Frank Z. Xing
Business Taxonomy Construction Using Concept-Level Hierarchical Clustering
Jun 24, 2019



Abstract:Business taxonomies are indispensable tools for investors to do equity research and make professional decisions. However, to identify the structure of industry sectors in an emerging market is challenging for two reasons. First, existing taxonomies are designed for mature markets, which may not be the appropriate classification for small companies with innovative business models. Second, emerging markets are fast-developing, thus the static business taxonomies cannot promptly reflect the new features. In this article, we propose a new method to construct business taxonomies automatically from the content of corporate annual reports. Extracted concepts are hierarchically clustered using greedy affinity propagation. Our method requires less supervision and is able to discover new terms. Experiments and evaluation on the Chinese National Equities Exchange and Quotations (NEEQ) market show several advantages of the business taxonomy we build. Our results provide an effective tool for understanding and investing in the new growth companies.
Fast Single Image Dehazing via Multilevel Wavelet Transform based Optimization
Apr 18, 2019


Abstract:The quality of images captured in outdoor environments can be affected by poor weather conditions such as fog, dust, and atmospheric scattering of other particles. This problem can bring extra challenges to high-level computer vision tasks like image segmentation and object detection. However, previous studies on image dehazing suffer from a huge computational workload and corruption of the original image, such as over-saturation and halos. In this paper, we present a novel image dehazing approach based on the optical model for haze images and regularized optimization. Specifically, we convert the non-convex, bilinear problem concerning the unknown haze-free image and light transmission distribution to a convex, linear optimization problem by estimating the atmosphere light constant. Our method is further accelerated by introducing a multilevel Haar wavelet transform. The optimization, instead, is applied to the low frequency sub-band decomposition of the original image. This dimension reduction significantly improves the processing speed of our method and exhibits the potential for real-time applications. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art dehazing algorithms in terms of both image reconstruction quality and computational efficiency. For implementation details, source code can be publicly accessed via http://github.com/JiaxiHe/Image-and-Video-Dehazing.
Discovering Bayesian Market Views for Intelligent Asset Allocation
Jun 29, 2018
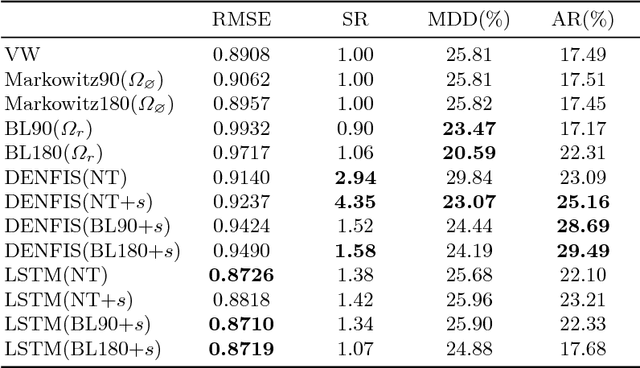
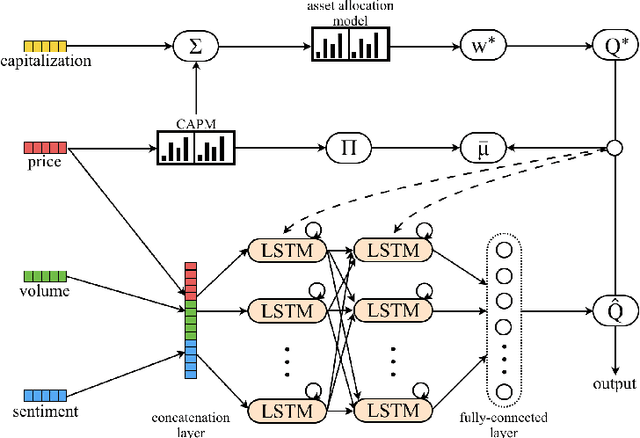

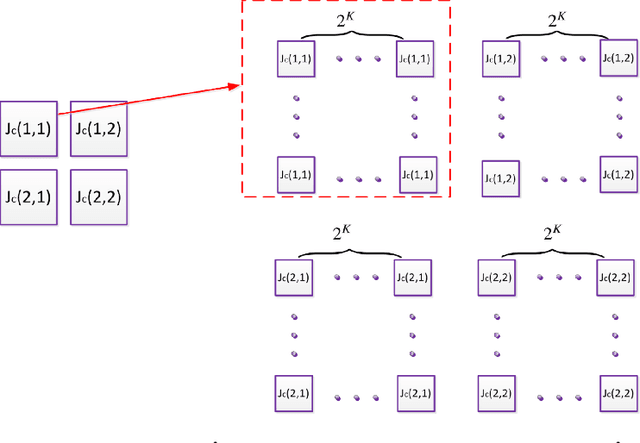
Abstract:Along with the advance of opinion mining techniques, public mood has been found to be a key element for stock market prediction. However, how market participants' behavior is affected by public mood has been rarely discussed. Consequently, there has been little progress in leveraging public mood for the asset allocation problem, which is preferred in a trusted and interpretable way. In order to address the issue of incorporating public mood analyzed from social media, we propose to formalize public mood into market views, because market views can be integrated into the modern portfolio theory. In our framework, the optimal market views will maximize returns in each period with a Bayesian asset allocation model. We train two neural models to generate the market views, and benchmark the model performance on other popular asset allocation strategies. Our experimental results suggest that the formalization of market views significantly increases the profitability (5% to 10% annually) of the simulated portfolio at a given risk level.
A Historical Review of Forty Years of Research on CMAC
Feb 08, 2017



Abstract:The Cerebellar Model Articulation Controller (CMAC) is an influential brain-inspired computing model in many relevant fields. Since its inception in the 1970s, the model has been intensively studied and many variants of the prototype, such as Kernel-CMAC, Self-Organizing Map CMAC, and Linguistic CMAC, have been proposed. This review article focus on how the CMAC model is gradually developed and refined to meet the demand of fast, adaptive, and robust control. Two perspective, CMAC as a neural network and CMAC as a table look-up technique are presented. Three aspects of the model: the architecture, learning algorithms and applications are discussed. In the end, some potential future research directions on this model are suggested.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge