Geir Thore Berge
The Convolutional Tsetlin Machine
May 25, 2019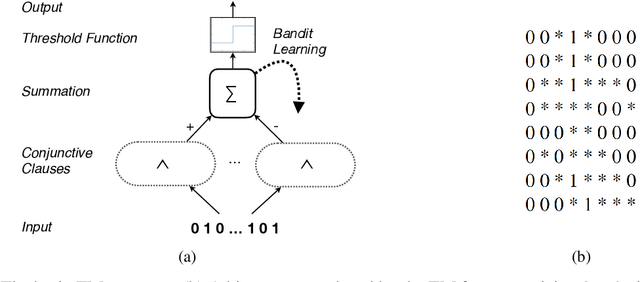
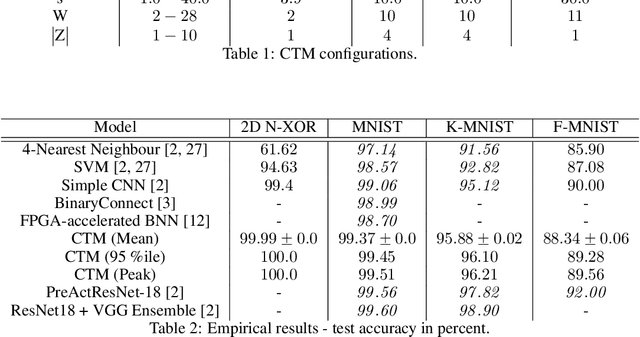
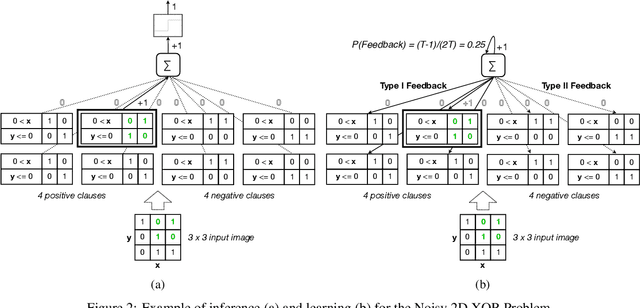
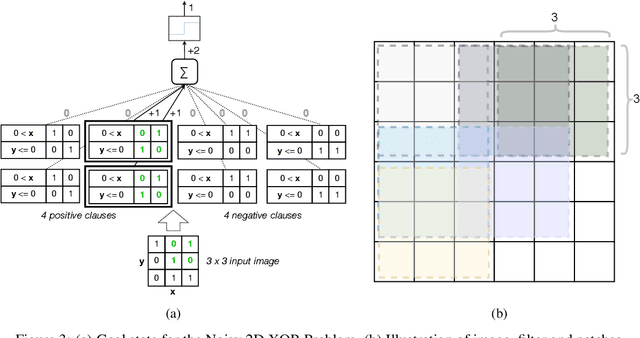
Abstract:Deep neural networks have obtained astounding successes for important pattern recognition tasks, but they suffer from high computational complexity and the lack of interpretability. The recent Tsetlin Machine (TM) attempts to address this lack by using easy-to-interpret conjunctive clauses in propositional logic to solve complex pattern recognition problems. The TM provides competitive accuracy in several benchmarks, while keeping the important property of interpretability. It further facilitates hardware-near implementation since inputs, patterns, and outputs are expressed as bits, while recognition and learning rely on straightforward bit manipulation. In this paper, we exploit the TM paradigm by introducing the Convolutional Tsetlin Machine (CTM), as an interpretable alternative to convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Whereas the TM categorizes an image by employing each clause once to the whole image, the CTM uses each clause as a convolution filter. That is, a clause is evaluated multiple times, once per image patch taking part in the convolution. To make the clauses location-aware, each patch is further augmented with its coordinates within the image. The output of a convolution clause is obtained simply by ORing the outcome of evaluating the clause on each patch. In the learning phase of the TM, clauses that evaluate to 1 are contrasted against the input. For the CTM, we instead contrast against one of the patches, randomly selected among the patches that made the clause evaluate to 1. Accordingly, the standard Type I and Type II feedback of the classic TM can be employed directly, without further modification. The CTM obtains a peak test accuracy of 99.51% on MNIST, 96.21% on Kuzushiji-MNIST, 89.56% on Fashion-MNIST, and 100.0% on the 2D Noisy XOR Problem, which is competitive with results reported for simple 4-layer CNNs, BinaryConnect, and a recent FPGA-accelerated Binary CNN.
Using the Tsetlin Machine to Learn Human-Interpretable Rules for High-Accuracy Text Categorization with Medical Applications
Sep 16, 2018



Abstract:Medical applications challenge today's text categorization techniques by demanding both high accuracy and ease-of-interpretation. Although deep learning has provided a leap ahead in accuracy, this leap comes at the sacrifice of interpretability. To address this accuracy-interpretability challenge, we here introduce, for the first time, a text categorization approach that leverages the recently introduced Tsetlin Machine. In all brevity, we represent the terms of a text as propositional variables. From these, we capture categories using simple propositional formulae, such as: if "rash" and "reaction" and "penicillin" then Allergy. The Tsetlin Machine learns these formulae from a labelled text, utilizing conjunctive clauses to represent the particular facets of each category. Indeed, even the absence of terms (negated features) can be used for categorization purposes. Our empirical comparison with Na\"ive Bayes, decision trees, linear support vector machines (SVMs), random forest, long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks, and other techniques, is quite conclusive. The Tsetlin Machine either performs on par with or outperforms all of the evaluated methods on both the 20 Newsgroups and IMDb datasets, as well as on a non-public clinical dataset. On average, the Tsetlin Machine delivers the best recall and precision scores across the datasets. Finally, our GPU implementation of the Tsetlin Machine executes 5 to 15 times faster than the CPU implementation, depending on the dataset. We thus believe that our novel approach can have a significant impact on a wide range of text analysis applications, forming a promising starting point for deeper natural language understanding with the Tsetlin Machine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge