Fengrui Zhang
VULCA-Bench: A Multicultural Vision-Language Benchmark for Evaluating Cultural Understanding
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:We introduce VULCA-Bench, a multicultural art-critique benchmark for evaluating Vision-Language Models' (VLMs) cultural understanding beyond surface-level visual perception. Existing VLM benchmarks predominantly measure L1-L2 capabilities (object recognition, scene description, and factual question answering) while under-evaluate higher-order cultural interpretation. VULCA-Bench contains 7,410 matched image-critique pairs spanning eight cultural traditions, with Chinese-English bilingual coverage. We operationalise cultural understanding using a five-layer framework (L1-L5, from Visual Perception to Philosophical Aesthetics), instantiated as 225 culture-specific dimensions and supported by expert-written bilingual critiques. Our pilot results indicate that higher-layer reasoning (L3-L5) is consistently more challenging than visual and technical analysis (L1-L2). The dataset, evaluation scripts, and annotation tools are available under CC BY 4.0 in the supplementary materials.
Cross-Cultural Expert-Level Art Critique Evaluation with Vision-Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at visual perception, yet their ability to interpret cultural meaning in art remains under-validated. We present a tri-tier evaluation framework for cross-cultural art-critique assessment: Tier I computes automated coverage and risk indicators offline; Tier II applies rubric-based scoring using a single primary judge across five dimensions; and Tier III calibrates the Tier II aggregate score to human ratings via isotonic regression, yielding a 5.2% reduction in MAE on a 152-sample held-out set. The framework outputs a calibrated cultural-understanding score for model selection and cultural-gap diagnosis, together with dimension-level diagnostics and risk indicators. We evaluate 15 VLMs on 294 expert anchors spanning six cultural traditions. Key findings are that (i) automated metrics are unreliable proxies for cultural depth, (ii) Western samples score higher than non-Western samples under our sampling and rubric, and (iii) cross-judge scale mismatch makes naive score averaging unreliable, motivating a single primary judge with explicit calibration. Dataset and code are available in the supplementary materials.
Catch Causal Signals from Edges for Label Imbalance in Graph Classification
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in causal research on graphs and its application to cracking label imbalance, the role of edge features in detecting the causal effects within graphs has been largely overlooked, leaving existing methods with untapped potential for further performance gains. In this paper, we enhance the causal attention mechanism through effectively leveraging edge information to disentangle the causal subgraph from the original graph, as well as further utilizing edge features to reshape graph representations. Capturing more comprehensive causal signals, our design leads to improved performance on graph classification tasks with label imbalance issues. We evaluate our approach on real-word datasets PTC, Tox21, and ogbg-molhiv, observing improvements over baselines. Overall, we highlight the importance of edge features in graph causal detection and provide a promising direction for addressing label imbalance challenges in graph-level tasks. The model implementation details and the codes are available on https://github.com/fengrui-z/ECAL
Data Valuation and Detections in Federated Learning
Nov 13, 2023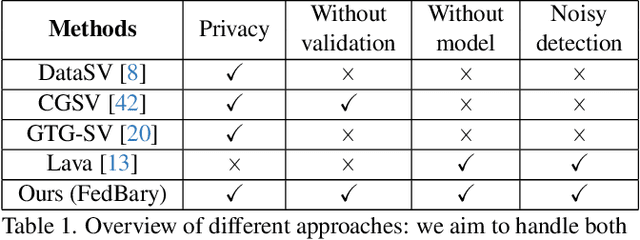
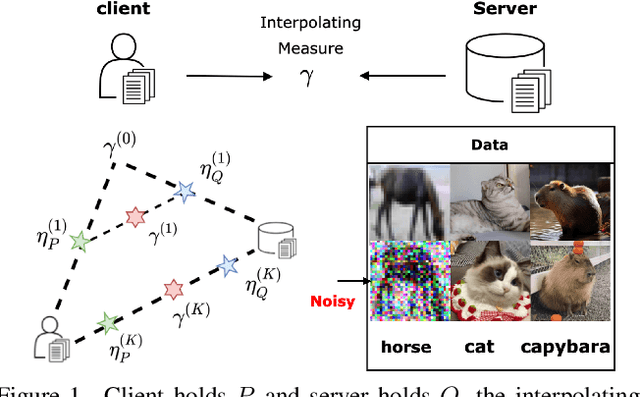
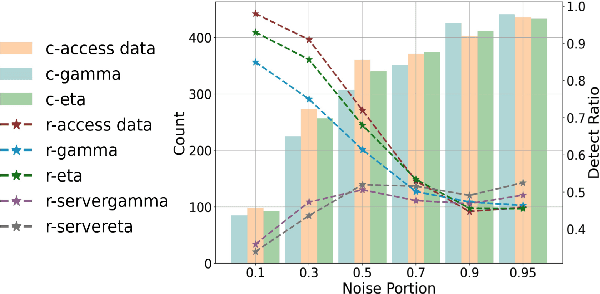
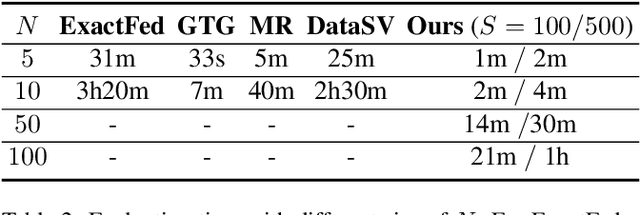
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training while preserving the privacy of raw data. A challenge in this framework is the fair and efficient valuation of data, which is crucial for incentivizing clients to contribute high-quality data in the FL task. In scenarios involving numerous data clients within FL, it is often the case that only a subset of clients and datasets are pertinent to a specific learning task, while others might have either a negative or negligible impact on the model training process. This paper introduces a novel privacy-preserving method for evaluating client contributions and selecting relevant datasets without a pre-specified training algorithm in an FL task. Our proposed approach FedBary, utilizes Wasserstein distance within the federated context, offering a new solution for data valuation in the FL framework. This method ensures transparent data valuation and efficient computation of the Wasserstein barycenter and reduces the dependence on validation datasets. Through extensive empirical experiments and theoretical analyses, we demonstrate the potential of this data valuation method as a promising avenue for FL research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge