Filip Wudarski
Sequential Reservoir Computing for Efficient High-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Forecasting
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Forecasting high-dimensional spatiotemporal systems remains computationally challenging for recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models due to gradient-based training and memory bottlenecks. Reservoir Computing (RC) mitigates these challenges by replacing backpropagation with fixed recurrent layers and a convex readout optimization, yet conventional RC architectures still scale poorly with input dimensionality. We introduce a Sequential Reservoir Computing (Sequential RC) architecture that decomposes a large reservoir into a series of smaller, interconnected reservoirs. This design reduces memory and computational costs while preserving long-term temporal dependencies. Using both low-dimensional chaotic systems (Lorenz63) and high-dimensional physical simulations (2D vorticity and shallow-water equations), Sequential RC achieves 15-25% longer valid forecast horizons, 20-30% lower error metrics (SSIM, RMSE), and up to three orders of magnitude lower training cost compared to LSTM and standard RNN baselines. The results demonstrate that Sequential RC maintains the simplicity and efficiency of conventional RC while achieving superior scalability for high-dimensional dynamical systems. This approach provides a practical path toward real-time, energy-efficient forecasting in scientific and engineering applications.
Optimizing quantum heuristics with meta-learning
Aug 08, 2019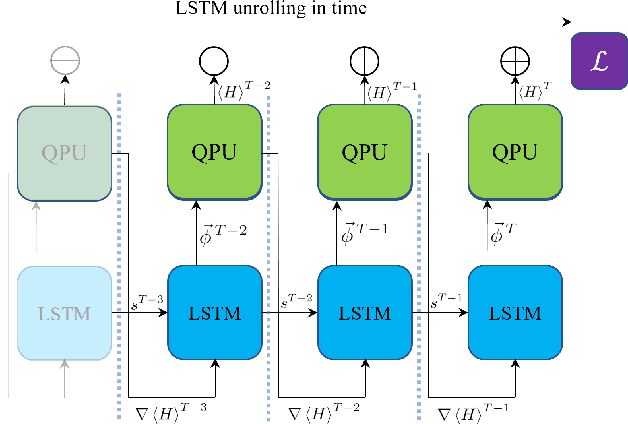
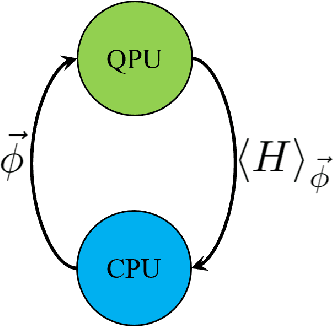
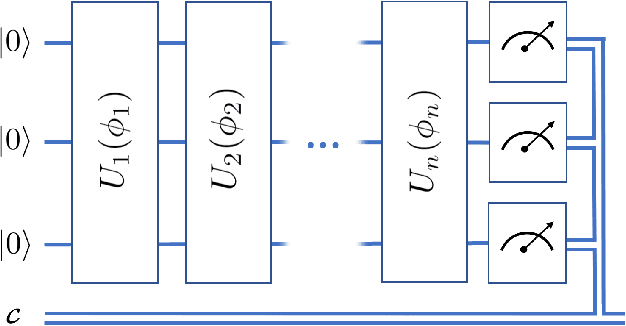
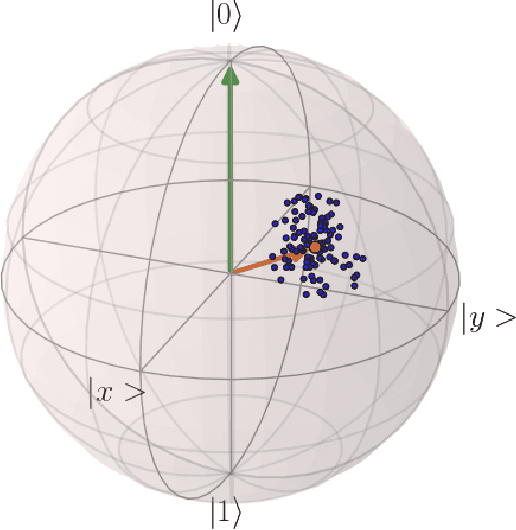
Abstract:Variational quantum algorithms, a class of quantum heuristics, are promising candidates for the demonstration of useful quantum computation. Finding the best way to amplify the performance of these methods on hardware is an important task. Here, we evaluate the optimization of quantum heuristics with an existing class of techniques called `meta-learners'. We compare the performance of a meta-learner to Bayesian optimization, evolutionary strategies, L-BFGS-B and Nelder-Mead approaches, for two quantum heuristics (quantum alternating operator ansatz and variational quantum eigensolver), on three problems, in three simulation environments. We show that the meta-learner comes near to the global optima more frequently than all other optimizers we tested in a noisy parameter setting environment. We also find that the meta-learner is generally more resistant to noise, for example seeing a smaller reduction in performance in Noisy and Sampling environments and performs better on average by a `gain' metric than its closest comparable competitor L-BFGS-B. These results are an important indication that meta-learning and associated machine learning methods will be integral to the useful application of noisy near-term quantum computers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge