Galit Nimrod
Older adults acceptance of SARs: The link between anticipated and actual interaction
Sep 04, 2022Abstract:This study demonstrates how anticipated and actual interactions shape the QE of SARs among older adults. The study consisted of two parts: an online survey to explore the anticipated interaction through video viewing of a SAR and an acceptance study where older adults interacted with the robot. Both parts of this study were completed with the assistance of Gymmy, a robotic system that our lab developed for training older adults in physical and cognitive activities. Both study parts exhibited similar user responses, indicating that users acceptance of SARs can be predicted by their anticipated interaction. Index Terms: Aging, human-robot interaction, older adults, quality evaluation, socially assistive robots, technology acceptance, technophobia, trust, user experience.
Exploratory evaluation of politeness in human-robot interaction
Mar 15, 2021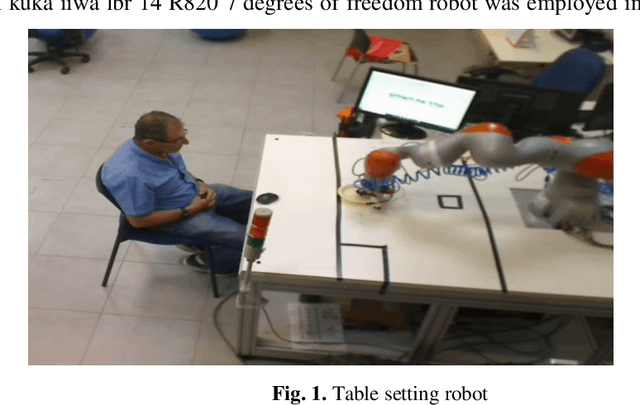
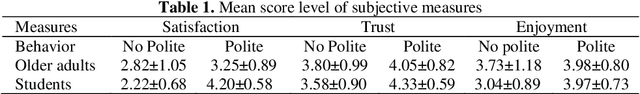
Abstract:Aiming to explore the impact of politeness on Human robot interaction, this study tested varying levels of politeness in a human robot collaborative table setting task. Polite behaviour was designed based on the politeness rules of Lakoff. A graphical user interface was developed for the interaction with the robot offering three levels of politeness, and an experiment was conducted with 20 older adults and 30 engineering students. Results indicated that the quality of interaction was influenced by politeness as participants significantly preferred the polite mode of the robot. However, the older adults were less able to distinguish between the three politeness levels. Future studies should thus include pre experiment training to increase the familiarity of the older adults with robotic technology. These studies should also include other permutations of the politeness rules of Lakoff.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge