Francois-Xavier Carton
RESECT-SEG: Open access annotations of intra-operative brain tumor ultrasound images
Jul 13, 2022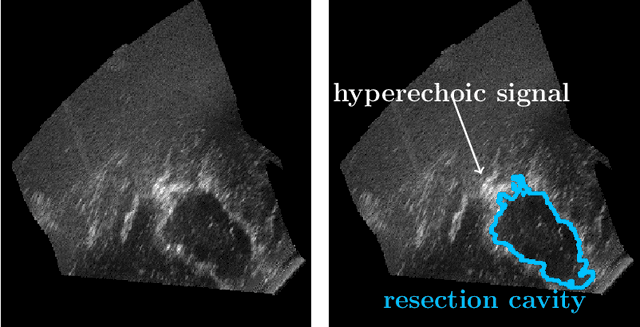
Abstract:Purpose: Registration and segmentation of magnetic resonance (MR) and ultrasound (US) images play an essential role in surgical planning and resection of brain tumors. However, validating these techniques is challenging due to the scarcity of publicly accessible sources with high-quality ground truth information. To this end, we propose a unique annotation dataset of tumor tissues and resection cavities from the previously published RESECT dataset (Xiao et al. 2017) to encourage a more rigorous assessments of image processing techniques. Acquisition and validation methods: The RESECT database consists of MR and intraoperative US (iUS) images of 23 patients who underwent resection surgeries. The proposed dataset contains tumor tissues and resection cavity annotations of the iUS images. The quality of annotations were validated by two highly experienced neurosurgeons through several assessment criteria. Data format and availability: Annotations of tumor tissues and resection cavities are provided in 3D NIFTI formats. Both sets of annotations are accessible online in the \url{https://osf.io/6y4db}. Discussion and potential applications: The proposed database includes tumor tissue and resection cavity annotations from real-world clinical ultrasound brain images to evaluate segmentation and registration methods. These labels could also be used to train deep learning approaches. Eventually, this dataset should further improve the quality of image guidance in neurosurgery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge