Gabriela Oana Cula
PSO-Net: Development of an automated psoriasis assessment system using attention-based interpretable deep neural networks
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that requires long-term treatment and monitoring. Although, the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) is utilized as a standard measurement to assess psoriasis severity in clinical trials, it has many drawbacks such as (1) patient burden for in-person clinic visits for assessment of psoriasis, (2) time required for investigator scoring and (3) variability of inter- and intra-rater scoring. To address these drawbacks, we propose a novel and interpretable deep learning architecture called PSO-Net, which maps digital images from different anatomical regions to derive attention-based scores. Regional scores are further combined to estimate an absolute PASI score. Moreover, we devise a novel regression activation map for interpretability through ranking attention scores. Using this approach, we achieved inter-class correlation scores of 82.2% [95% CI: 77- 87%] and 87.8% [95% CI: 84-91%] with two different clinician raters, respectively.
Automatic Estimation of Ulcerative Colitis Severity from Endoscopy Videos using Ordinal Multi-Instance Learning
Sep 29, 2021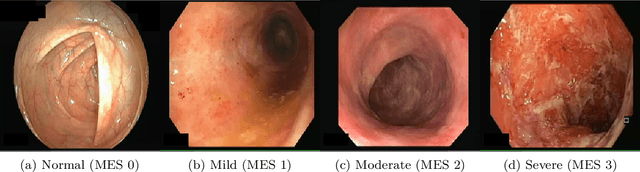
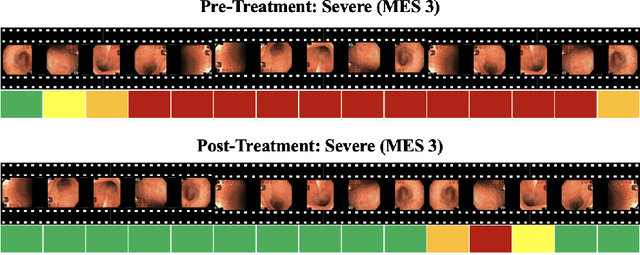
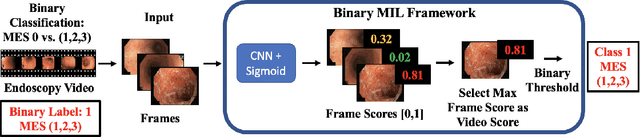
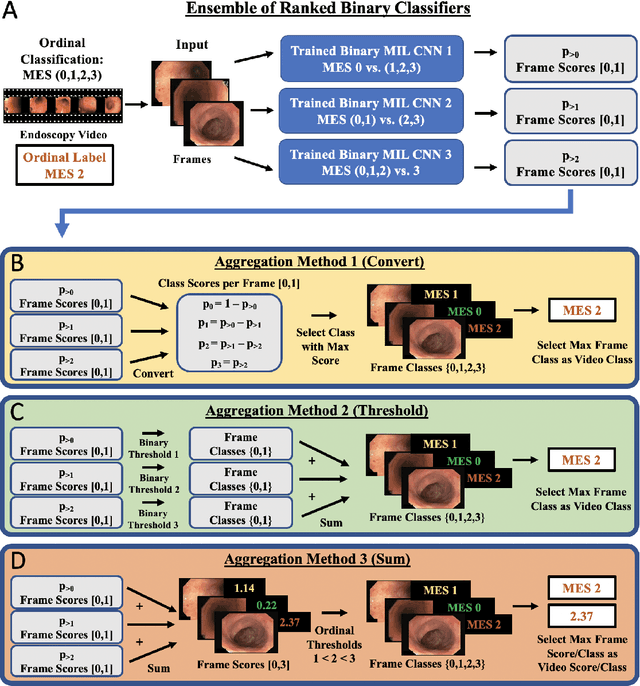
Abstract:Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by relapsing inflammation of the large intestine. The severity of UC is often represented by the Mayo Endoscopic Subscore (MES) which quantifies mucosal disease activity from endoscopy videos. In clinical trials, an endoscopy video is assigned an MES based upon the most severe disease activity observed in the video. For this reason, severe inflammation spread throughout the colon will receive the same MES as an otherwise healthy colon with severe inflammation restricted to a small, localized segment. Therefore, the extent of disease activity throughout the large intestine, and overall response to treatment, may not be completely captured by the MES. In this work, we aim to automatically estimate UC severity for each frame in an endoscopy video to provide a higher resolution assessment of disease activity throughout the colon. Because annotating severity at the frame-level is expensive, labor-intensive, and highly subjective, we propose a novel weakly supervised, ordinal classification method to estimate frame severity from video MES labels alone. Using clinical trial data, we first achieved 0.92 and 0.90 AUC for predicting mucosal healing and remission of UC, respectively. Then, for severity estimation, we demonstrate that our models achieve substantial Cohen's Kappa agreement with ground truth MES labels, comparable to the inter-rater agreement of expert clinicians. These findings indicate that our framework could serve as a foundation for novel clinical endpoints, based on a more localized scoring system, to better evaluate UC drug efficacy in clinical trials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge