Furkan Durmus
Effects of Using Synthetic Data on Deep Recommender Models' Performance
Jun 26, 2024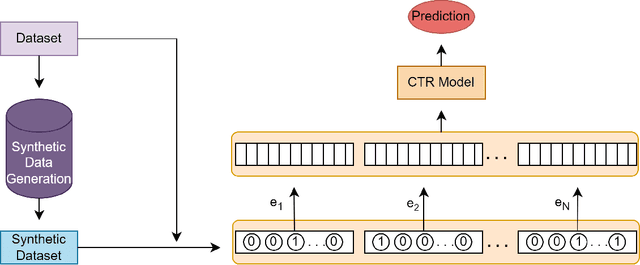
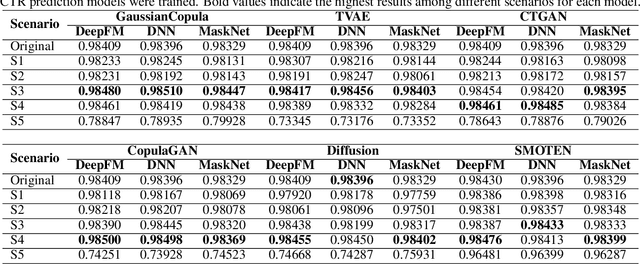
Abstract:Recommender systems are essential for enhancing user experiences by suggesting items based on individual preferences. However, these systems frequently face the challenge of data imbalance, characterized by a predominance of negative interactions over positive ones. This imbalance can result in biased recommendations favoring popular items. This study investigates the effectiveness of synthetic data generation in addressing data imbalances within recommender systems. Six different methods were used to generate synthetic data. Our experimental approach involved generating synthetic data using these methods and integrating the generated samples into the original dataset. Our results show that the inclusion of generated negative samples consistently improves the Area Under the Curve (AUC) scores. The significant impact of synthetic negative samples highlights the potential of data augmentation strategies to address issues of data sparsity and imbalance, ultimately leading to improved performance of recommender systems.
Pairwise Ranking Loss for Multi-Task Learning in Recommender Systems
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Multi-Task Learning (MTL) plays a crucial role in real-world advertising applications such as recommender systems, aiming to achieve robust representations while minimizing resource consumption. MTL endeavors to simultaneously optimize multiple tasks to construct a unified model serving diverse objectives. In online advertising systems, tasks like Click-Through Rate (CTR) and Conversion Rate (CVR) are often treated as MTL problems concurrently. However, it has been overlooked that a conversion ($y_{cvr}=1$) necessitates a preceding click ($y_{ctr}=1$). In other words, while certain CTR tasks are associated with corresponding conversions, others lack such associations. Moreover, the likelihood of noise is significantly higher in CTR tasks where conversions do not occur compared to those where they do, and existing methods lack the ability to differentiate between these two scenarios. In this study, exposure labels corresponding to conversions are regarded as definitive indicators, and a novel task-specific loss is introduced by calculating a \textbf{p}air\textbf{wise} \textbf{r}anking (PWiseR) loss between model predictions, manifesting as pairwise ranking loss, to encourage the model to rely more on them. To demonstrate the effect of the proposed loss function, experiments were conducted on different MTL and Single-Task Learning (STL) models using four distinct public MTL datasets, namely Alibaba FR, NL, US, and CCP, along with a proprietary industrial dataset. The results indicate that our proposed loss function outperforms the BCE loss function in most cases in terms of the AUC metric.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge