene functions in genome-scale metabolic network models
May 10, 2024Abstract:Techniques to autonomously drive research have been prominent in Computational Scientific Discovery, while Synthetic Biology is a field of science that focuses on designing and constructing new biological systems for useful purposes. Here we seek to apply logic-based machine learning techniques to facilitate cellular engineering and drive biological discovery. Comprehensive databases of metabolic processes called genome-scale metabolic network models (GEMs) are often used to evaluate cellular engineering strategies to optimise target compound production. However, predicted host behaviours are not always correctly described by GEMs, often due to errors in the models. The task of learning the intricate genetic interactions within GEMs presents computational and empirical challenges. To address these, we describe a novel approach called Boolean Matrix Logic Programming (BMLP) by leveraging boolean matrices to evaluate large logic programs. We introduce a new system, $BMLP_{active}$, which efficiently explores the genomic hypothesis space by guiding informative experimentation through active learning. In contrast to sub-symbolic methods, $BMLP_{active}$ encodes a state-of-the-art GEM of a widely accepted bacterial host in an interpretable and logical representation using datalog logic programs. Notably, $BMLP_{active}$ can successfully learn the interaction between a gene pair with fewer training examples than random experimentation, overcoming the increase in experimental design space. $BMLP_{active}$ enables rapid optimisation of metabolic models to reliably engineer biological systems for producing useful compounds. It offers a realistic approach to creating a self-driving lab for microbial engineering.
Human Comprehensible Active Learning of Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks
Aug 31, 2023
Abstract:An important application of Synthetic Biology is the engineering of the host cell system to yield useful products. However, an increase in the scale of the host system leads to huge design space and requires a large number of validation trials with high experimental costs. A comprehensible machine learning approach that efficiently explores the hypothesis space and guides experimental design is urgently needed for the Design-Build-Test-Learn (DBTL) cycle of the host cell system. We introduce a novel machine learning framework ILP-iML1515 based on Inductive Logic Programming (ILP) that performs abductive logical reasoning and actively learns from training examples. In contrast to numerical models, ILP-iML1515 is built on comprehensible logical representations of a genome-scale metabolic model and can update the model by learning new logical structures from auxotrophic mutant trials. The ILP-iML1515 framework 1) allows high-throughput simulations and 2) actively selects experiments that reduce the experimental cost of learning gene functions in comparison to randomly selected experiments.
Automated Biodesign Engineering by Abductive Meta-Interpretive Learning
May 17, 2021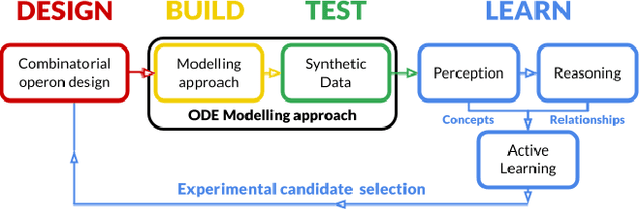
Abstract:The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to synthetic biology will provide the foundation for the creation of a high throughput automated platform for genetic design, in which a learning machine is used to iteratively optimise the system through a design-build-test-learn (DBTL) cycle. However, mainstream machine learning techniques represented by deep learning lacks the capability to represent relational knowledge and requires prodigious amounts of annotated training data. These drawbacks strongly restrict AI's role in synthetic biology in which experimentation is inherently resource and time intensive. In this work, we propose an automated biodesign engineering framework empowered by Abductive Meta-Interpretive Learning ($Meta_{Abd}$), a novel machine learning approach that combines symbolic and sub-symbolic machine learning, to further enhance the DBTL cycle by enabling the learning machine to 1) exploit domain knowledge and learn human-interpretable models that are expressed by formal languages such as first-order logic; 2) simultaneously optimise the structure and parameters of the models to make accurate numerical predictions; 3) reduce the cost of experiments and effort on data annotation by actively generating hypotheses and examples. To verify the effectiveness of $Meta_{Abd}$, we have modelled a synthetic dataset for the production of proteins from a three gene operon in a microbial host, which represents a common synthetic biology problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge