Frédéric Armetta
SyCoSMA, LIRIS
Large Language Models and Algorithm Execution: Application to an Arithmetic Function
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently developed new advanced functionalities. Their effectiveness relies on statistical learning and generalization capabilities. However, they face limitations in internalizing the data they process and struggle, for instance, to autonomously execute algorithms. In this paper, we investigate the possibility of extending these models' capabilities to algorithm execution through specialized supervised training focused on reasoning decomposition. We introduce a training model called LLM-DAL (Large Language Model - Decompositional Algorithmic Learning), through which we demonstrate that LLMs' ability to perform complex algorithmic inferences and generalize can be significantly improved when the training method is properly designed to guide the model in its learning process.
Leveraging Graph Structures and Large Language Models for End-to-End Synthetic Task-Oriented Dialogues
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:Training task-oriented dialogue systems is both costly and time-consuming, due to the need for high-quality datasets encompassing diverse intents. Traditional methods depend on extensive human annotation, while recent advancements leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate synthetic data. However, these approaches often require custom prompts or code, limiting accessibility for non-technical users. We introduce GraphTOD, an end-to-end framework that simplifies the generation of task-oriented dialogues. Users can create dialogues by specifying transition graphs in JSON format. Our evaluation demonstrates that GraphTOD generates high-quality dialogues across various domains, significantly lowering the cost and complexity of dataset creation.
Sequential annotations for naturally-occurring HRI: first insights
Aug 29, 2023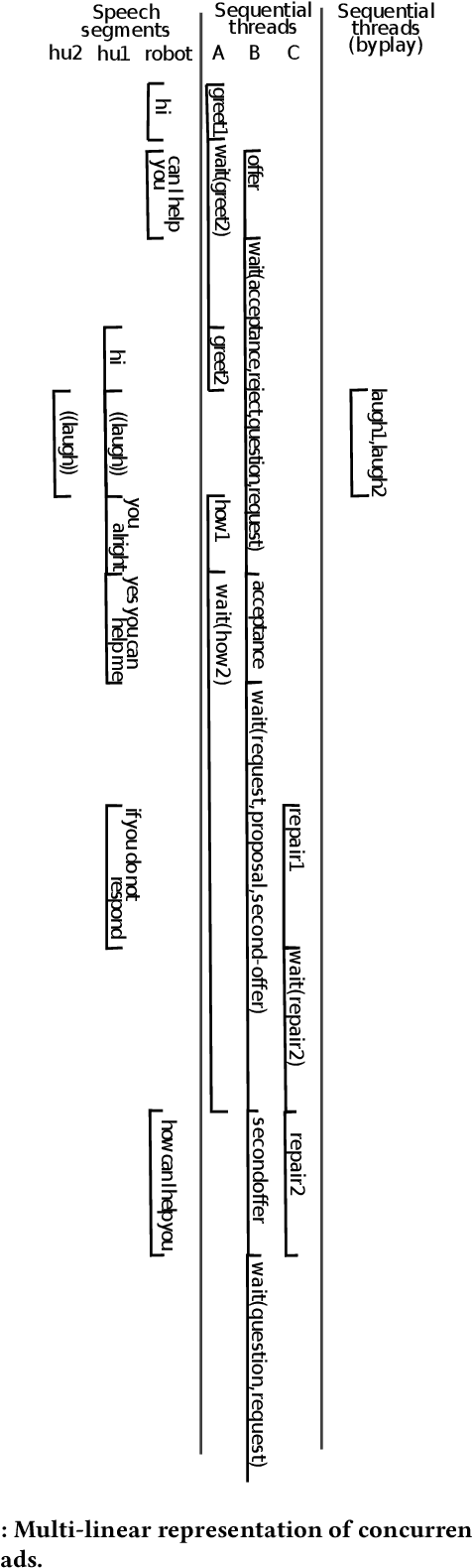
Abstract:We explain the methodology we developed for improving the interactions accomplished by an embedded conversational agent, drawing from Conversation Analytic sequential and multimodal analysis. The use case is a Pepper robot that is expected to inform and orient users in a library. In order to propose and learn better interactive schema, we are creating a corpus of naturally-occurring interactions that will be made available to the community. To do so, we propose an annotation practice based on some theoretical underpinnings about the use of language and multimodal resources in human-robot interaction. CCS CONCEPTS $\bullet$ Computing methodologies $\rightarrow$ Discourse, dialogue and pragmatics; $\bullet$ Human-centered computing $\rightarrow$ Text input; HCI theory, concepts and models; Field studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge