Florian Frommlet
Reversible Genetically Modified Mode Jumping MCMC
Oct 15, 2021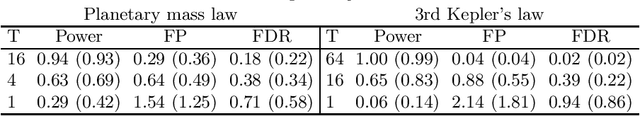
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a reversible version of a genetically modified mode jumping Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm (GMJMCMC) for inference on posterior model probabilities in complex model spaces, where the number of explanatory variables is prohibitively large for classical Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods. Unlike the earlier proposed GMJMCMC algorithm, the introduced algorithm is a proper MCMC and its limiting distribution corresponds to the posterior marginal model probabilities in the explored model space under reasonable regularity conditions.
* 6 pages, 2 table, based on arXiv:1806.02160, which got divided into two revised articles
Rejoinder for the discussion of the paper "A novel algorithmic approach to Bayesian Logic Regression"
May 01, 2020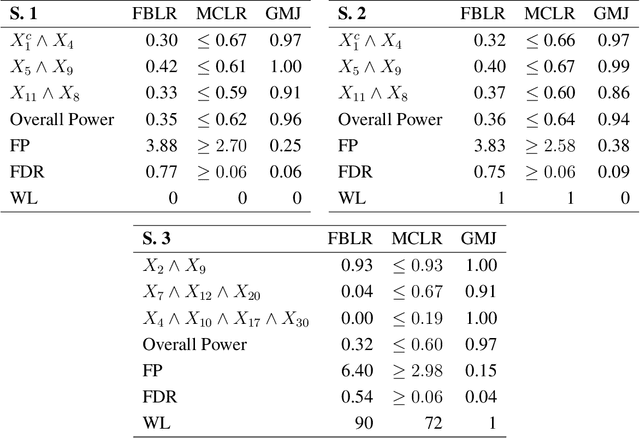
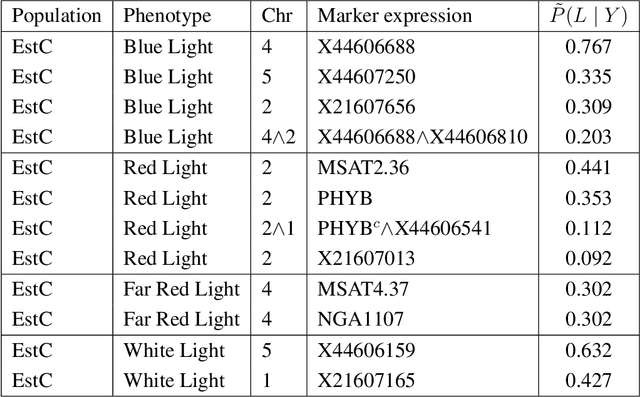
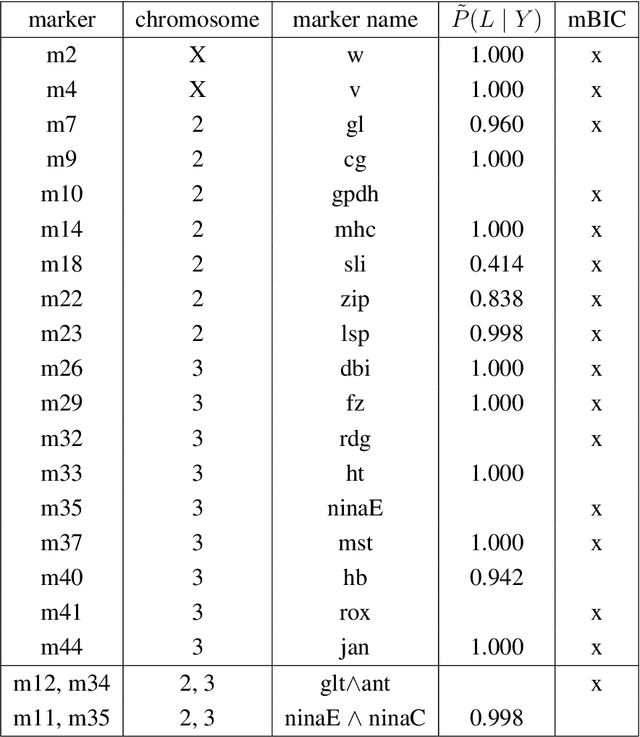
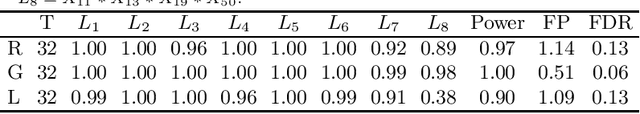
Abstract:In this rejoinder we summarize the comments, questions and remarks on the paper "A novel algorithmic approach to Bayesian Logic Regression" from the discussants. We then respond to those comments, questions and remarks, provide several extensions of the original model and give a tutorial on our R-package EMJMCMC (http://aliaksah.github.io/EMJMCMC2016/)
* published in Bayesian Analysis, Volume 15, Number 1 (2020)
Flexible Bayesian Nonlinear Model Configuration
Mar 05, 2020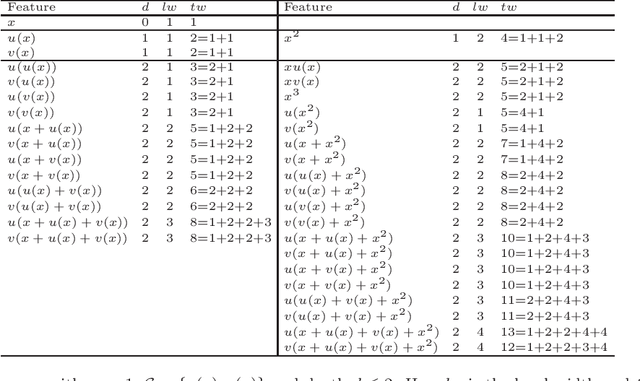
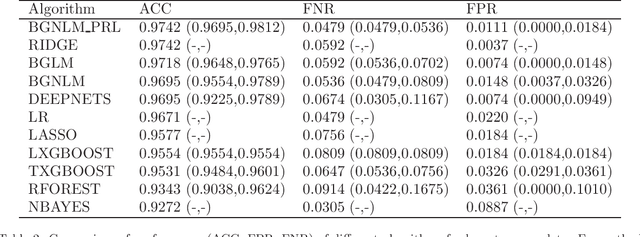
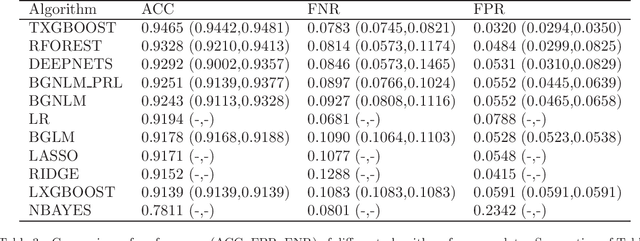
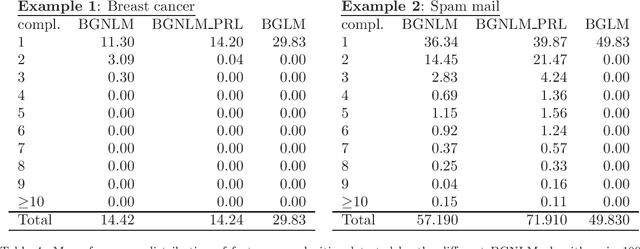
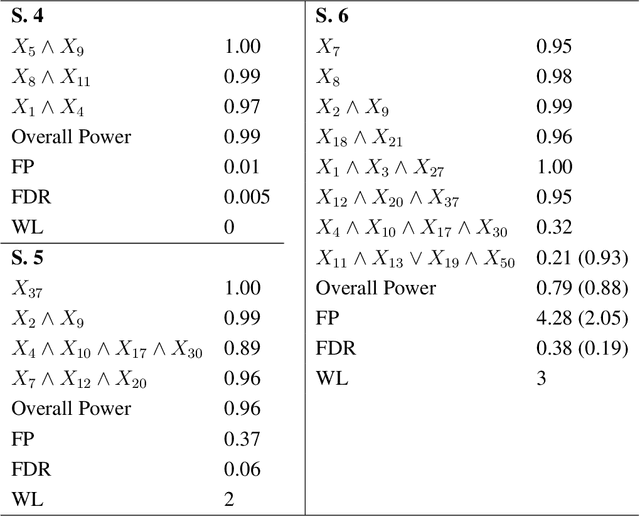
Abstract:Regression models are used in a wide range of applications providing a powerful scientific tool for researchers from different fields. Linear models are often not sufficient to describe the complex relationship between input variables and a response. This relationship can be better described by non-linearities and complex functional interactions. Deep learning models have been extremely successful in terms of prediction although they are often difficult to specify and potentially suffer from overfitting. In this paper, we introduce a class of Bayesian generalized nonlinear regression models with a comprehensive non-linear feature space. Non-linear features are generated hierarchically, similarly to deep learning, but have additional flexibility on the possible types of features to be considered. This flexibility, combined with variable selection, allows us to find a small set of important features and thereby more interpretable models. A genetically modified Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm is developed to make inference. Model averaging is also possible within our framework. In various applications, we illustrate how our approach is used to obtain meaningful non-linear models. Additionally, we compare its predictive performance with a number of machine learning algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge