Frederick Epstein
Multimodal Learning To Improve Cardiac Late Mechanical Activation Detection From Cine MR Images
Feb 28, 2024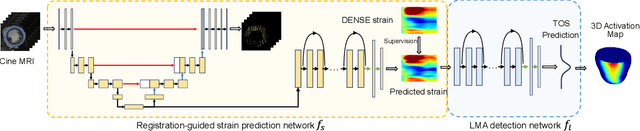
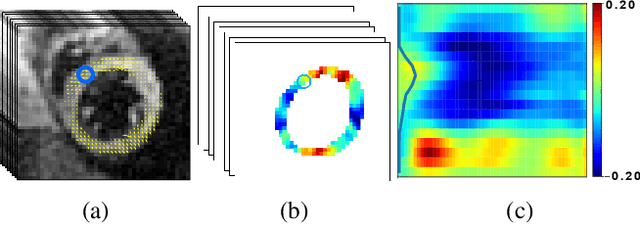
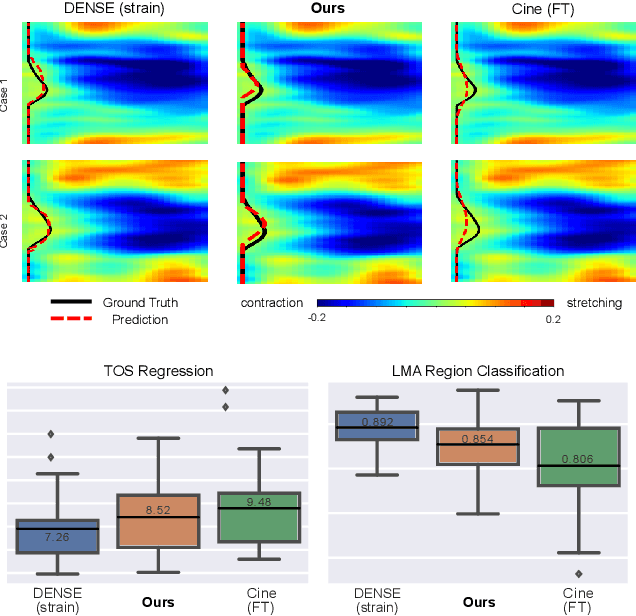
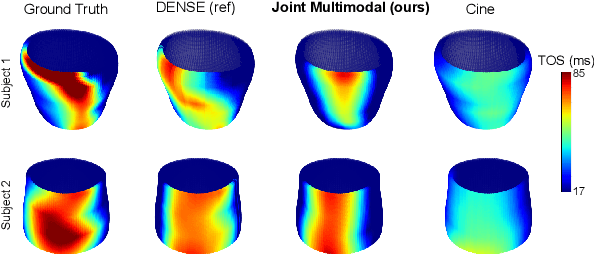
Abstract:This paper presents a multimodal deep learning framework that utilizes advanced image techniques to improve the performance of clinical analysis heavily dependent on routinely acquired standard images. More specifically, we develop a joint learning network that for the first time leverages the accuracy and reproducibility of myocardial strains obtained from Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echo (DENSE) to guide the analysis of cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in late mechanical activation (LMA) detection. An image registration network is utilized to acquire the knowledge of cardiac motions, an important feature estimator of strain values, from standard cine CMRs. Our framework consists of two major components: (i) a DENSE-supervised strain network leveraging latent motion features learned from a registration network to predict myocardial strains; and (ii) a LMA network taking advantage of the predicted strain for effective LMA detection. Experimental results show that our proposed work substantially improves the performance of strain analysis and LMA detection from cine CMR images, aligning more closely with the achievements of DENSE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge