Fedor Kitashov
Foreign English Accent Adjustment by Learning Phonetic Patterns
Jul 09, 2018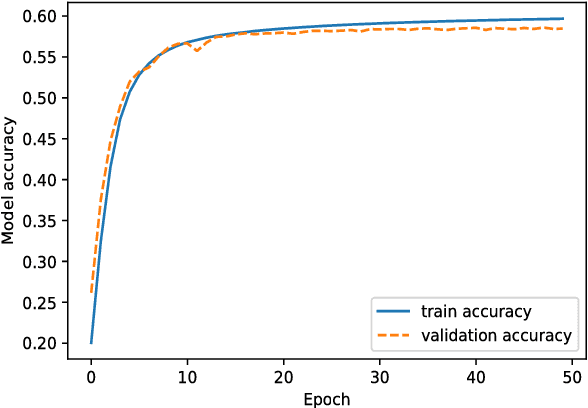
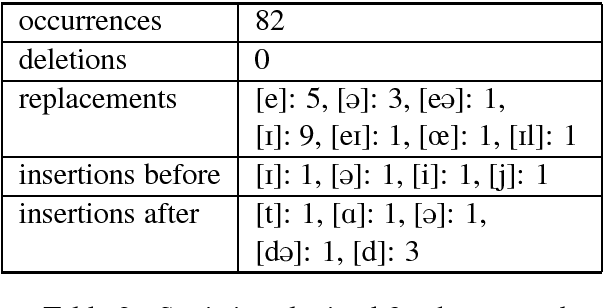
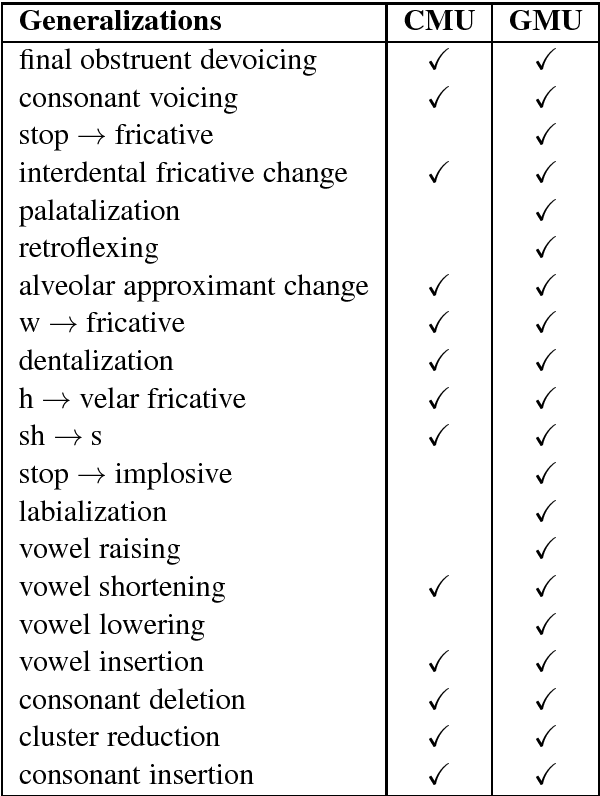
Abstract:State-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems struggle with the lack of data for rare accents. For sufficiently large datasets, neural engines tend to outshine statistical models in most natural language processing problems. However, a speech accent remains a challenge for both approaches. Phonologists manually create general rules describing a speaker's accent, but their results remain underutilized. In this paper, we propose a model that automatically retrieves phonological generalizations from a small dataset. This method leverages the difference in pronunciation between a particular dialect and General American English (GAE) and creates new accented samples of words. The proposed model is able to learn all generalizations that previously were manually obtained by phonologists. We use this statistical method to generate a million phonological variations of words from the CMU Pronouncing Dictionary and train a sequence-to-sequence RNN to recognize accented words with 59% accuracy.
RNN-based Early Cyber-Attack Detection for the Tennessee Eastman Process
Sep 07, 2017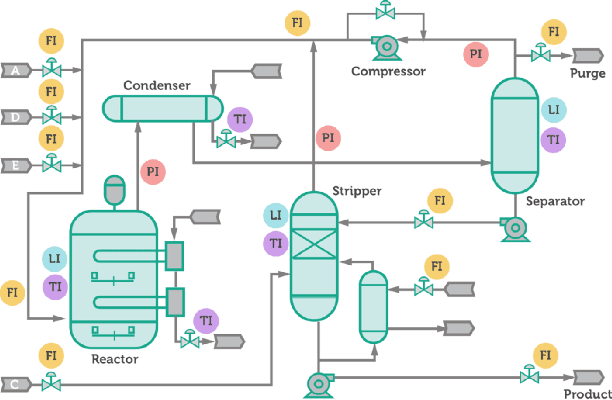
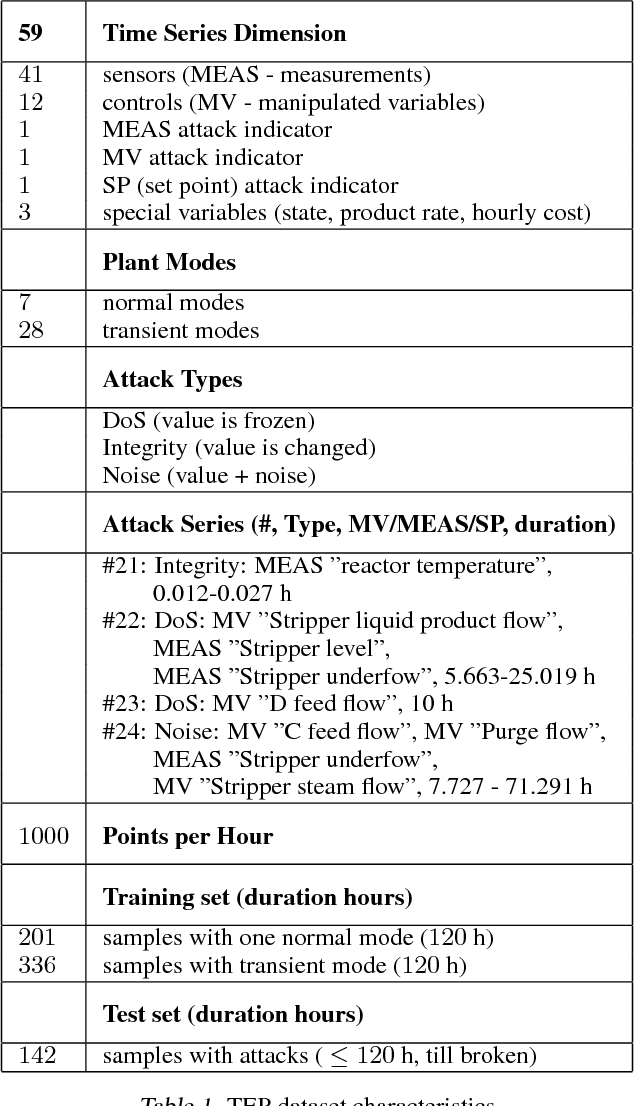
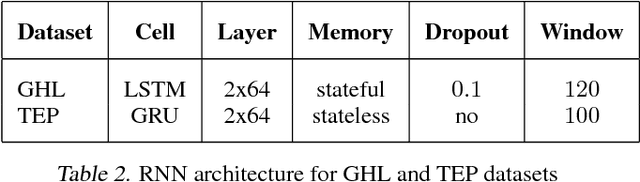
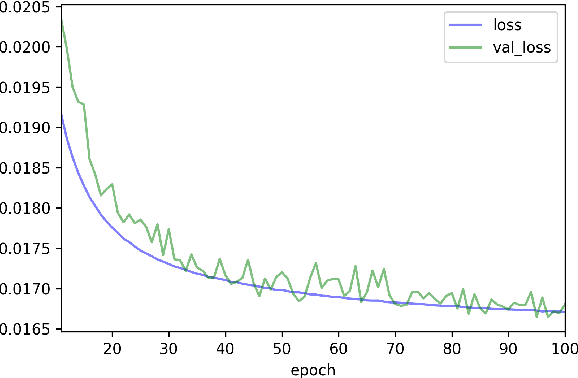
Abstract:An RNN-based forecasting approach is used to early detect anomalies in industrial multivariate time series data from a simulated Tennessee Eastman Process (TEP) with many cyber-attacks. This work continues a previously proposed LSTM-based approach to the fault detection in simpler data. It is considered necessary to adapt the RNN network to deal with data containing stochastic, stationary, transitive and a rich variety of anomalous behaviours. There is particular focus on early detection with special NAB-metric. A comparison with the DPCA approach is provided. The generated data set is made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge