Francesca Tozzi
Boosting 3D Liver Shape Datasets with Diffusion Models and Implicit Neural Representations
Apr 28, 2025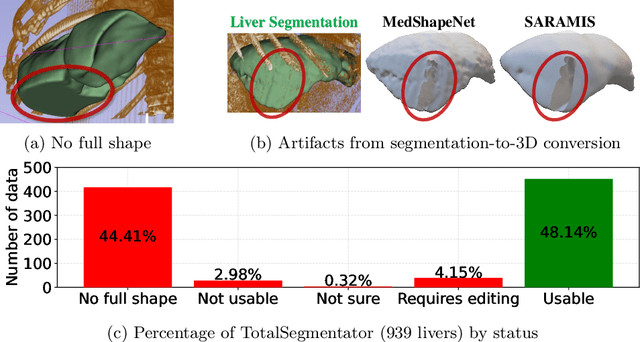

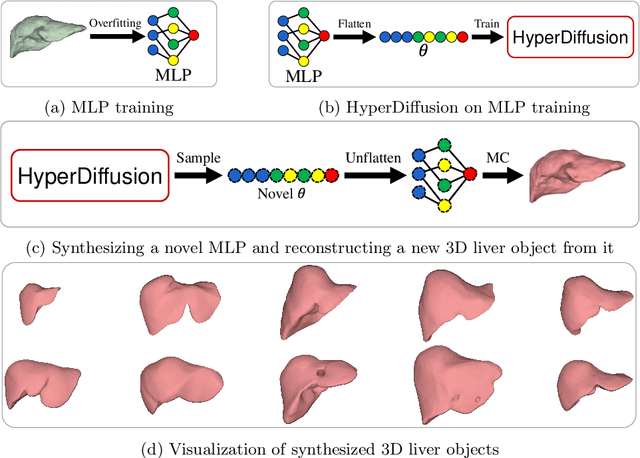

Abstract:While the availability of open 3D medical shape datasets is increasing, offering substantial benefits to the research community, we have found that many of these datasets are, unfortunately, disorganized and contain artifacts. These issues limit the development and training of robust models, particularly for accurate 3D reconstruction tasks. In this paper, we examine the current state of available 3D liver shape datasets and propose a solution using diffusion models combined with implicit neural representations (INRs) to augment and expand existing datasets. Our approach utilizes the generative capabilities of diffusion models to create realistic, diverse 3D liver shapes, capturing a wide range of anatomical variations and addressing the problem of data scarcity. Experimental results indicate that our method enhances dataset diversity, providing a scalable solution to improve the accuracy and reliability of 3D liver reconstruction and generation in medical applications. Finally, we suggest that diffusion models can also be applied to other downstream tasks in 3D medical imaging.
One Patient's Annotation is Another One's Initialization: Towards Zero-Shot Surgical Video Segmentation with Cross-Patient Initialization
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Video object segmentation is an emerging technology that is well-suited for real-time surgical video segmentation, offering valuable clinical assistance in the operating room by ensuring consistent frame tracking. However, its adoption is limited by the need for manual intervention to select the tracked object, making it impractical in surgical settings. In this work, we tackle this challenge with an innovative solution: using previously annotated frames from other patients as the tracking frames. We find that this unconventional approach can match or even surpass the performance of using patients' own tracking frames, enabling more autonomous and efficient AI-assisted surgical workflows. Furthermore, we analyze the benefits and limitations of this approach, highlighting its potential to enhance segmentation accuracy while reducing the need for manual input. Our findings provide insights into key factors influencing performance, offering a foundation for future research on optimizing cross-patient frame selection for real-time surgical video analysis.
Less is More? Revisiting the Importance of Frame Rate in Real-Time Zero-Shot Surgical Video Segmentation
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Real-time video segmentation is a promising feature for AI-assisted surgery, providing intraoperative guidance by identifying surgical tools and anatomical structures. However, deploying state-of-the-art segmentation models, such as SAM2, in real-time settings is computationally demanding, which makes it essential to balance frame rate and segmentation performance. In this study, we investigate the impact of frame rate on zero-shot surgical video segmentation, evaluating SAM2's effectiveness across multiple frame sampling rates for cholecystectomy procedures. Surprisingly, our findings indicate that in conventional evaluation settings, frame rates as low as a single frame per second can outperform 25 FPS, as fewer frames smooth out segmentation inconsistencies. However, when assessed in a real-time streaming scenario, higher frame rates yield superior temporal coherence and stability, particularly for dynamic objects such as surgical graspers. Finally, we investigate human perception of real-time surgical video segmentation among professionals who work closely with such data and find that respondents consistently prefer high FPS segmentation mask overlays, reinforcing the importance of real-time evaluation in AI-assisted surgery.
Towards Abdominal 3-D Scene Rendering from Laparoscopy Surgical Videos using NeRFs
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Given that a conventional laparoscope only provides a two-dimensional (2-D) view, the detection and diagnosis of medical ailments can be challenging. To overcome the visual constraints associated with laparoscopy, the use of laparoscopic images and videos to reconstruct the three-dimensional (3-D) anatomical structure of the abdomen has proven to be a promising approach. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have recently gained attention thanks to their ability to generate photorealistic images from a 3-D static scene, thus facilitating a more comprehensive exploration of the abdomen through the synthesis of new views. This distinguishes NeRFs from alternative methods such as Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) and depth estimation. In this paper, we present a comprehensive examination of NeRFs in the context of laparoscopy surgical videos, with the goal of rendering abdominal scenes in 3-D. Although our experimental results are promising, the proposed approach encounters substantial challenges, which require further exploration in future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge