Frédéric Guyard
Learning sparse auto-encoders for green AI image coding
Sep 09, 2022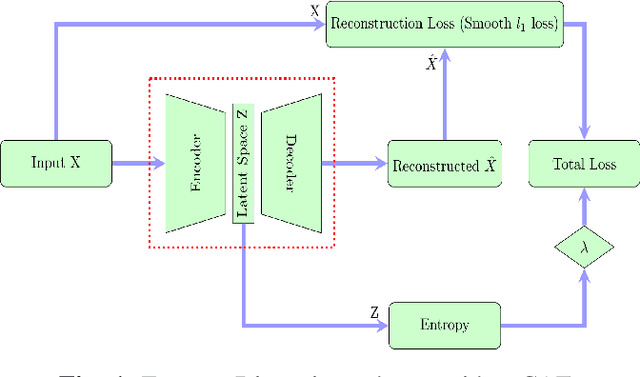
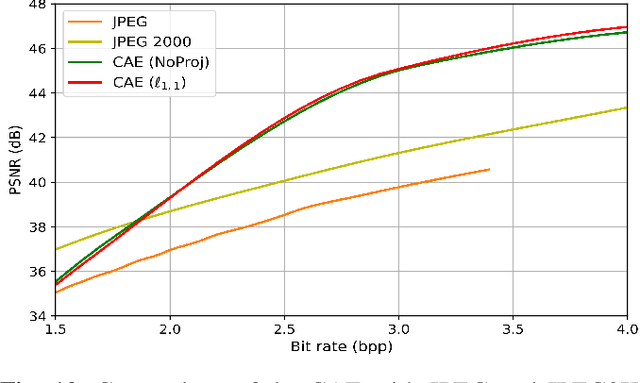
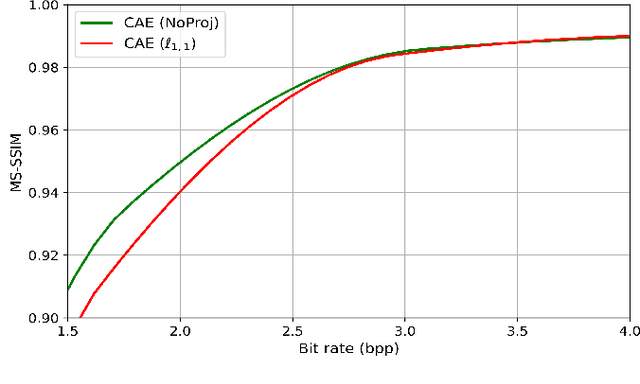
Abstract:Recently, convolutional auto-encoders (CAE) were introduced for image coding. They achieved performance improvements over the state-of-the-art JPEG2000 method. However, these performances were obtained using massive CAEs featuring a large number of parameters and whose training required heavy computational power.\\ In this paper, we address the problem of lossy image compression using a CAE with a small memory footprint and low computational power usage. In order to overcome the computational cost issue, the majority of the literature uses Lagrangian proximal regularization methods, which are time consuming themselves.\\ In this work, we propose a constrained approach and a new structured sparse learning method. We design an algorithm and test it on three constraints: the classical $\ell_1$ constraint, the $\ell_{1,\infty}$ and the new $\ell_{1,1}$ constraint. Experimental results show that the $\ell_{1,1}$ constraint provides the best structured sparsity, resulting in a high reduction of memory and computational cost, with similar rate-distortion performance as with dense networks.
Do Deep Neural Networks Contribute to Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection?
Apr 04, 2022



Abstract:Anomaly detection in time series is a complex task that has been widely studied. In recent years, the ability of unsupervised anomaly detection algorithms has received much attention. This trend has led researchers to compare only learning-based methods in their articles, abandoning some more conventional approaches. As a result, the community in this field has been encouraged to propose increasingly complex learning-based models mainly based on deep neural networks. To our knowledge, there are no comparative studies between conventional, machine learning-based and, deep neural network methods for the detection of anomalies in multivariate time series. In this work, we study the anomaly detection performance of sixteen conventional, machine learning-based and, deep neural network approaches on five real-world open datasets. By analyzing and comparing the performance of each of the sixteen methods, we show that no family of methods outperforms the others. Therefore, we encourage the community to reincorporate the three categories of methods in the anomaly detection in multivariate time series benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge