Félix do Carmo
Automatically Generating Chinese Homophone Words to Probe Machine Translation Estimation Systems
Mar 20, 2025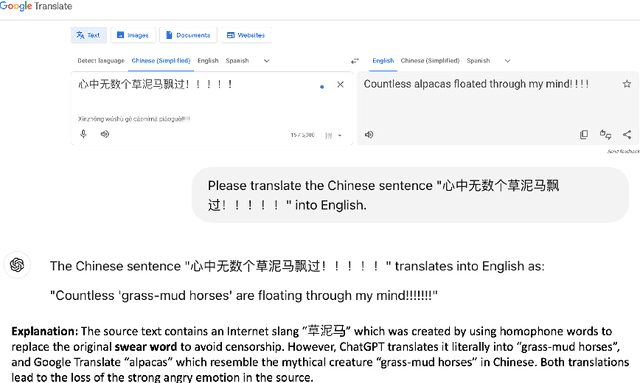

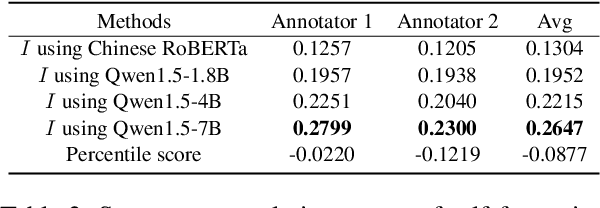
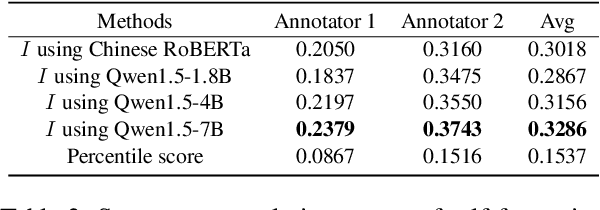
Abstract:Evaluating machine translation (MT) of user-generated content (UGC) involves unique challenges such as checking whether the nuance of emotions from the source are preserved in the target text. Recent studies have proposed emotion-related datasets, frameworks and models to automatically evaluate MT quality of Chinese UGC, without relying on reference translations. However, whether these models are robust to the challenge of preserving emotional nuances has been left largely unexplored. To address this gap, we introduce a novel method inspired by information theory which generates challenging Chinese homophone words related to emotions, by leveraging the concept of self-information. Our approach generates homophones that were observed to cause translation errors in emotion preservation, and exposes vulnerabilities in MT systems and their evaluation methods when tackling emotional UGC. We evaluate the efficacy of our method using human evaluation for the quality of these generated homophones, and compare it with an existing one, showing that our method achieves higher correlation with human judgments. The generated Chinese homophones, along with their manual translations, are utilized to generate perturbations and to probe the robustness of existing quality evaluation models, including models trained using multi-task learning, fine-tuned variants of multilingual language models, as well as large language models (LLMs). Our results indicate that LLMs with larger size exhibit higher stability and robustness to such perturbations. We release our data and code for reproducibility and further research.
Edit Distances and Their Applications to Downstream Tasks in Research and Commercial Contexts
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:The tutorial describes the concept of edit distances applied to research and commercial contexts. We use Translation Edit Rate (TER), Levenshtein, Damerau-Levenshtein, Longest Common Subsequence and $n$-gram distances to demonstrate the frailty of statistical metrics when comparing text sequences. Our discussion disassembles them into their essential components. We discuss the centrality of four editing actions: insert, delete, replace and move words, and show their implementations in openly available packages and toolkits. The application of edit distances in downstream tasks often assumes that these accurately represent work done by post-editors and real errors that need to be corrected in MT output. We discuss how imperfect edit distances are in capturing the details of this error correction work and the implications for researchers and for commercial applications, of these uses of edit distances. In terms of commercial applications, we discuss their integration in computer-assisted translation tools and how the perception of the connection between edit distances and post-editor effort affects the definition of translator rates.
Are Large Language Models State-of-the-art Quality Estimators for Machine Translation of User-generated Content?
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates whether large language models (LLMs) are state-of-the-art quality estimators for machine translation of user-generated content (UGC) that contains emotional expressions, without the use of reference translations. To achieve this, we employ an existing emotion-related dataset with human-annotated errors and calculate quality evaluation scores based on the Multi-dimensional Quality Metrics. We compare the accuracy of several LLMs with that of our fine-tuned baseline models, under in-context learning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) scenarios. We find that PEFT of LLMs leads to better performance in score prediction with human interpretable explanations than fine-tuned models. However, a manual analysis of LLM outputs reveals that they still have problems such as refusal to reply to a prompt and unstable output while evaluating machine translation of UGC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge