Gaël Le Lan
LIUM
Supervised and Unsupervised Alignments for Spoofing Behavioral Biometrics
Aug 14, 2024
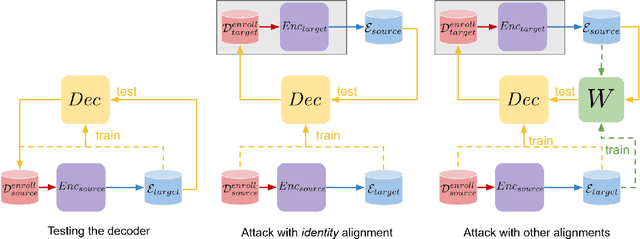
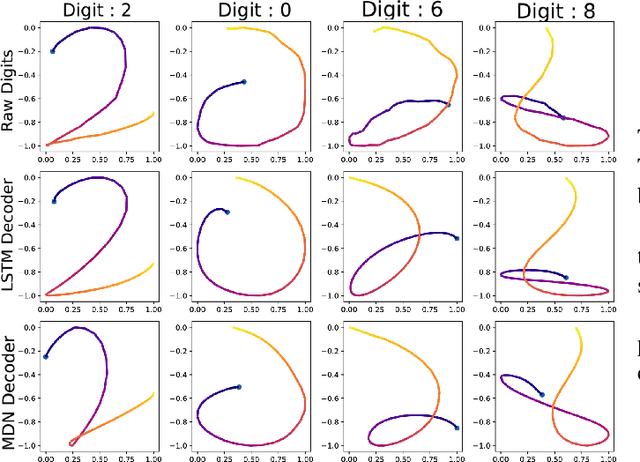
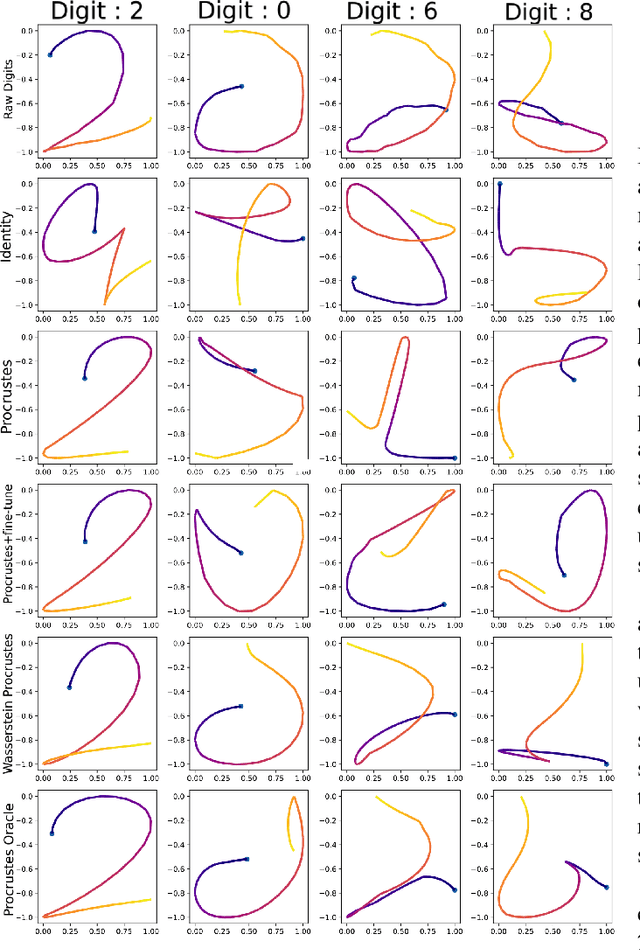
Abstract:Biometric recognition systems are security systems based on intrinsic properties of their users, usually encoded in high dimension representations called embeddings, which potential theft would represent a greater threat than a temporary password or a replaceable key. To study the threat of embedding theft, we perform spoofing attacks on two behavioral biometric systems (an automatic speaker verification system and a handwritten digit analysis system) using a set of alignment techniques. Biometric recognition systems based on embeddings work in two phases: enrollment - where embeddings are collected and stored - then authentication - when new embeddings are compared to the stored ones -.The threat of stolen enrollment embeddings has been explored by the template reconstruction attack literature: reconstructing the original data to spoof an authentication system is doable with black-box access to their encoder. In this document, we explore the options available to perform template reconstruction attacks without any access to the encoder. To perform those attacks, we suppose general rules over the distribution of embeddings across encoders and use supervised and unsupervised algorithms to align an unlabeled set of embeddings with a set from a known encoder. The use of an alignment algorithm from the unsupervised translation literature gives promising results on spoofing two behavioral biometric systems.
On the invertibility of a voice privacy system using embedding alignement
Oct 08, 2021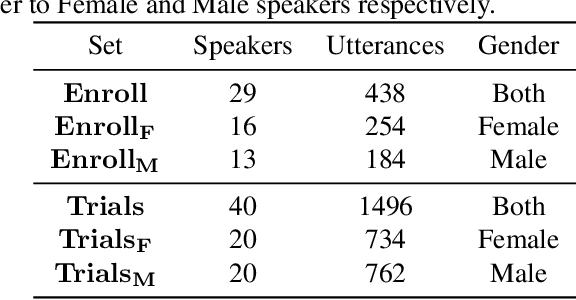
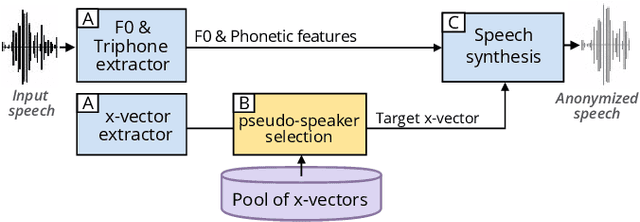
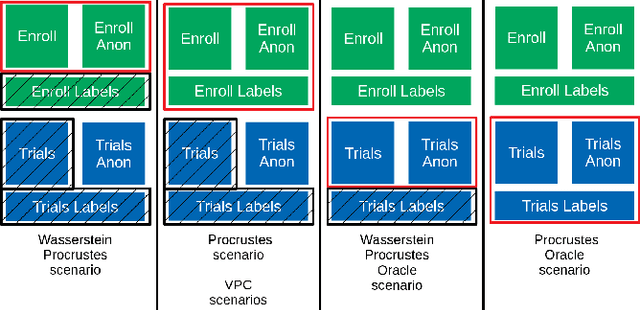
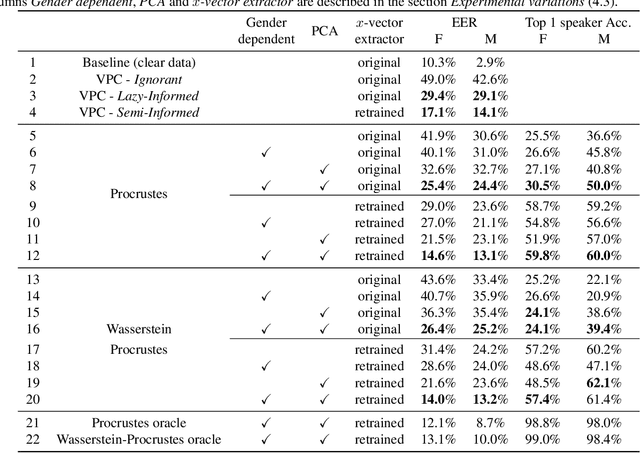
Abstract:This paper explores various attack scenarios on a voice anonymization system using embeddings alignment techniques. We use Wasserstein-Procrustes (an algorithm initially designed for unsupervised translation) or Procrustes analysis to match two sets of x-vectors, before and after voice anonymization, to mimic this transformation as a rotation function. We compute the optimal rotation and compare the results of this approximation to the official Voice Privacy Challenge results. We show that a complex system like the baseline of the Voice Privacy Challenge can be approximated by a rotation, estimated using a limited set of x-vectors. This paper studies the space of solutions for voice anonymization within the specific scope of rotations. Rotations being reversible, the proposed method can recover up to 62% of the speaker identities from anonymized embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge