Fabian Wolf
CM1 -- A Dataset for Evaluating Few-Shot Information Extraction with Large Vision Language Models
May 07, 2025Abstract:The automatic extraction of key-value information from handwritten documents is a key challenge in document analysis. A reliable extraction is a prerequisite for the mass digitization efforts of many archives. Large Vision Language Models (LVLM) are a promising technology to tackle this problem especially in scenarios where little annotated training data is available. In this work, we present a novel dataset specifically designed to evaluate the few-shot capabilities of LVLMs. The CM1 documents are a historic collection of forms with handwritten entries created in Europe to administer the Care and Maintenance program after World War Two. The dataset establishes three benchmarks on extracting name and birthdate information and, furthermore, considers different training set sizes. We provide baseline results for two different LVLMs and compare performances to an established full-page extraction model. While the traditional full-page model achieves highly competitive performances, our experiments show that when only a few training samples are available the considered LVLMs benefit from their size and heavy pretraining and outperform the classical approach.
Self-Training of Handwritten Word Recognition for Synthetic-to-Real Adaptation
Jun 07, 2022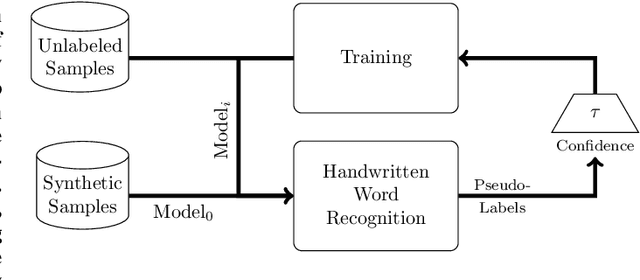
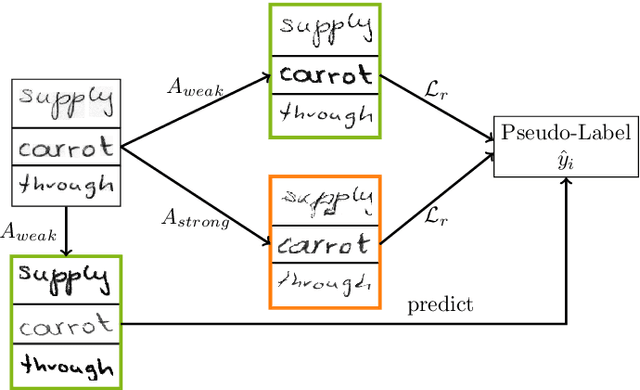

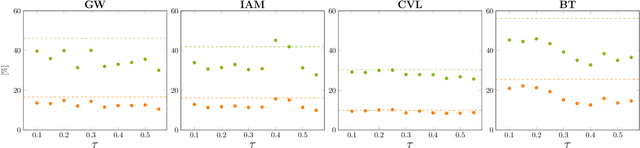
Abstract:Performances of Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) models are largely determined by the availability of labeled and representative training samples. However, in many application scenarios labeled samples are scarce or costly to obtain. In this work, we propose a self-training approach to train a HTR model solely on synthetic samples and unlabeled data. The proposed training scheme uses an initial model trained on synthetic data to make predictions for the unlabeled target dataset. Starting from this initial model with rather poor performance, we show that a considerable adaptation is possible by training against the predicted pseudo-labels. Moreover, the investigated self-training strategy does not require any manually annotated training samples. We evaluate the proposed method on four widely used benchmark datasets and show its effectiveness on closing the gap to a model trained in a fully-supervised manner.
Recognition-free Question Answering on Handwritten Document Collections
Feb 12, 2022Abstract:In recent years, considerable progress has been made in the research area of Question Answering (QA) on document images. Current QA approaches from the Document Image Analysis community are mainly focusing on machine-printed documents and perform rather limited on handwriting. This is mainly due to the reduced recognition performance on handwritten documents. To tackle this problem, we propose a recognition-free QA approach, especially designed for handwritten document image collections. We present a robust document retrieval method, as well as two QA models. Our approaches outperform the state-of-the-art recognition-free models on the challenging BenthamQA and HW-SQuAD datasets.
Annotation-free Learning of Deep Representations for Word Spotting using Synthetic Data and Self Labeling
Apr 09, 2020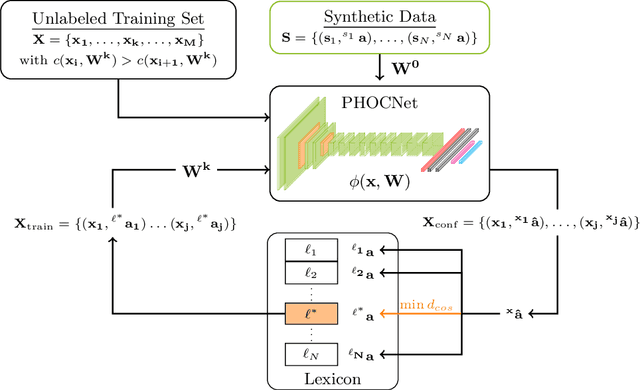
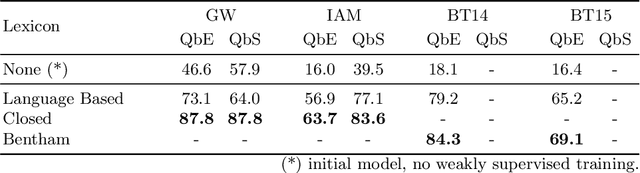
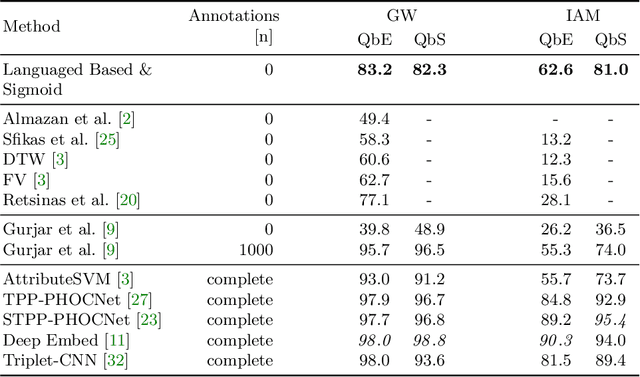
Abstract:Word spotting is a popular tool for supporting the first exploration of historic, handwritten document collections. Today, the best performing methods rely on machine learning techniques, which require a high amount of annotated training material. As training data is usually not available in the application scenario, annotation-free methods aim at solving the retrieval task without representative training samples. In this work, we present an annotation-free method that still employs machine learning techniques and therefore outperforms other learning-free approaches. The weakly supervised training scheme relies on a lexicon, that does not need to precisely fit the dataset. In combination with a confidence based selection of pseudo-labeled training samples, we achieve state-of-the-art query-by-example performances. Furthermore, our method allows to perform query-by-string, which is usually not the case for other annotation-free methods.
Exploring Confidence Measures for Word Spotting in Heterogeneous Datasets
Mar 26, 2019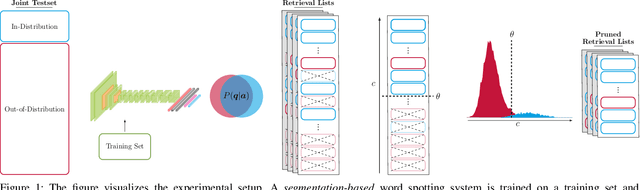
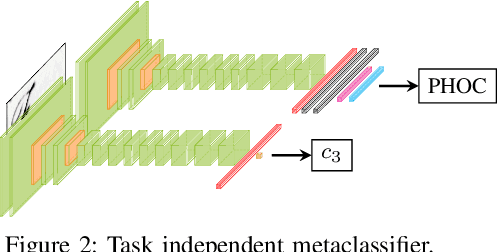
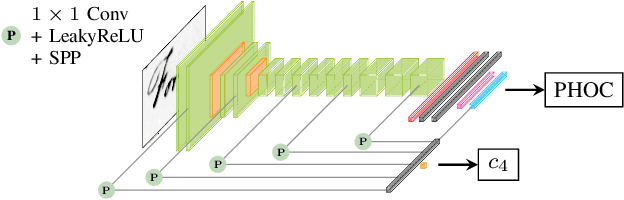
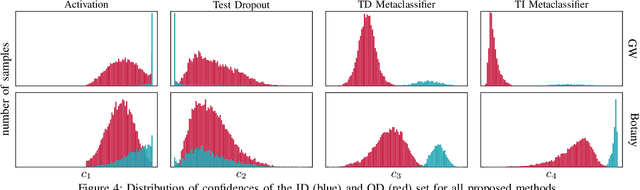
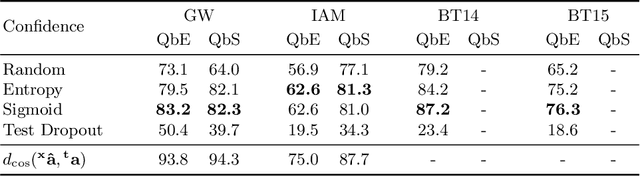
Abstract:In recent years, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) took over the field of document analysis and they became the predominant model for word spotting. Especially attribute CNNs, which learn the mapping between a word image and an attribute representation, showed exceptional performances. The drawback of this approach is the overconfidence of neural networks when used out of their training distribution. In this paper, we explore different metrics for quantifying the confidence of a CNN in its predictions, specifically on the retrieval problem of word spotting. With these confidence measures, we limit the inability of a retrieval list to reject certain candidates. We investigate four different approaches that are either based on the network's attribute estimations or make use of a surrogate model. Our approach also aims at answering the question for which part of a dataset the retrieval system gives reliable results. We further show that there exists a direct relation between the proposed confidence measures and the quality of an estimated attribute representation.
Expolring Architectures for CNN-Based Word Spotting
Jun 28, 2018

Abstract:The goal in word spotting is to retrieve parts of document images which are relevant with respect to a certain user-defined query. The recent past has seen attribute-based Convolutional Neural Networks take over this field of research. As is common for other fields of computer vision, the CNNs used for this task are already considerably deep. The question that arises, however, is: How complex does a CNN have to be for word spotting? Are increasingly deeper models giving increasingly bet- ter results or does performance behave asymptotically for these architectures? On the other hand, can similar results be obtained with a much smaller CNN? The goal of this paper is to give an answer to these questions. Therefore, the recently successful TPP- PHOCNet will be compared to a Residual Network, a Densely Connected Convolutional Network and a LeNet architecture empirically. As will be seen in the evaluation, a complex model can be beneficial for word spotting on harder tasks such as the IAM Offline Database but gives no advantage for easier benchmarks such as the George Washington Database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge