Ervin Dervishaj
Post-Training Denoising of User Profiles with LLMs in Collaborative Filtering Recommendation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Implicit feedback -- the main data source for training Recommender Systems (RSs) -- is inherently noisy and has been shown to negatively affect recommendation effectiveness. Denoising has been proposed as a method for removing noisy implicit feedback and improving recommendations. Prior work has focused on in-training denoising, however this requires additional data, changes to the model architecture and training procedure or fine-tuning, all of which can be costly and data hungry. In this work, we focus on post-training denoising. Different from in-training denoising, post-training denoising does not involve changing the architecture of the model nor its training procedure, and does not require additional data. Specifically, we present a method for post-training denoising user profiles using Large Language Models (LLMs) for Collaborative Filtering (CF) recommendations. Our approach prompts LLMs with (i) a user profile (user interactions), (ii) a candidate item, and (iii) its rank as given by the CF recommender, and asks the LLM to remove items from the user profile to improve the rank of the candidate item. Experiments with a state-of-the-art CF recommender and 4 open and closed source LLMs in 3 datasets show that our denoising yields improvements up to 13% in effectiveness over the original user profiles. Our code is available at https://github.com/edervishaj/denoising-user-profiles-LLM.
Are Representation Disentanglement and Interpretability Linked in Recommendation Models? A Critical Review and Reproducibility Study
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Unsupervised learning of disentangled representations has been closely tied to enhancing the representation intepretability of Recommender Systems (RSs). This has been achieved by making the representation of individual features more distinctly separated, so that it is easier to attribute the contribution of features to the model's predictions. However, such advantages in interpretability and feature attribution have mainly been explored qualitatively. Moreover, the effect of disentanglement on the model's recommendation performance has been largely overlooked. In this work, we reproduce the recommendation performance, representation disentanglement and representation interpretability of five well-known recommendation models on four RS datasets. We quantify disentanglement and investigate the link of disentanglement with recommendation effectiveness and representation interpretability. While several existing work in RSs have proposed disentangled representations as a gateway to improved effectiveness and interpretability, our findings show that disentanglement is not necessarily related to effectiveness but is closely related to representation interpretability. Our code and results are publicly available at https://github.com/edervishaj/disentanglement-interpretability-recsys.
GAN-based Matrix Factorization for Recommender Systems
Jan 20, 2022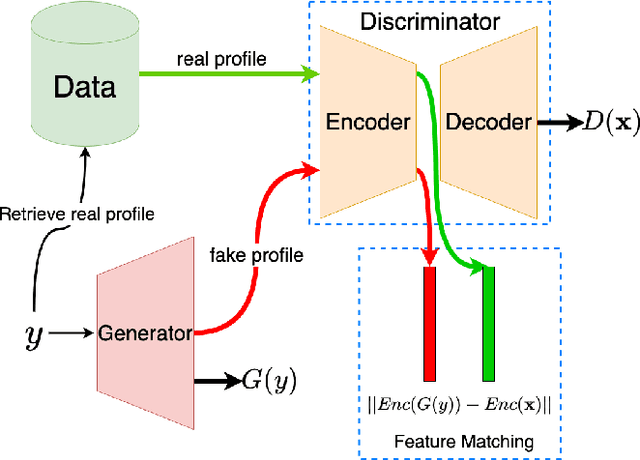
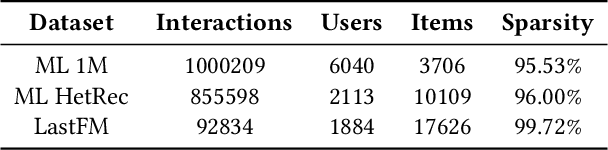
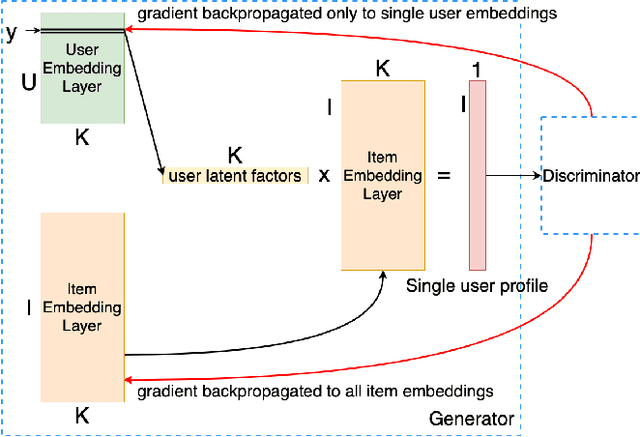
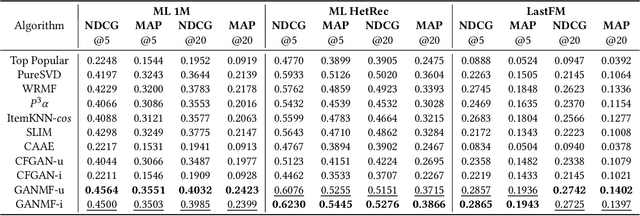
Abstract:Proposed in 2014, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) initiated a fresh interest in generative modelling. They immediately achieved state-of-the-art in image synthesis, image-to-image translation, text-to-image generation, image inpainting and have been used in sciences ranging from medicine to high-energy particle physics. Despite their popularity and ability to learn arbitrary distributions, GAN have not been widely applied in recommender systems (RS). Moreover, only few of the techniques that have introduced GAN in RS have employed them directly as a collaborative filtering (CF) model. In this work we propose a new GAN-based approach that learns user and item latent factors in a matrix factorization setting for the generic top-N recommendation problem. Following the vector-wise GAN training approach for RS introduced by CFGAN, we identify 2 unique issues when utilizing GAN for CF. We propose solutions for both of them by using an autoencoder as discriminator and incorporating an additional loss function for the generator. We evaluate our model, GANMF, through well-known datasets in the RS community and show improvements over traditional CF approaches and GAN-based models. Through an ablation study on the components of GANMF we aim to understand the effects of our architectural choices. Finally, we provide a qualitative evaluation of the matrix factorization performance of GANMF.
Artist-driven layering and user's behaviour impact on recommendations in a playlist continuation scenario
Oct 13, 2020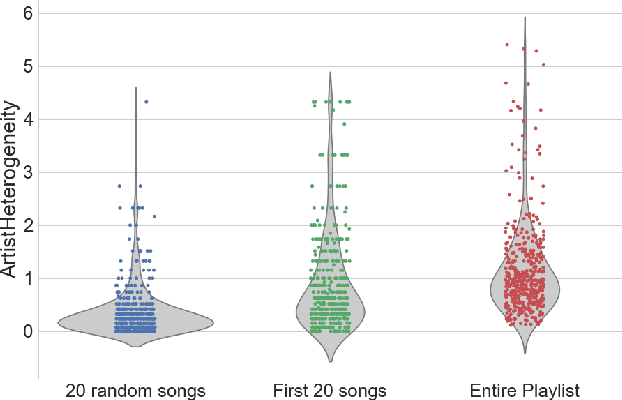
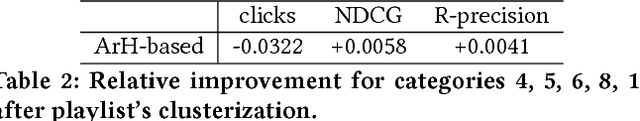
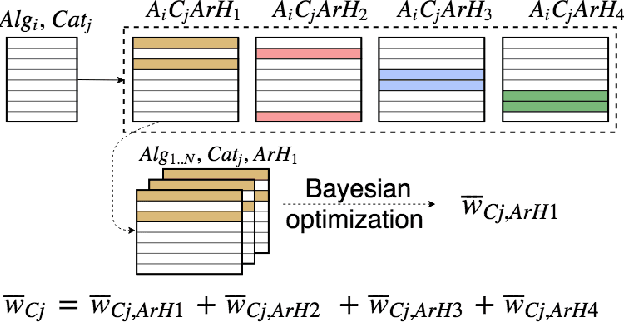
Abstract:In this paper we provide an overview of the approach we used as team Creamy Fireflies for the ACM RecSys Challenge 2018. The competition, organized by Spotify, focuses on the problem of playlist continuation, that is suggesting which tracks the user may add to an existing playlist. The challenge addresses this issue in many use cases, from playlist cold start to playlists already composed by up to a hundred tracks. Our team proposes a solution based on a few well known models both content based and collaborative, whose predictions are aggregated via an ensembling step. Moreover by analyzing the underlying structure of the data, we propose a series of boosts to be applied on top of the final predictions and improve the recommendation quality. The proposed approach leverages well-known algorithms and is able to offer a high recommendation quality while requiring a limited amount of computational resources.
* Source code available here: https://github.com/MaurizioFD/spotify-recsys-challenge
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge