Fahim Hafiz
An Energy-Efficient Smart Bus Transport Management System with Blind-Spot Collision Detection Ability
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Public bus transport systems in developing countries often suffer from a lack of real-time location updates and for users, making commuting inconvenient and unreliable for passengers. Furthermore, stopping at undesired locations rather than designated bus stops creates safety risks and contributes to roadblocks, often causing traffic congestion. Additionally, issues such as blind spots, along with a lack of following traffic laws, increase the chances of accidents. In this work, we address these challenges by proposing a smart public bus system along with intelligent bus stops that enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Our approach includes a deep learning-based blind-spot warning system to help drivers avoid accidents with automated bus-stop detection to accurately identify bus stops, improving transit efficiency. We also introduce IoT-based solar-powered smart bus stops that show real-time passenger counts, along with an RFID-based card system to track where passengers board and exit. A smart door system ensures safer and more organised boarding, while real-time bus tracking keeps passengers informed. To connect all these features, we use an HTTP-based server for seamless communication between the interconnected network systems. Our proposed system demonstrated approximately 99% efficiency in real-time blind spot detection while stopping precisely at the bus stops. Furthermore, the server showed real-time location updates both to the users and at the bus stops, enhancing commuting efficiency. The proposed energy-efficient bus stop demonstrated 12.71kWh energy saving, promoting sustainable architecture. Full implementation and source code are available at: https://github.com/sadman-adib/MoveMe-IoT
GBDTSVM: Combined Support Vector Machine and Gradient Boosting Decision Tree Framework for efficient snoRNA-disease association prediction
May 10, 2025Abstract:Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are increasingly recognized for their critical role in the pathogenesis and characterization of various human diseases. Consequently, the precise identification of snoRNA-disease associations (SDAs) is essential for the progression of diseases and the advancement of treatment strategies. However, conventional biological experimental approaches are costly, time-consuming, and resource-intensive; therefore, machine learning-based computational methods offer a promising solution to mitigate these limitations. This paper proposes a model called 'GBDTSVM', representing a novel and efficient machine learning approach for predicting snoRNA-disease associations by leveraging a Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) and Support Vector Machine (SVM). 'GBDTSVM' effectively extracts integrated snoRNA-disease feature representations utilizing GBDT and SVM is subsequently utilized to classify and identify potential associations. Furthermore, the method enhances the accuracy of these predictions by incorporating Gaussian kernel profile similarity for both snoRNAs and diseases. Experimental evaluation of the GBDTSVM model demonstrated superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods in the field, achieving an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) of 0.96 and an area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.95 on MDRF dataset. Moreover, our model shows superior performance on two more datasets named LSGT and PsnoD. Additionally, a case study on the predicted snoRNA-disease associations verified the top 10 predicted snoRNAs across nine prevalent diseases, further validating the efficacy of the GBDTSVM approach. These results underscore the model's potential as a robust tool for advancing snoRNA-related disease research. Source codes and datasets our proposed framework can be obtained from: https://github.com/mariamuna04/gbdtsvm
MosquitoMiner: A Light Weight Rover for Detecting and Eliminating Mosquito Breeding Sites
Sep 12, 2024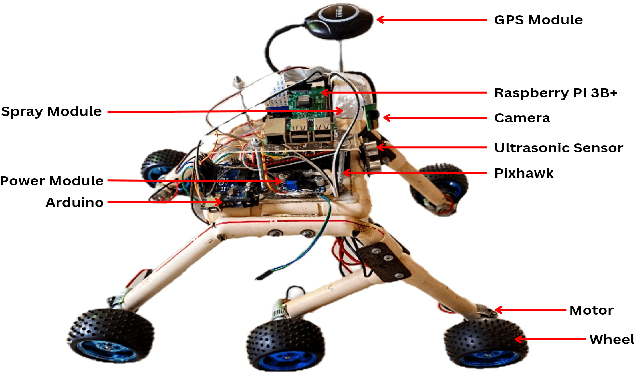
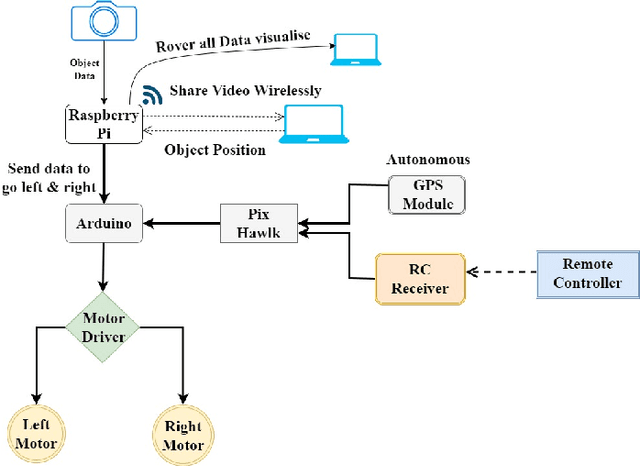


Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach to the development and deployment of an autonomous mosquito breeding place detector rover with the object and obstacle detection capabilities to control mosquitoes. Mosquito-borne diseases continue to pose significant health threats globally, with conventional control methods proving slow and inefficient. Amidst rising concerns over the rapid spread of these diseases, there is an urgent need for innovative and efficient strategies to manage mosquito populations and prevent disease transmission. To mitigate the limitations of manual labor and traditional methods, our rover employs autonomous control strategies. Leveraging our own custom dataset, the rover can autonomously navigate along a pre-defined path, identifying and mitigating potential breeding grounds with precision. It then proceeds to eliminate these breeding grounds by spraying a chemical agent, effectively eradicating mosquito habitats. Our project demonstrates the effectiveness that is absent in traditional ways of controlling and safeguarding public health. The code for this project is available on GitHub at - https://github.com/faiyazabdullah/MosquitoMiner
MosquitoFusion: A Multiclass Dataset for Real-Time Detection of Mosquitoes, Swarms, and Breeding Sites Using Deep Learning
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present an integrated approach to real-time mosquito detection using our multiclass dataset (MosquitoFusion) containing 1204 diverse images and leverage cutting-edge technologies, specifically computer vision, to automate the identification of Mosquitoes, Swarms, and Breeding Sites. The pre-trained YOLOv8 model, trained on this dataset, achieved a mean Average Precision (mAP@50) of 57.1%, with precision at 73.4% and recall at 50.5%. The integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) further enriches the depth of our analysis, providing valuable insights into spatial patterns. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/faiyazabdullah/MosquitoFusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge