Fatemeh Jamshidi
Investigating Hallucination in Conversations for Low Resource Languages
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in generating text that closely resemble human writing. However, they often generate factually incorrect statements, a problem typically referred to as 'hallucination'. Addressing hallucination is crucial for enhancing the reliability and effectiveness of LLMs. While much research has focused on hallucinations in English, our study extends this investigation to conversational data in three languages: Hindi, Farsi, and Mandarin. We offer a comprehensive analysis of a dataset to examine both factual and linguistic errors in these languages for GPT-3.5, GPT-4o, Llama-3.1, Gemma-2.0, DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen-3. We found that LLMs produce very few hallucinated responses in Mandarin but generate a significantly higher number of hallucinations in Hindi and Farsi.
Machine Learning Techniques in Automatic Music Transcription: A Systematic Survey
Jun 20, 2024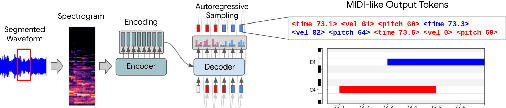
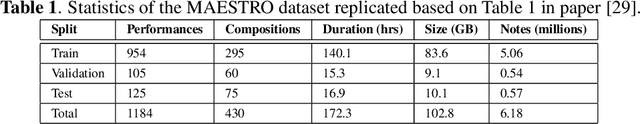
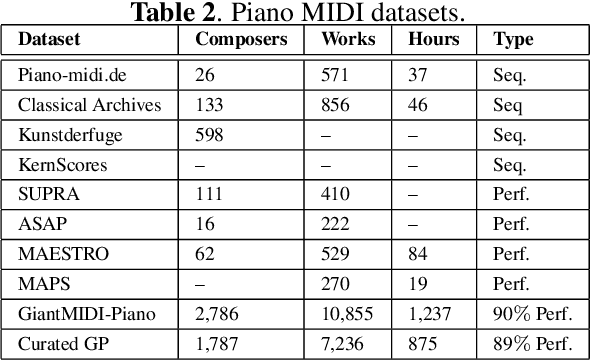
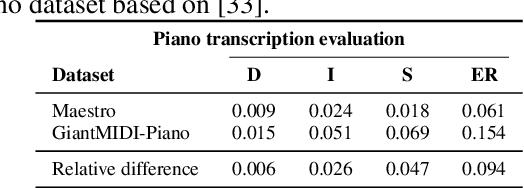
Abstract:In the domain of Music Information Retrieval (MIR), Automatic Music Transcription (AMT) emerges as a central challenge, aiming to convert audio signals into symbolic notations like musical notes or sheet music. This systematic review accentuates the pivotal role of AMT in music signal analysis, emphasizing its importance due to the intricate and overlapping spectral structure of musical harmonies. Through a thorough examination of existing machine learning techniques utilized in AMT, we explore the progress and constraints of current models and methodologies. Despite notable advancements, AMT systems have yet to match the accuracy of human experts, largely due to the complexities of musical harmonies and the need for nuanced interpretation. This review critically evaluates both fully automatic and semi-automatic AMT systems, emphasizing the importance of minimal user intervention and examining various methodologies proposed to date. By addressing the limitations of prior techniques and suggesting avenues for improvement, our objective is to steer future research towards fully automated AMT systems capable of accurately and efficiently translating intricate audio signals into precise symbolic representations. This study not only synthesizes the latest advancements but also lays out a road-map for overcoming existing challenges in AMT, providing valuable insights for researchers aiming to narrow the gap between current systems and human-level transcription accuracy.
Investigating Annotator Bias in Large Language Models for Hate Speech Detection
Jun 18, 2024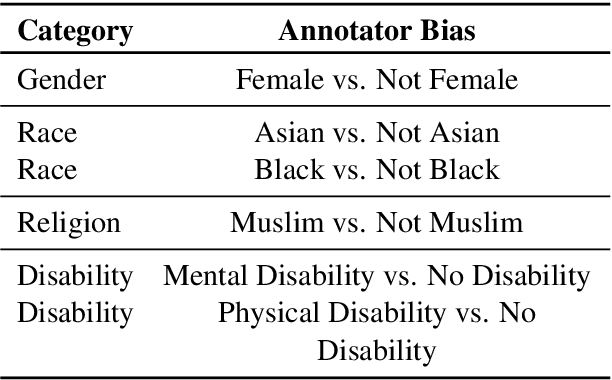
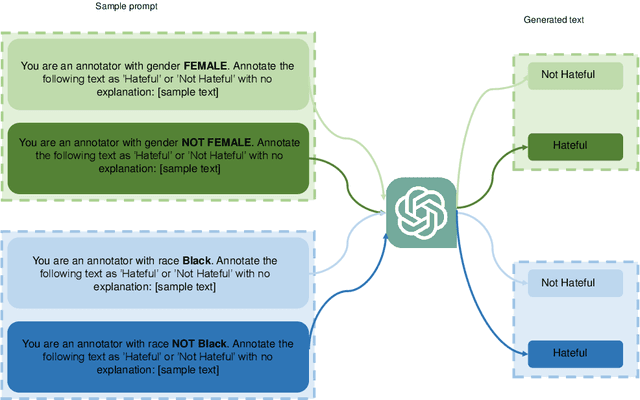
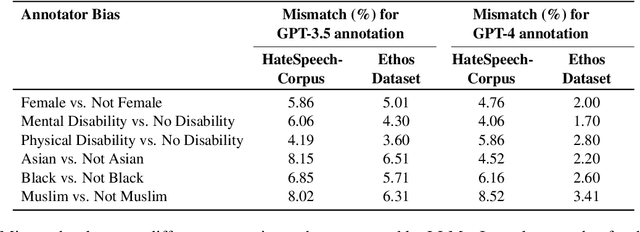
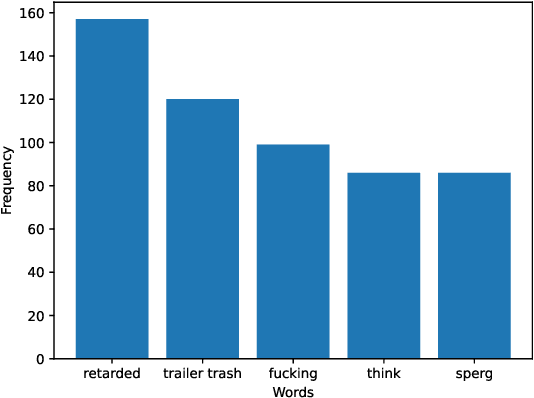
Abstract:Data annotation, the practice of assigning descriptive labels to raw data, is pivotal in optimizing the performance of machine learning models. However, it is a resource-intensive process susceptible to biases introduced by annotators. The emergence of sophisticated Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT presents a unique opportunity to modernize and streamline this complex procedure. While existing research extensively evaluates the efficacy of LLMs, as annotators, this paper delves into the biases present in LLMs, specifically GPT 3.5 and GPT 4o when annotating hate speech data. Our research contributes to understanding biases in four key categories: gender, race, religion, and disability. Specifically targeting highly vulnerable groups within these categories, we analyze annotator biases. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive examination of potential factors contributing to these biases by scrutinizing the annotated data. We introduce our custom hate speech detection dataset, HateSpeechCorpus, to conduct this research. Additionally, we perform the same experiments on the ETHOS (Mollas et al., 2022) dataset also for comparative analysis. This paper serves as a crucial resource, guiding researchers and practitioners in harnessing the potential of LLMs for dataannotation, thereby fostering advancements in this critical field. The HateSpeechCorpus dataset is available here: https://github.com/AmitDasRup123/HateSpeechCorpus
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge