Farzad Toutounchi
Advanced Super-Resolution using Lossless Pooling Convolutional Networks
Dec 14, 2018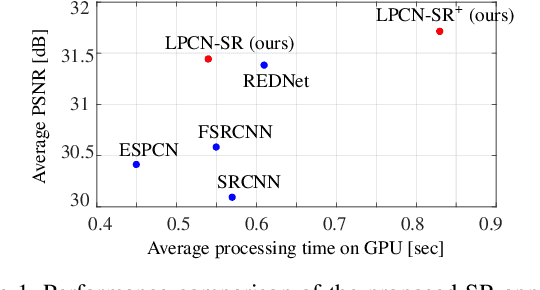
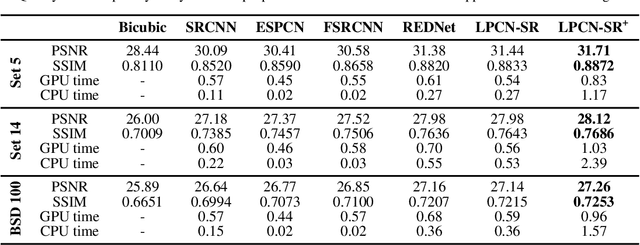
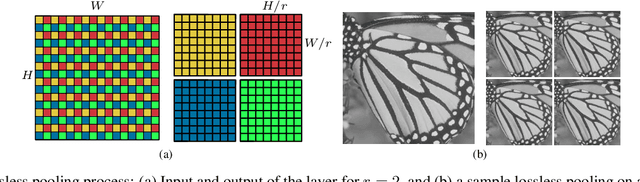
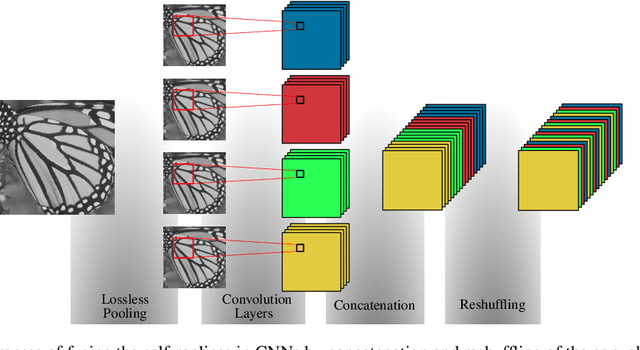
Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel deep learning-based approach for still image super-resolution, that unlike the mainstream models does not rely solely on the input low resolution image for high quality upsampling, and takes advantage of a set of artificially created auxiliary self-replicas of the input image that are incorporated in the neural network to create an enhanced and accurate upscaling scheme. Inclusion of the proposed lossless pooling layers, and the fusion of the input self-replicas enable the model to exploit the high correlation between multiple instances of the same content, and eventually result in significant improvements in the quality of the super-resolution, which is confirmed by extensive evaluations.
Convolutional Neural Networks for Video Quality Assessment
Sep 26, 2018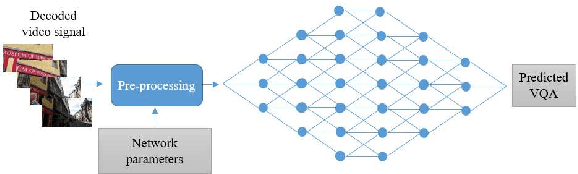
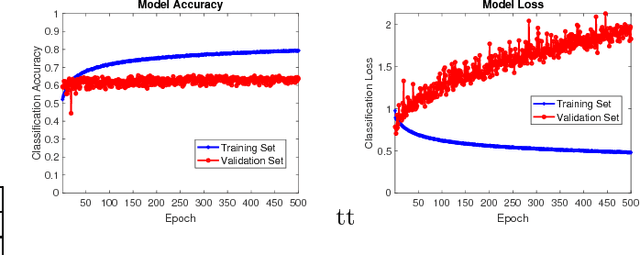


Abstract:Video Quality Assessment (VQA) is a very challenging task due to its highly subjective nature. Moreover, many factors influence VQA. Compression of video content, while necessary for minimising transmission and storage requirements, introduces distortions which can have detrimental effects on the perceived quality. Especially when dealing with modern video coding standards, it is extremely difficult to model the effects of compression due to the unpredictability of encoding on different content types. Moreover, transmission also introduces delays and other distortion types which affect the perceived quality. Therefore, it would be highly beneficial to accurately predict the perceived quality of video to be distributed over modern content distribution platforms, so that specific actions could be undertaken to maximise the Quality of Experience (QoE) of the users. Traditional VQA techniques based on feature extraction and modelling may not be sufficiently accurate. In this paper, a novel Deep Learning (DL) framework is introduced for effectively predicting VQA of video content delivery mechanisms based on end-to-end feature learning. The proposed framework is based on Convolutional Neural Networks, taking into account compression distortion as well as transmission delays. Training and evaluation of the proposed framework are performed on a user annotated VQA dataset specifically created to undertake this work. The experiments show that the proposed methods can lead to high accuracy of the quality estimation, showcasing the potential of using DL in complex VQA scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge