Fredrik Milani
Agentic Business Process Management Systems
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Since the early 90s, the evolution of the Business Process Management (BPM) discipline has been punctuated by successive waves of automation technologies. Some of these technologies enable the automation of individual tasks, while others focus on orchestrating the execution of end-to-end processes. The rise of Generative and Agentic Artificial Intelligence (AI) is opening the way for another such wave. However, this wave is poised to be different because it shifts the focus from automation to autonomy and from design-driven management of business processes to data-driven management, leveraging process mining techniques. This position paper, based on a keynote talk at the 2025 Workshop on AI for BPM, outlines how process mining has laid the foundations on top of which agents can sense process states, reason about improvement opportunities, and act to maintain and optimize performance. The paper proposes an architectural vision for Agentic Business Process Management Systems (A-BPMS): a new class of platforms that integrate autonomy, reasoning, and learning into process management and execution. The paper contends that such systems must support a continuum of processes, spanning from human-driven to fully autonomous, thus redefining the boundaries of process automation and governance.
Predicting Case Suffixes With Activity Start and End Times: A Sweep-Line Based Approach
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Predictive process monitoring techniques support the operational decision making by predicting future states of ongoing cases of a business process. A subset of these techniques predict the remaining sequence of activities of an ongoing case (case suffix prediction). Existing approaches for case suffix prediction generate sequences of activities with a single timestamp (e.g. the end timestamp). This output is insufficient for resource capacity planning, where we need to reason about the periods of time when resources will be busy performing work. This paper introduces a technique for predicting case suffixes consisting of activities with start and end timestamps. In other words, the proposed technique predicts both the waiting time and the processing time of each activity. Since the waiting time of an activity in a case depends on how busy resources are in other cases, the technique adopts a sweep-line approach, wherein the suffixes of all ongoing cases in the process are predicted in lockstep, rather than predictions being made for each case in isolation. An evaluation on real-life and synthetic datasets compares the accuracy of different instantiations of this approach, demonstrating the advantages of a multi-model approach to case suffix prediction.
Enhancing the Accuracy of Predictors of Activity Sequences of Business Processes
Dec 09, 2023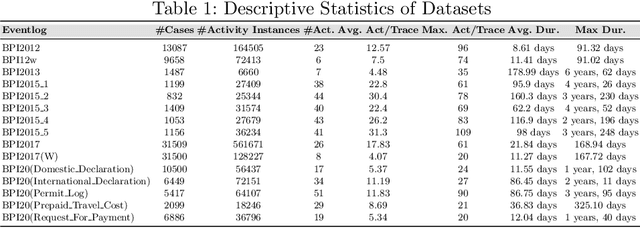
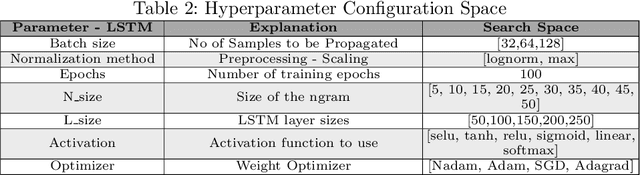
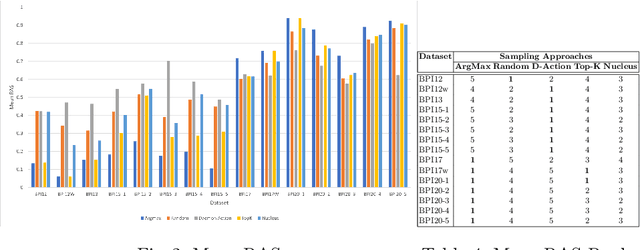
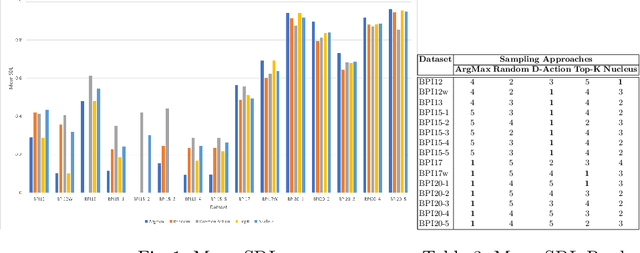
Abstract:Predictive process monitoring is an evolving research field that studies how to train and use predictive models for operational decision-making. One of the problems studied in this field is that of predicting the sequence of upcoming activities in a case up to its completion, a.k.a. the case suffix. The prediction of case suffixes provides input to estimate short-term workloads and execution times under different resource schedules. Existing methods to address this problem often generate suffixes wherein some activities are repeated many times, whereas this pattern is not observed in the data. Closer examination shows that this shortcoming stems from the approach used to sample the successive activity instances to generate a case suffix. Accordingly, the paper introduces a sampling approach aimed at reducing repetitions of activities in the predicted case suffixes. The approach, namely Daemon action, strikes a balance between exploration and exploitation when generating the successive activity instances. We enhance a deep learning approach for case suffix predictions using this sampling approach, and experimentally show that the enhanced approach outperforms the unenhanced ones with respect to control-flow accuracy measures.
Prescriptive Process Monitoring: Quo Vadis?
Dec 03, 2021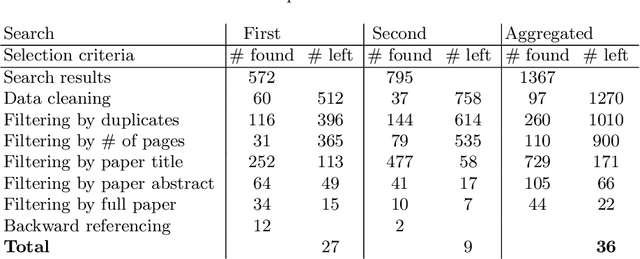
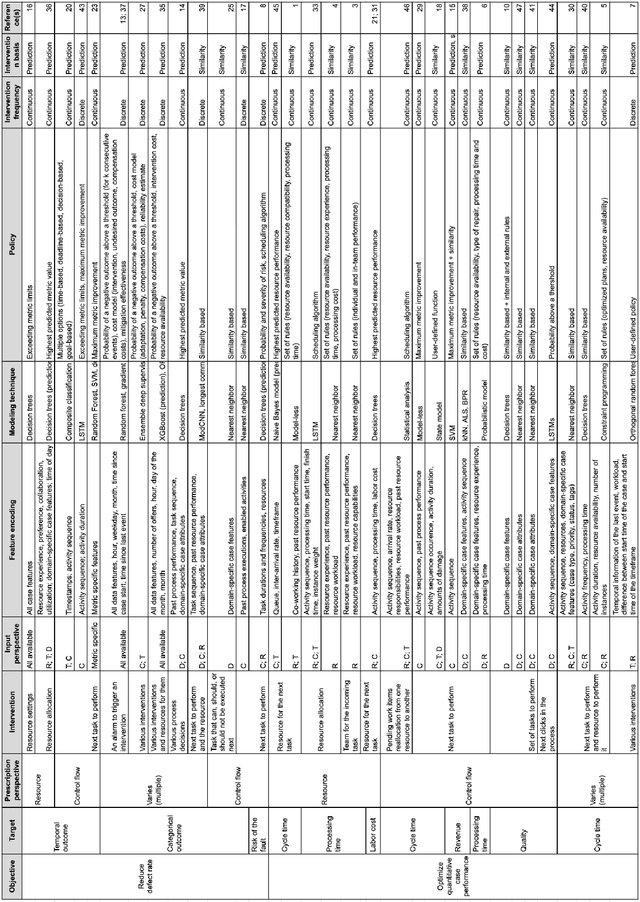
Abstract:Prescriptive process monitoring methods seek to optimize a business process by recommending interventions at runtime to prevent negative outcomes or poorly performing cases. In recent years, various prescriptive process monitoring methods have been proposed. This paper studies existing methods in this field via a Systematic Literature Review (SLR). In order to structure the field, the paper proposes a framework for characterizing prescriptive process monitoring methods according to their performance objective, performance metrics, intervention types, modeling techniques, data inputs, and intervention policies. The SLR provides insights into challenges and areas for future research that could enhance the usefulness and applicability of prescriptive process monitoring methods. The paper highlights the need to validate existing and new methods in real-world settings, to extend the types of interventions beyond those related to the temporal and cost perspectives, and to design policies that take into account causality and second-order effects.
Predictive Process Monitoring Methods: Which One Suits Me Best?
Apr 06, 2018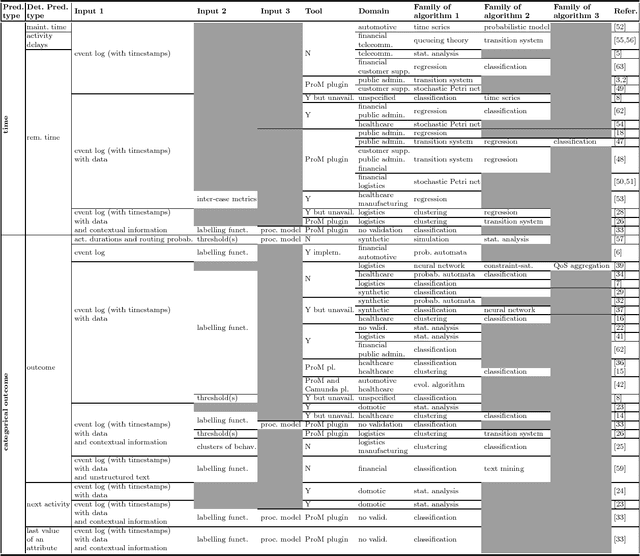
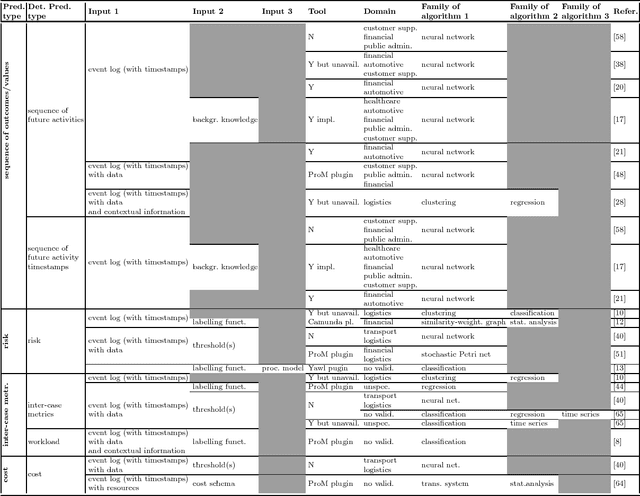
Abstract:Predictive process monitoring has recently gained traction in academia and is maturing also in companies. However, with the growing body of research, it might be daunting for companies to navigate in this domain in order to find, provided certain data, what can be predicted and what methods to use. The main objective of this paper is developing a value-driven framework for classifying existing work on predictive process monitoring. This objective is achieved by systematically identifying, categorizing, and analyzing existing approaches for predictive process monitoring. The review is then used to develop a value-driven framework that can support organizations to navigate in the predictive process monitoring field and help them to find value and exploit the opportunities enabled by these analysis techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge