Florian Hinterwimmer
Unintended Memorization of Sensitive Information in Fine-Tuned Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) on sensitive datasets carries a substantial risk of unintended memorization and leakage of Personally Identifiable Information (PII), which can violate privacy regulations and compromise individual safety. In this work, we systematically investigate a critical and underexplored vulnerability: the exposure of PII that appears only in model inputs, not in training targets. Using both synthetic and real-world datasets, we design controlled extraction probes to quantify unintended PII memorization and study how factors such as language, PII frequency, task type, and model size influence memorization behavior. We further benchmark four privacy-preserving approaches including differential privacy, machine unlearning, regularization, and preference alignment, evaluating their trade-offs between privacy and task performance. Our results show that post-training methods generally provide more consistent privacy-utility trade-offs, while differential privacy achieves strong reduction in leakage in specific settings, although it can introduce training instability. These findings highlight the persistent challenge of memorization in fine-tuned LLMs and emphasize the need for robust, scalable privacy-preserving techniques.
A Practical Guide to Fine-tuning Language Models with Limited Data
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:Employing pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) has become the de facto standard in Natural Language Processing (NLP) despite their extensive data requirements. Motivated by the recent surge in research focused on training LLMs with limited data, particularly in low-resource domains and languages, this paper surveys recent transfer learning approaches to optimize model performance in downstream tasks where data is scarce. We first address initial and continued pre-training strategies to better leverage prior knowledge in unseen domains and languages. We then examine how to maximize the utility of limited data during fine-tuning and few-shot learning. The final section takes a task-specific perspective, reviewing models and methods suited for different levels of data scarcity. Our goal is to provide practitioners with practical guidelines for overcoming the challenges posed by constrained data while also highlighting promising directions for future research.
Spotlight on nerves: Portable multispectral optoacoustic imaging of peripheral nerve vascularization and morphology
Jul 28, 2022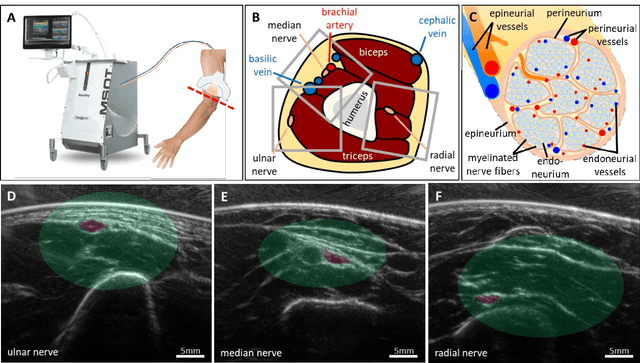

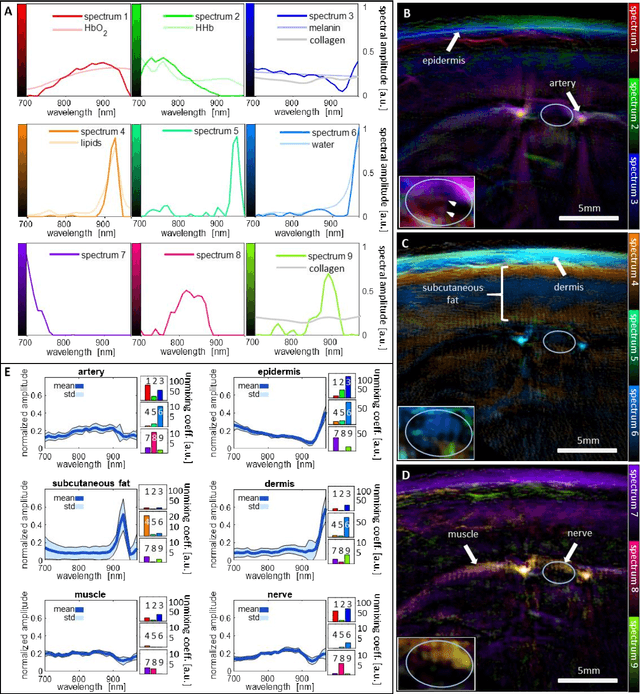
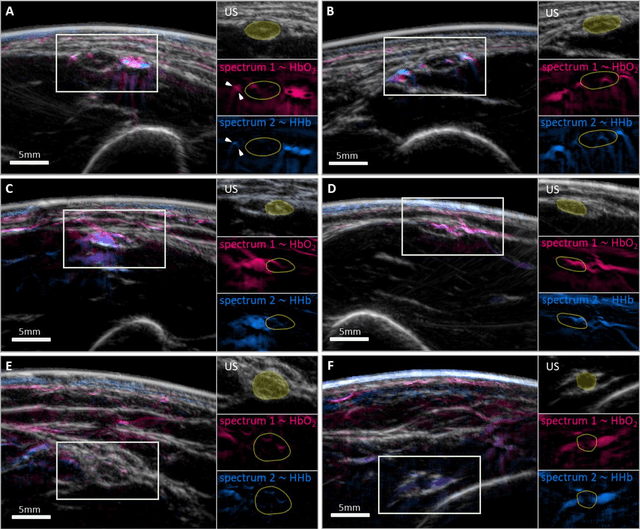
Abstract:Various morphological and functional parameters of peripheral nerves and their vascular supply are indicative of pathological changes due to injury or disease. Based on recent improvements in optoacoustic image quality, we explore the ability of multispectral optoacoustic tomography, in tandem with ultrasound imaging (OPUS), to investigate the vascular environment and morphology of peripheral nerves in vivo in a pilot study on healthy volunteers. We showcase the unique ability of optoacoustic imaging to visualize the vasa nervorum by observing intraneurial vessels in healthy nerves in vivo for the first time. In addition, we demonstrate that the label-free spectral optoacoustic contrast of the perfused connective tissue of peripheral nerves can be linked to the endogenous contrast of haemoglobin and collagen. We introduce metrics to analyze the composition of tissue based on its optoacoustic contrast and show that the high-resolution spectral contrast reveals specific differences between nervous tissue and reference tissue in the nerve's surrounding. We discuss how this showcased extraction of peripheral nerve characteristics using multispectral optoacoustic and ultrasound imaging can offer new insights into the pathophysiology of nerve damage and neuropathies, for example, in the context of diabetes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge