Franco Palau
DNS Tunneling: A Deep Learning based Lexicographical Detection Approach
Jun 14, 2020
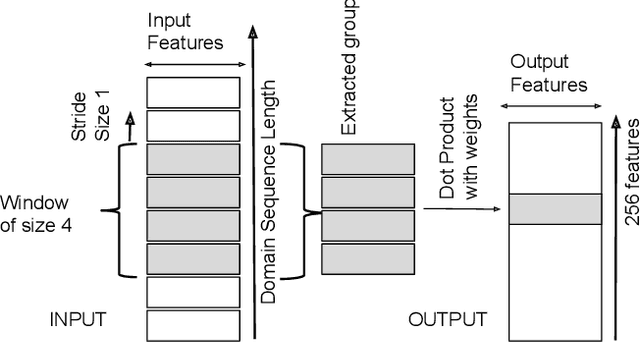


Abstract:Domain Name Service is a trusted protocol made for name resolution, but during past years some approaches have been developed to use it for data transfer. DNS Tunneling is a method where data is encoded inside DNS queries, allowing information exchange through the DNS. This characteristic is attractive to hackers who exploit DNS Tunneling method to establish bidirectional communication with machines infected with malware with the objective of exfiltrating data or sending instructions in an obfuscated way. To detect these threats fast and accurately, the present work proposes a detection approach based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with a minimal architecture complexity. Due to the lack of quality datasets for evaluating DNS Tunneling connections, we also present a detailed construction and description of a novel dataset that contains DNS Tunneling domains generated with five well-known DNS tools. Despite its simple architecture, the resulting CNN model correctly detected more than 92% of total Tunneling domains with a false positive rate close to 0.8%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge