Fengchen Gu
MTS: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Portfolio Management Framework with Time-Awareness and Short-Selling
Mar 06, 2025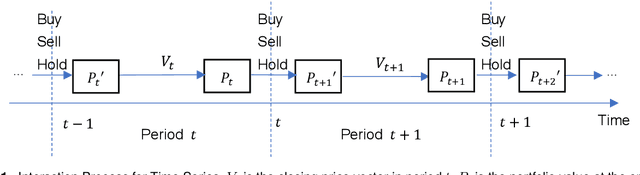
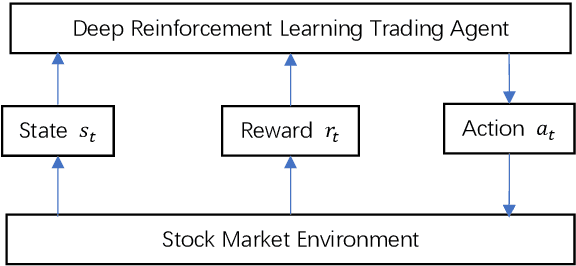
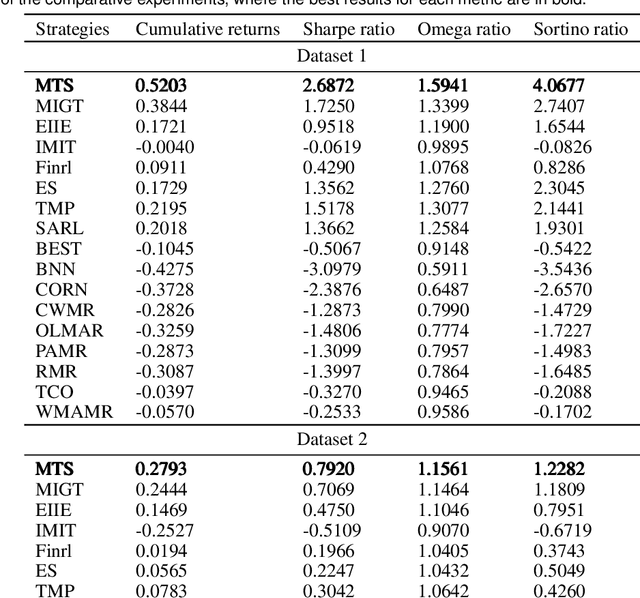
Abstract:Portfolio management remains a crucial challenge in finance, with traditional methods often falling short in complex and volatile market environments. While deep reinforcement approaches have shown promise, they still face limitations in dynamic risk management, exploitation of temporal markets, and incorporation of complex trading strategies such as short-selling. These limitations can lead to suboptimal portfolio performance, increased vulnerability to market volatility, and missed opportunities in capturing potential returns from diverse market conditions. This paper introduces a Deep Reinforcement Learning Portfolio Management Framework with Time-Awareness and Short-Selling (MTS), offering a robust and adaptive strategy for sustainable investment performance. This framework utilizes a novel encoder-attention mechanism to address the limitations by incorporating temporal market characteristics, a parallel strategy for automated short-selling based on market trends, and risk management through innovative Incremental Conditional Value at Risk, enhancing adaptability and performance. Experimental validation on five diverse datasets from 2019 to 2023 demonstrates MTS's superiority over traditional algorithms and advanced machine learning techniques. MTS consistently achieves higher cumulative returns, Sharpe, Omega, and Sortino ratios, underscoring its effectiveness in balancing risk and return while adapting to market dynamics. MTS demonstrates an average relative increase of 30.67% in cumulative returns and 29.33% in Sharpe ratio compared to the next best-performing strategies across various datasets.
MIGT: Memory Instance Gated Transformer Framework for Financial Portfolio Management
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has been applied in financial portfolio management to improve returns in changing market conditions. However, unlike most fields where DRL is widely used, the stock market is more volatile and dynamic as it is affected by several factors such as global events and investor sentiment. Therefore, it remains a challenge to construct a DRL-based portfolio management framework with strong return capability, stable training, and generalization ability. This study introduces a new framework utilizing the Memory Instance Gated Transformer (MIGT) for effective portfolio management. By incorporating a novel Gated Instance Attention module, which combines a transformer variant, instance normalization, and a Lite Gate Unit, our approach aims to maximize investment returns while ensuring the learning process's stability and reducing outlier impacts. Tested on the Dow Jones Industrial Average 30, our framework's performance is evaluated against fifteen other strategies using key financial metrics like the cumulative return and risk-return ratios (Sharpe, Sortino, and Omega ratios). The results highlight MIGT's advantage, showcasing at least a 9.75% improvement in cumulative returns and a minimum 2.36% increase in risk-return ratios over competing strategies, marking a significant advancement in DRL for portfolio management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge