Fuyou Tian
Land use mapping in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on semantic segmentation deep learning method
Mar 18, 2018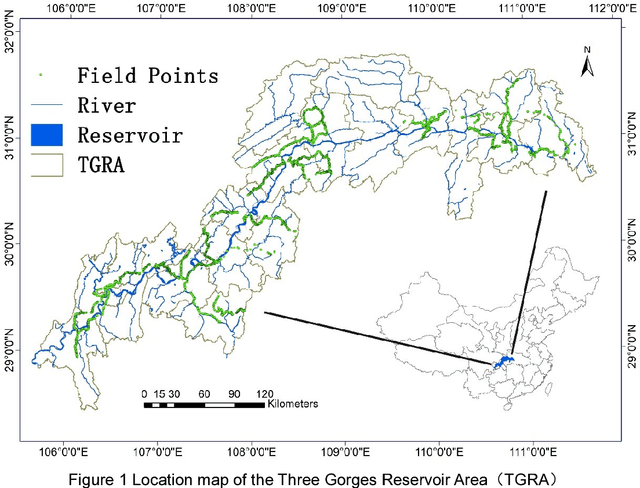

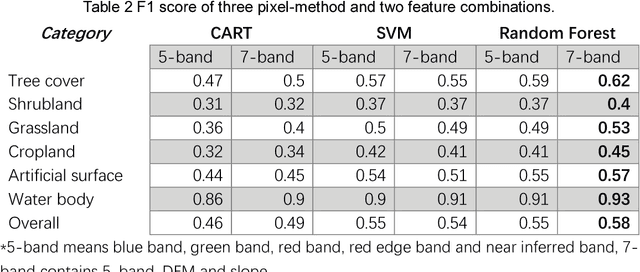
Abstract:The Three Gorges Dam, a massive cross-century project spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, located in Yichang, Hubei province, China, was built to provide great power, improve the River shipping, control floods in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, and increase the dry season flow in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Benefits are enormous and comprehensive. However, the social and environmental impacts are also immense and far-reaching to its surrounding areas. Mapping land use /land cover changed (LUCC) is critical for tracking the impacts. Remote sensing has been proved to be an effective way to map and monitor land use change in real time and in large areas such as the Three Gorges Reservoir Area(TGRA) by using pixel based or oriented based classifier in different resolution. In this paper, we first test the state of the art semantic segmentation deep learning classifiers for LUCC mapping with 7 categories in the TGRA area with rapideye 5m resolution data. The topographic information was also added for better accuracy in mountain area. By compared with the pixel-based classifier, the semantic segmentation deep learning method has better accuracy and robustness at 5m resolution level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge