Feng Cao
HuiduRep: A Robust Self-Supervised Framework for Learning Neural Representations from Extracellular Spikes
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Extracellular recordings are brief voltage fluctuations recorded near neurons, widely used in neuroscience as the basis for decoding brain activity at single-neuron resolution. Spike sorting, which assigns each spike to its source neuron, is a critical step in brain sensing pipelines. However, it remains challenging under low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), electrode drift, and cross-session variability. In this paper, we propose HuiduRep, a robust self-supervised representation learning framework that extracts discriminative and generalizable features from extracellular spike waveforms. By combining contrastive learning with a denoising autoencoder, HuiduRep learns latent representations that are robust to noise and drift. Built on HuiduRep, we develop a spike sorting pipeline that clusters spike representations without supervision. Experiments on hybrid and real-world datasets demonstrate that HuiduRep achieves strong robustness and the pipeline matches or outperforms state-of-the-art tools such as KiloSort4 and MountainSort5. These findings demonstrate the potential of self-supervised spike representation learning as a foundational tool for robust and generalizable processing of extracellular recordings.
CNMBert: A Model For Hanyu Pinyin Abbreviation to Character Conversion Task
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:The task of converting Hanyu Pinyin abbreviations to Chinese characters represents a significant branch within the domain of Chinese Spelling Correction (CSC). This task is typically one of text-length alignment, however, due to the limited informational content in pinyin abbreviations, achieving accurate conversion is challenging. In this paper, we propose CNMBert which stands for zh-CN Pinyin Multi-mask Bert Model as a solution to this issue. CNMBert surpasses few-shot GPT models, achieving a 59.63% MRR on a 10,424-sample Hanyu Pinyin abbreviation test dataset.
Insect-Computer Hybrid System for Autonomous Search and Rescue Mission
Jun 04, 2021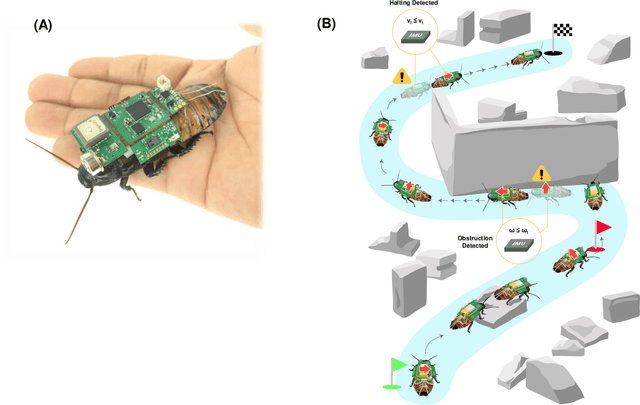
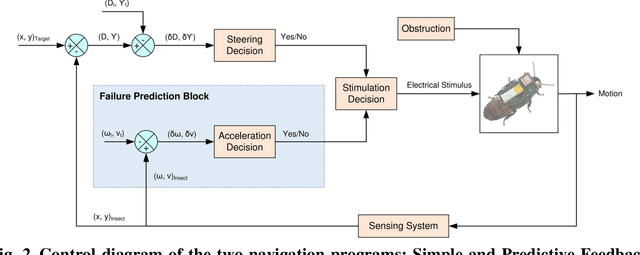
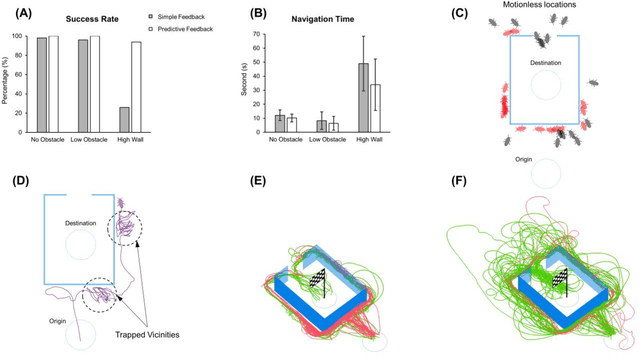
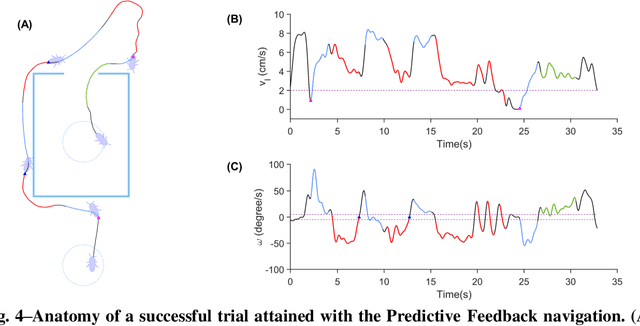
Abstract:There is still a long way to go before artificial mini robots are really used for search and rescue missions in disaster-hit areas due to hindrance in power consumption, computation load of the locomotion, and obstacle-avoidance system. Insect-computer hybrid system, which is the fusion of living insect platform and microcontroller, emerges as an alternative solution. This study demonstrates the first-ever insect-computer hybrid system conceived for search and rescue missions, which is capable of autonomous navigation and human presence detection in an unstructured environment. Customized navigation control algorithm utilizing the insect's intrinsic navigation capability achieved exploration and negotiation of complex terrains. On-board high-accuracy human presence detection using infrared camera was achieved with a custom machine learning model. Low power consumption suggests system suitability for hour-long operations and its potential for realization in real-life missions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge