Fabio Caccioli
Graph Regularized PCA
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:High-dimensional data often exhibit dependencies among variables that violate the isotropic-noise assumption under which principal component analysis (PCA) is optimal. For cases where the noise is not independent and identically distributed across features (i.e., the covariance is not spherical) we introduce Graph Regularized PCA (GR-PCA). It is a graph-based regularization of PCA that incorporates the dependency structure of the data features by learning a sparse precision graph and biasing loadings toward the low-frequency Fourier modes of the corresponding graph Laplacian. Consequently, high-frequency signals are suppressed, while graph-coherent low-frequency ones are preserved, yielding interpretable principal components aligned with conditional relationships. We evaluate GR-PCA on synthetic data spanning diverse graph topologies, signal-to-noise ratios, and sparsity levels. Compared to mainstream alternatives, it concentrates variance on the intended support, produces loadings with lower graph-Laplacian energy, and remains competitive in out-of-sample reconstruction. When high-frequency signals are present, the graph Laplacian penalty prevents overfitting, reducing the reconstruction accuracy but improving structural fidelity. The advantage over PCA is most pronounced when high-frequency signals are graph-correlated, whereas PCA remains competitive when such signals are nearly rotationally invariant. The procedure is simple to implement, modular with respect to the precision estimator, and scalable, providing a practical route to structure-aware dimensionality reduction that improves structural fidelity without sacrificing predictive performance.
Data-Driven Malaria Prevalence Prediction in Large Densely-Populated Urban Holoendemic sub-Saharan West Africa: Harnessing Machine Learning Approaches and 22-years of Prospectively Collected Data
Jun 18, 2019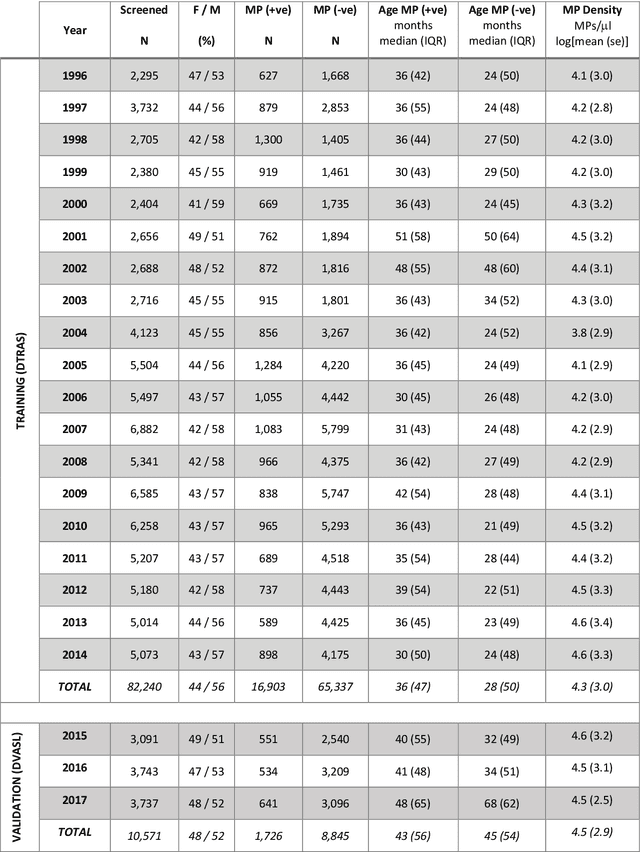
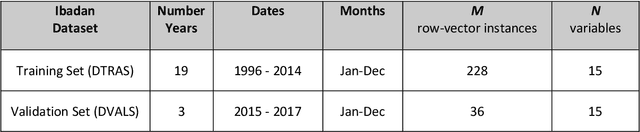
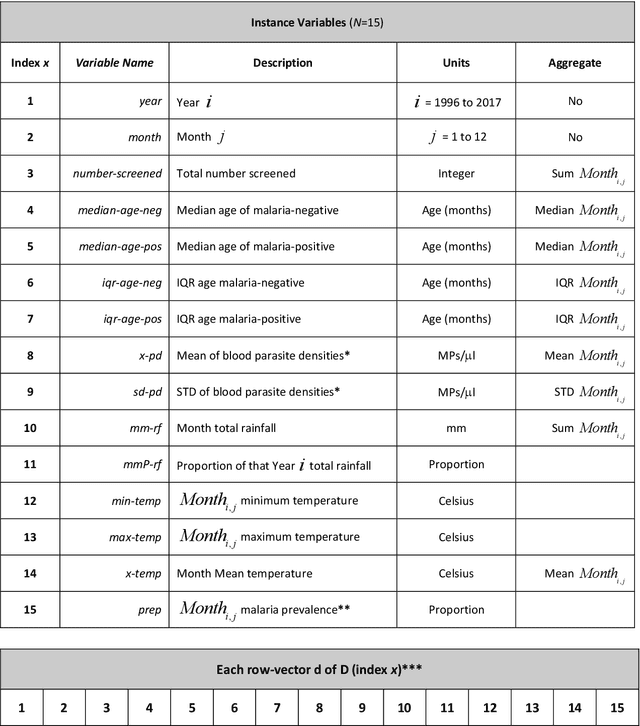
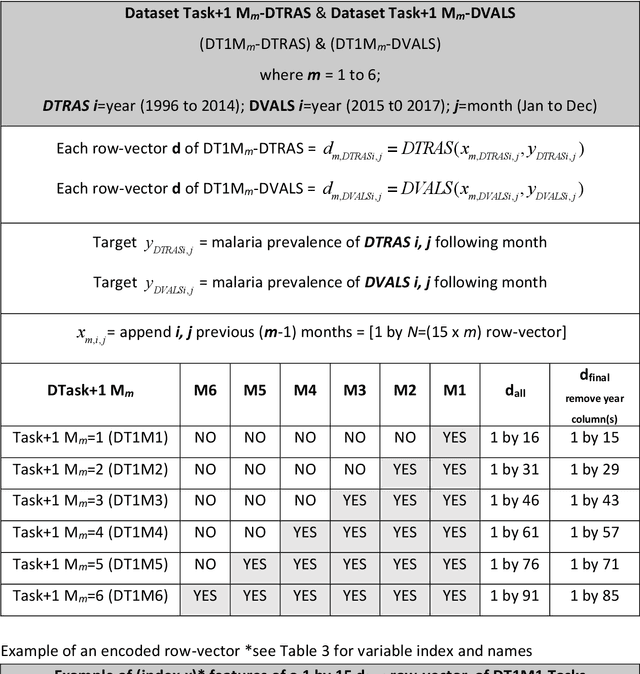
Abstract:Plasmodium falciparum malaria still poses one of the greatest threats to human life with over 200 million cases globally leading to half-million deaths annually. Of these, 90% of cases and of the mortality occurs in sub-Saharan Africa, mostly among children. Although malaria prediction systems are central to the 2016-2030 malaria Global Technical Strategy, currently these are inadequate at capturing and estimating the burden of disease in highly endemic countries. We developed and validated a computational system that exploits the predictive power of current Machine Learning approaches on 22-years of prospective data from the high-transmission holoendemic malaria urban-densely-populated sub-Saharan West-Africa metropolis of Ibadan. Our dataset of >9x104 screened study participants attending our clinical and community services from 1996 to 2017 contains monthly prevalence, temporal, environmental and host features. Our Locality-specific Elastic-Net based Malaria Prediction System (LEMPS) achieves good generalization performance, both in magnitude and direction of the prediction, when tasked to predict monthly prevalence on previously unseen validation data (MAE<=6x10-2, MSE<=7x10-3) within a range of (+0.1 to -0.05) error-tolerance which is relevant and usable for aiding decision-support in a holoendemic setting. LEMPS is well-suited for malaria prediction, where there are multiple features which are correlated with one another, and trading-off between regularization-strength L1-norm and L2-norm allows the system to retain stability. Data-driven systems are critical for regionally-adaptable surveillance, management of control strategies and resource allocation across stretched healthcare systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge