Francesco Varoli
Improved Memories Learning
Aug 24, 2020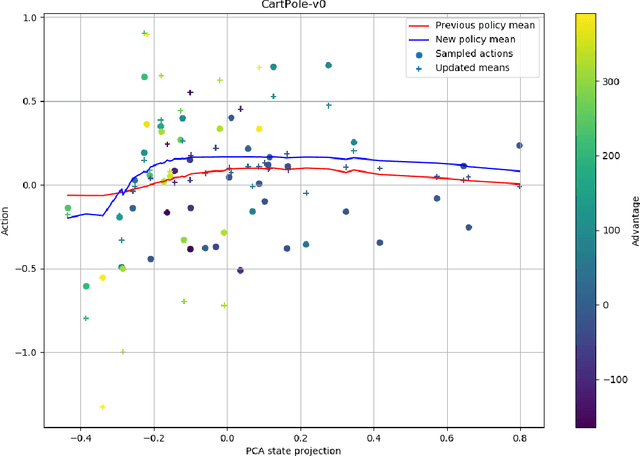


Abstract:We propose Improved Memories Learning (IMeL), a novel algorithm that turns reinforcement learning (RL) into a supervised learning (SL) problem and delimits the role of neural networks (NN) to interpolation. IMeL consists of two components. The first is a reservoir of experiences. Each experience is updated based on a non-parametric procedural improvement of the policy, computed as a bounded one-sample Monte Carlo estimate. The second is a NN regressor, which receives as input improved experiences from the reservoir (context points) and computes the policy by interpolation. The NN learns to measure the similarity between states in order to compute long-term forecasts by averaging experiences, rather than by encoding the problem structure in the NN parameters. We present preliminary results and propose IMeL as a baseline method for assessing the merits of more complex models and inductive biases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge