Gary Simons
Extending Dublin Core Metadata to Support the Description and Discovery of Language Resources
Aug 14, 2003
Abstract:As language data and associated technologies proliferate and as the language resources community expands, it is becoming increasingly difficult to locate and reuse existing resources. Are there any lexical resources for such-and-such a language? What tool works with transcripts in this particular format? What is a good format to use for linguistic data of this type? Questions like these dominate many mailing lists, since web search engines are an unreliable way to find language resources. This paper reports on a new digital infrastructure for discovering language resources being developed by the Open Language Archives Community (OLAC). At the core of OLAC is its metadata format, which is designed to facilitate description and discovery of all kinds of language resources, including data, tools, or advice. The paper describes OLAC metadata, its relationship to Dublin Core metadata, and its dissemination using the metadata harvesting protocol of the Open Archives Initiative.
* 12 pages, 1 figure
The Open Language Archives Community: An infrastructure for distributed archiving of language resources
Jun 10, 2003

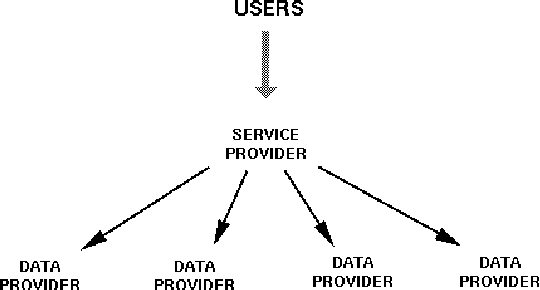
Abstract:New ways of documenting and describing language via electronic media coupled with new ways of distributing the results via the World-Wide Web offer a degree of access to language resources that is unparalleled in history. At the same time, the proliferation of approaches to using these new technologies is causing serious problems relating to resource discovery and resource creation. This article describes the infrastructure that the Open Language Archives Community (OLAC) has built in order to address these problems. Its technical and usage infrastructures address problems of resource discovery by constructing a single virtual library of distributed resources. Its governance infrastructure addresses problems of resource creation by providing a mechanism through which the language-resource community can express its consensus on recommended best practices.
Building an Open Language Archives Community on the OAI Foundation
Feb 14, 2003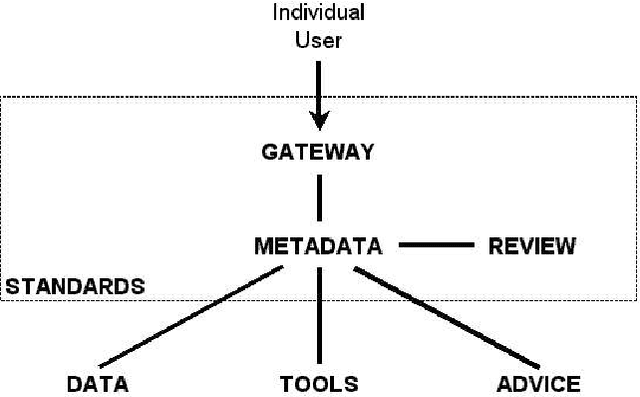
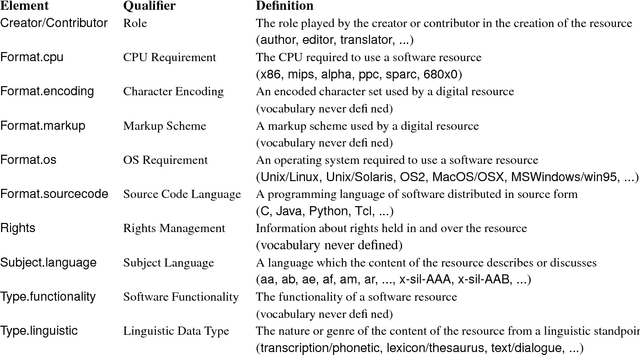
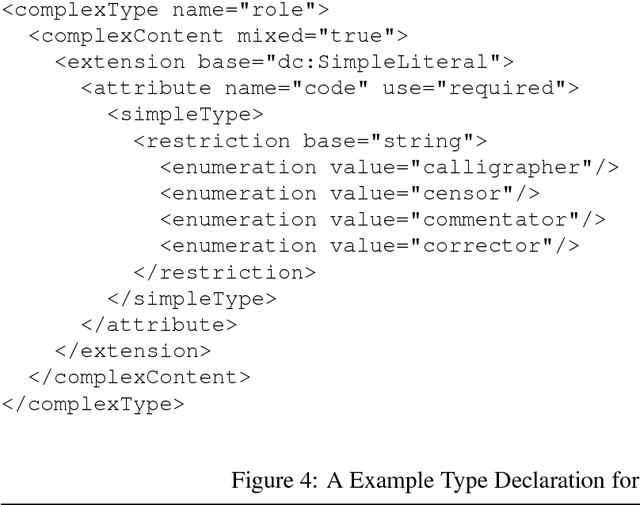
Abstract:The Open Language Archives Community (OLAC) is an international partnership of institutions and individuals who are creating a worldwide virtual library of language resources. The Dublin Core (DC) Element Set and the OAI Protocol have provided a solid foundation for the OLAC framework. However, we need more precision in community-specific aspects of resource description than is offered by DC. Furthermore, many of the institutions and individuals who might participate in OLAC do not have the technical resources to support the OAI protocol. This paper presents our solutions to these two problems. To address the first, we have developed an extensible application profile for language resource metadata. To address the second, we have implemented Vida (the virtual data provider) and Viser (the virtual service provider), which permit community members to provide data and services without having to implement the OAI protocol. These solutions are generic and could be adopted by other specialized subcommunities.
* 12 pages
Seven Dimensions of Portability for Language Documentation and Description
Apr 10, 2002Abstract:The process of documenting and describing the world's languages is undergoing radical transformation with the rapid uptake of new digital technologies for capture, storage, annotation and dissemination. However, uncritical adoption of new tools and technologies is leading to resources that are difficult to reuse and which are less portable than the conventional printed resources they replace. We begin by reviewing current uses of software tools and digital technologies for language documentation and description. This sheds light on how digital language documentation and description are created and managed, leading to an analysis of seven portability problems under the following headings: content, format, discovery, access, citation, preservation and rights. After characterizing each problem we provide a series of value statements, and this provides the framework for a broad range of best practice recommendations.
* 8 pages
The Open Language Archives Community and Asian Language Resources
Oct 03, 2001

Abstract:The Open Language Archives Community (OLAC) is a new project to build a worldwide system of federated language archives based on the Open Archives Initiative and the Dublin Core Metadata Initiative. This paper aims to disseminate the OLAC vision to the language resources community in Asia, and to show language technologists and linguists how they can document their tools and data in such a way that others can easily discover them. We describe OLAC and the OLAC Metadata Set, then discuss two key issues in the Asian context: language classification and multilingual resource classification.
* 8 pages, 2 figures
The OLAC Metadata Set and Controlled Vocabularies
May 21, 2001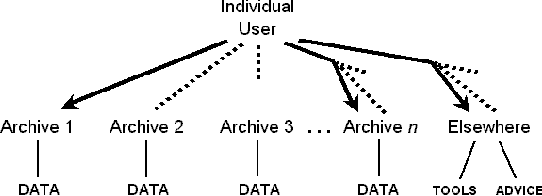
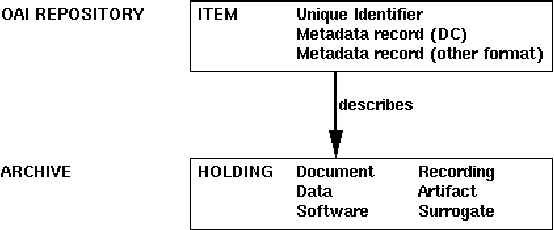

Abstract:As language data and associated technologies proliferate and as the language resources community rapidly expands, it has become difficult to locate and reuse existing resources. Are there any lexical resources for such-and-such a language? What tool can work with transcripts in this particular format? What is a good format to use for linguistic data of this type? Questions like these dominate many mailing lists, since web search engines are an unreliable way to find language resources. This paper describes a new digital infrastructure for language resource discovery, based on the Open Archives Initiative, and called OLAC -- the Open Language Archives Community. The OLAC Metadata Set and the associated controlled vocabularies facilitate consistent description and focussed searching. We report progress on the metadata set and controlled vocabularies, describing current issues and soliciting input from the language resources community.
* 12 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge