Fahed Abdallah
Effect of Prior-based Losses on Segmentation Performance: A Benchmark
Jan 12, 2022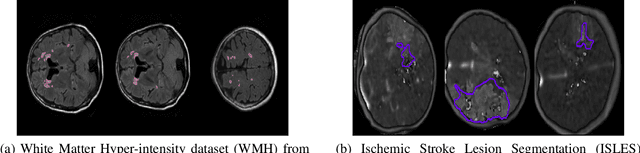
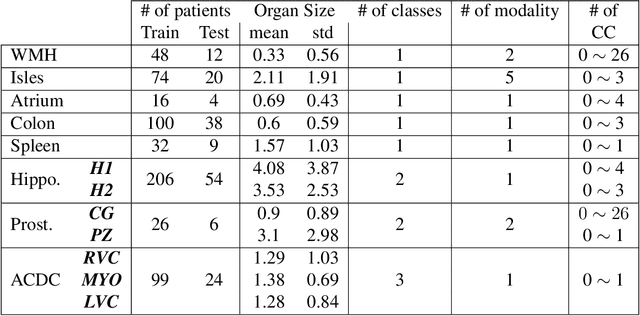
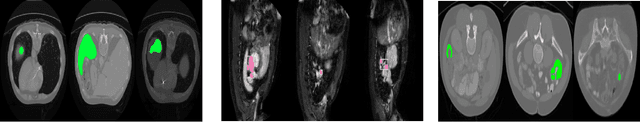

Abstract:Today, deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance for medical image segmentation, on various imaging modalities and tasks. Despite early success, segmentation networks may still generate anatomically aberrant segmentations, with holes or inaccuracies near the object boundaries. To enforce anatomical plausibility, recent research studies have focused on incorporating prior knowledge such as object shape or boundary, as constraints in the loss function. Prior integrated could be low-level referring to reformulated representations extracted from the ground-truth segmentations, or high-level representing external medical information such as the organ's shape or size. Over the past few years, prior-based losses exhibited a rising interest in the research field since they allow integration of expert knowledge while still being architecture-agnostic. However, given the diversity of prior-based losses on different medical imaging challenges and tasks, it has become hard to identify what loss works best for which dataset. In this paper, we establish a benchmark of recent prior-based losses for medical image segmentation. The main objective is to provide intuition onto which losses to choose given a particular task or dataset. To this end, four low-level and high-level prior-based losses are selected. The considered losses are validated on 8 different datasets from a variety of medical image segmentation challenges including the Decathlon, the ISLES and the WMH challenge. Results show that whereas low-level prior-based losses can guarantee an increase in performance over the Dice loss baseline regardless of the dataset characteristics, high-level prior-based losses can increase anatomical plausibility as per data characteristics.
High-level Prior-based Loss Functions for Medical Image Segmentation: A Survey
Nov 22, 2020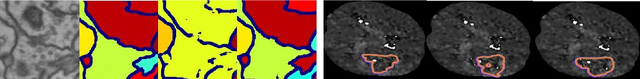
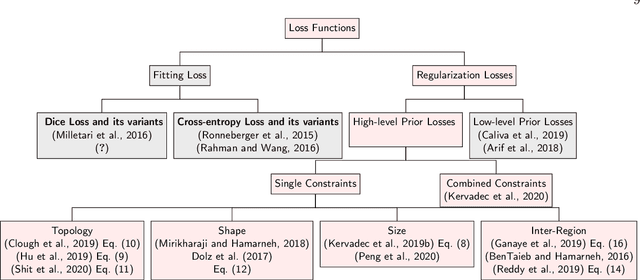
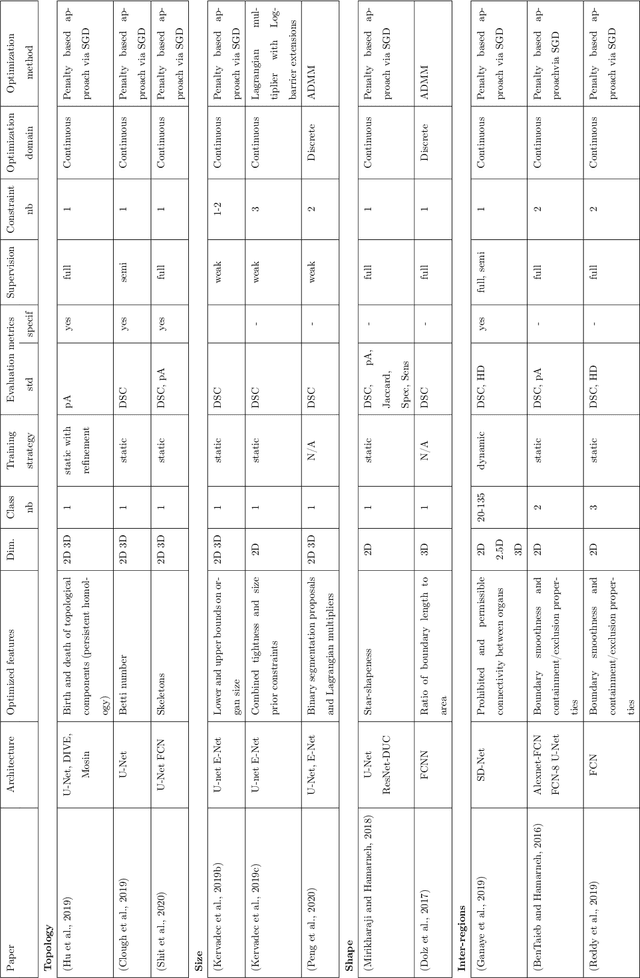
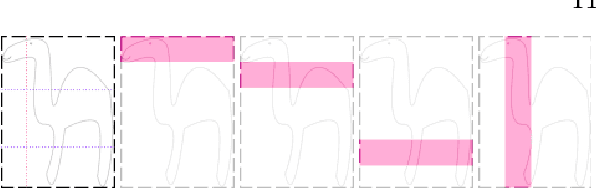
Abstract:Today, deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have demonstrated state of the art performance for supervised medical image segmentation, across various imaging modalities and tasks. Despite early success, segmentation networks may still generate anatomically aberrant segmentations, with holes or inaccuracies near the object boundaries. To mitigate this effect, recent research works have focused on incorporating spatial information or prior knowledge to enforce anatomically plausible segmentation. If the integration of prior knowledge in image segmentation is not a new topic in classical optimization approaches, it is today an increasing trend in CNN based image segmentation, as shown by the growing literature on the topic. In this survey, we focus on high level prior, embedded at the loss function level. We categorize the articles according to the nature of the prior: the object shape, size, topology, and the inter-regions constraints. We highlight strengths and limitations of current approaches, discuss the challenge related to the design and the integration of prior-based losses, and the optimization strategies, and draw future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge