Farshid Faal
Language Alignment via Nash-learning and Adaptive feedback
Jun 22, 2024
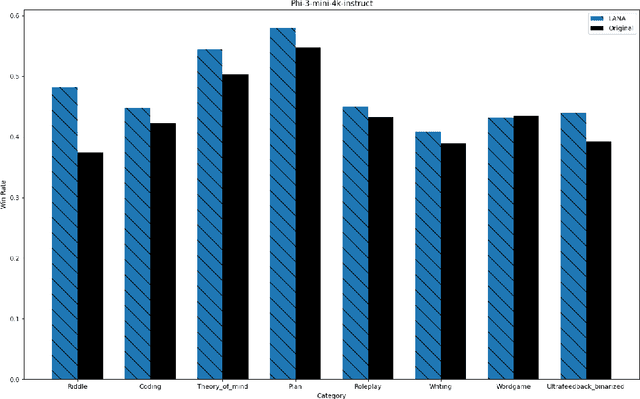

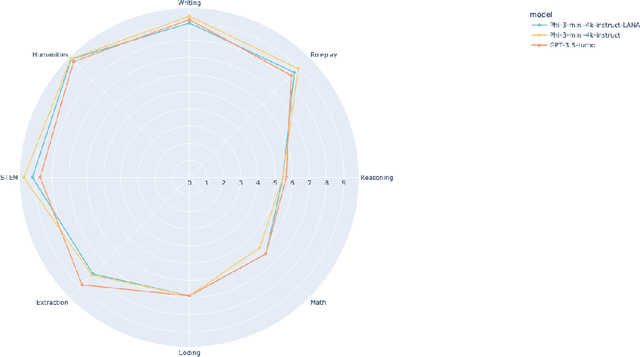
Abstract:Recent research has shown the potential of Nash Learning via Human Feedback for large language model alignment by incorporating the notion of a preference model in a minimax game setup. We take this idea further by casting the alignment as a mirror descent algorithm against the adaptive feedback of an improved opponent, thereby removing the need for learning a preference model or the existence of an annotated dataset altogether. The resulting algorithm, which we refer to as Language Alignment via Nash-learning and Adaptive feedback (LANA), is capable of self-alignment without the need for a human-annotated preference dataset. We support this statement with various experiments and mathematical discussion.
Reward Modeling for Mitigating Toxicity in Transformer-based Language Models
Feb 28, 2022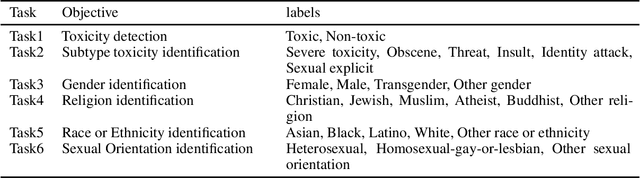
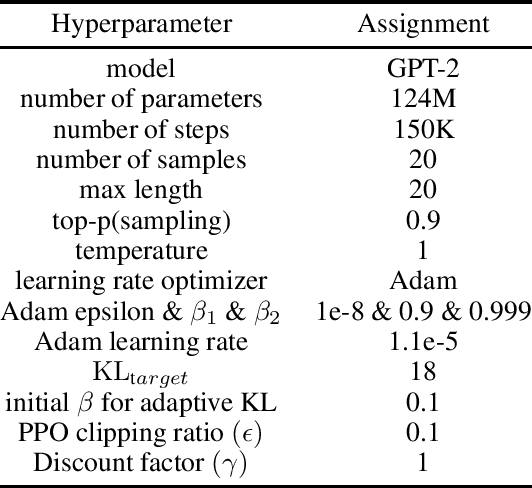
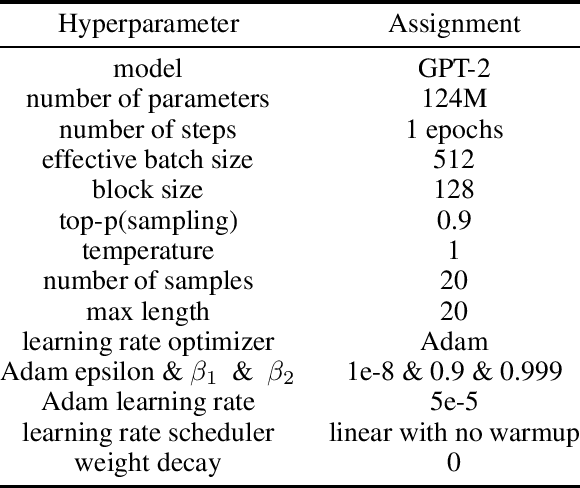

Abstract:Transformer-based language models are able to generate fluent text and be efficiently adapted across various natural language generation tasks. However, language models that are pretrained on large unlabeled web text corpora have been shown to suffer from degenerating toxic content and social bias behaviors, consequently hindering their safe deployment. Various detoxification methods were proposed to mitigate the language model's toxicity; however, these methods struggled to detoxify language models when conditioned on prompts that contain specific social identities related to gender, race, or religion. In this study, we propose Reinforce-Detoxify; A reinforcement learning-based method for mitigating toxicity in language models. We address the challenge of safety in language models and propose a new reward model that is able to detect toxic content and mitigate unintended bias towards social identities in toxicity prediction. The experiments demonstrate that the Reinforce-Detoxify method for language model detoxification outperforms existing detoxification approaches in automatic evaluation metrics, indicating the ability of our approach in language model detoxification and less prone to unintended bias toward social identities in generated content.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge