Fatemeh Salmani
Russia-Ukraine war: Modeling and Clustering the Sentiments Trends of Various Countries
Jan 02, 2023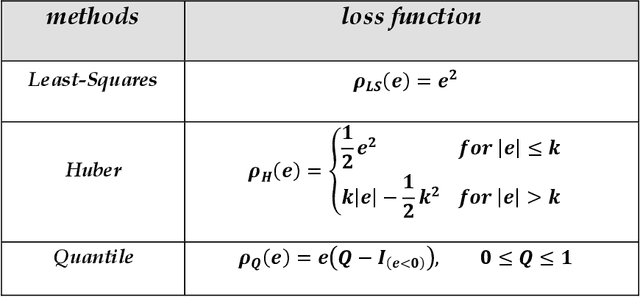
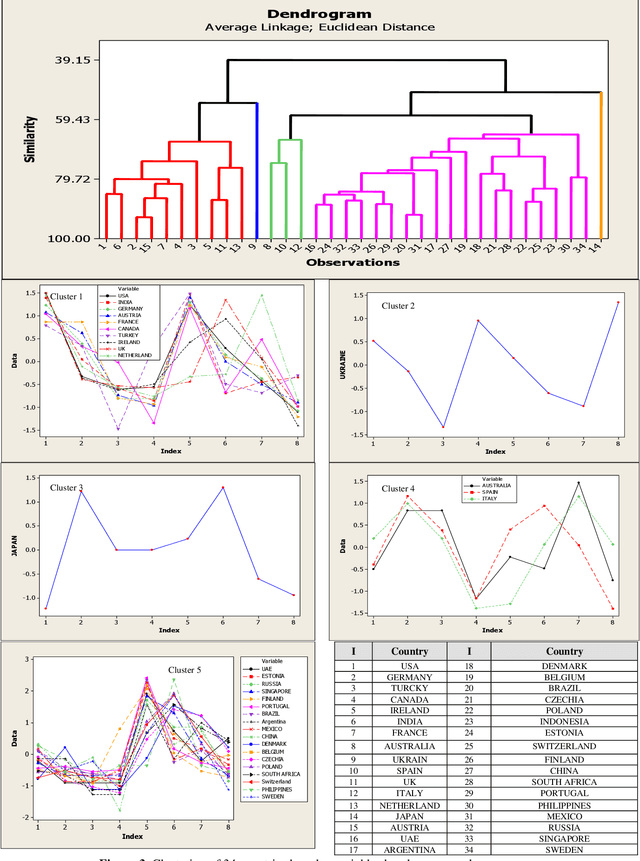
Abstract:With Twitter's growth and popularity, a huge number of views are shared by users on various topics, making this platform a valuable information source on various political, social, and economic issues. This paper investigates English tweets on the Russia-Ukraine war to analyze trends reflecting users' opinions and sentiments regarding the conflict. The tweets' positive and negative sentiments are analyzed using a BERT-based model, and the time series associated with the frequency of positive and negative tweets for various countries is calculated. Then, we propose a method based on the neighborhood average for modeling and clustering the time series of countries. The clustering results provide valuable insight into public opinion regarding this conflict. Among other things, we can mention the similar thoughts of users from the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and most Western European countries versus the shared views of Eastern European, Scandinavian, Asian, and South American nations toward the conflict.
Extracting Feelings of People Regarding COVID-19 by Social Network Mining
Oct 12, 2021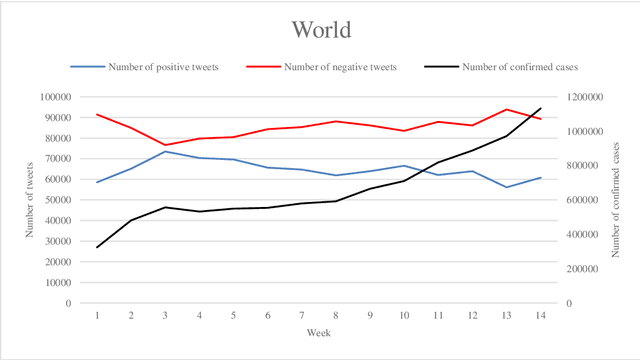
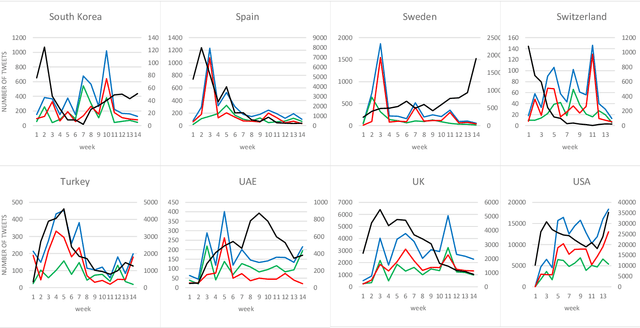
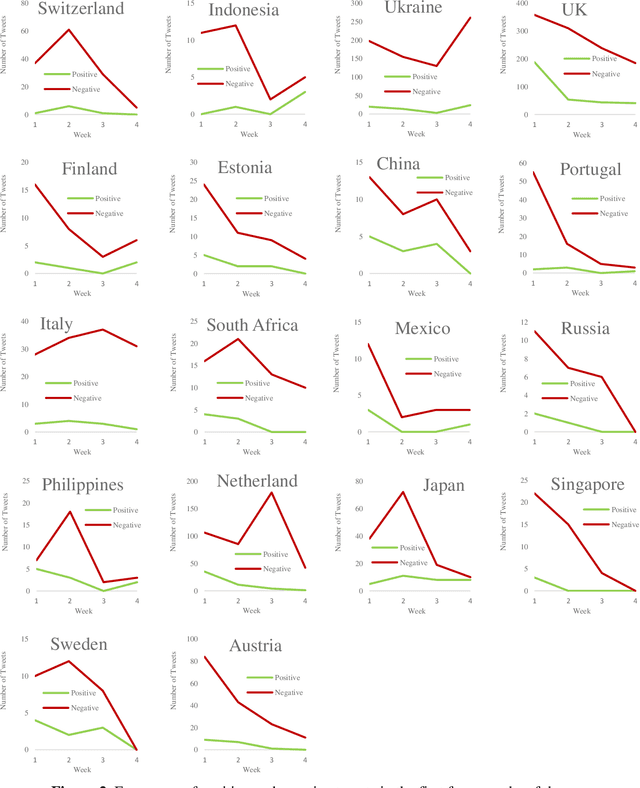
Abstract:In 2020, COVID-19 became the chief concern of the world and is still reflected widely in all social networks. Each day, users post millions of tweets and comments on this subject, which contain significant implicit information about the public opinion. In this regard, a dataset of COVID-related tweets in English language is collected, which consists of more than two million tweets from March 23 to June 23 of 2020 to extract the feelings of the people in various countries in the early stages of this outbreak. To this end, first, we use a lexicon-based approach in conjunction with the GeoNames geographic database to label the tweets with their locations. Next, a method based on the recently introduced and widely cited RoBERTa model is proposed to analyze their sentimental content. After that, the trend graphs of the frequency of tweets as well as sentiments are produced for the world and the nations that were more engaged with COVID-19. Graph analysis shows that the frequency graphs of the tweets for the majority of nations are significantly correlated with the official statistics of the daily afflicted in them. Moreover, several implicit knowledge is extracted and discussed.
Analyzing the Impact of COVID-19 on Economy from the Perspective of Users Reviews
Oct 05, 2021
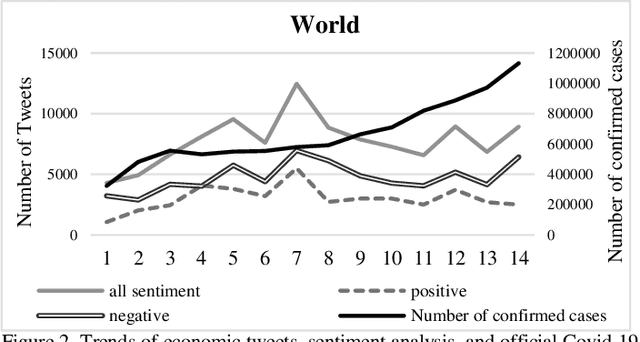
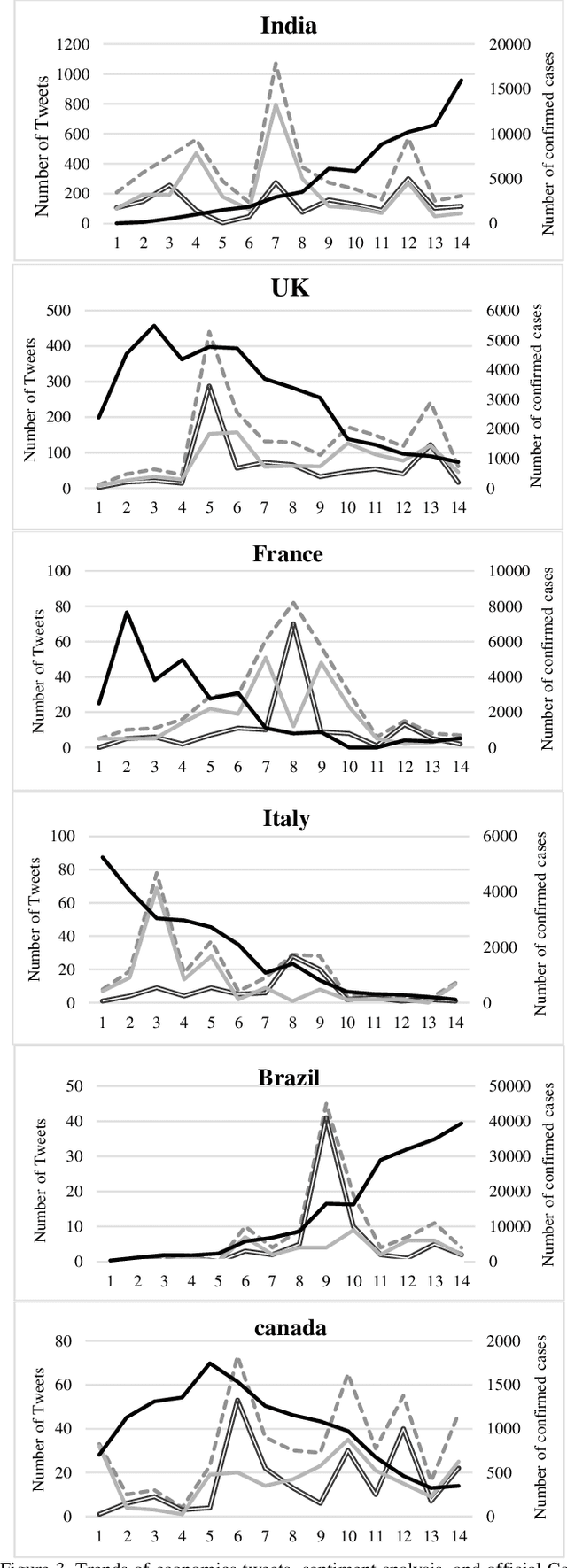
Abstract:One of the most important incidents in the world in 2020 is the outbreak of the Coronavirus. Users on social networks publish a large number of comments about this event. These comments contain important hidden information of public opinion regarding this pandemic. In this research, a large number of Coronavirus-related tweets are considered and analyzed using natural language processing and information retrieval science. Initially, the location of the tweets is determined using a dictionary prepared through the Geo-Names geographic database, which contains detailed and complete information of places such as city names, streets, and postal codes. Then, using a large dictionary prepared from the terms of economics, related tweets are extracted and sentiments corresponded to tweets are analyzed with the help of the RoBERTa language-based model, which has high accuracy and good performance. Finally, the frequency chart of tweets related to the economy and their sentiment scores (positive and negative tweets) is plotted over time for the entire world and the top 10 economies. From the analysis of the charts, we learn that the reason for publishing economic tweets is not only the increase in the number of people infected with the Coronavirus but also imposed restrictions and lockdowns in countries. The consequences of these restrictions include the loss of millions of jobs and the economic downturn.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge