Ergys Ristani
AirGlove: Exploring Egocentric 3D Hand Tracking and Appearance Generalization for Sensing Gloves
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Sensing gloves have become important tools for teleoperation and robotic policy learning as they are able to provide rich signals like speed, acceleration and tactile feedback. A common approach to track gloved hands is to directly use the sensor signals (e.g., angular velocity, gravity orientation) to estimate 3D hand poses. However, sensor-based tracking can be restrictive in practice as the accuracy is often impacted by sensor signal and calibration quality. Recent advances in vision-based approaches have achieved strong performance on human hands via large-scale pre-training, but their performance on gloved hands with distinct visual appearances remains underexplored. In this work, we present the first systematic evaluation of vision-based hand tracking models on gloved hands under both zero-shot and fine-tuning setups. Our analysis shows that existing bare-hand models suffer from substantial performance degradation on sensing gloves due to large appearance gap between bare-hand and glove designs. We therefore propose AirGlove, which leverages existing gloves to generalize the learned glove representations towards new gloves with limited data. Experiments with multiple sensing gloves show that AirGlove effectively generalizes the hand pose models to new glove designs and achieves a significant performance boost over the compared schemes.
Features for Multi-Target Multi-Camera Tracking and Re-Identification
Mar 28, 2018



Abstract:Multi-Target Multi-Camera Tracking (MTMCT) tracks many people through video taken from several cameras. Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) retrieves from a gallery images of people similar to a person query image. We learn good features for both MTMCT and Re-ID with a convolutional neural network. Our contributions include an adaptive weighted triplet loss for training and a new technique for hard-identity mining. Our method outperforms the state of the art both on the DukeMTMC benchmarks for tracking, and on the Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-ReID benchmarks for Re-ID. We examine the correlation between good Re-ID and good MTMCT scores, and perform ablation studies to elucidate the contributions of the main components of our system. Code is available.
Performance Measures and a Data Set for Multi-Target, Multi-Camera Tracking
Sep 19, 2016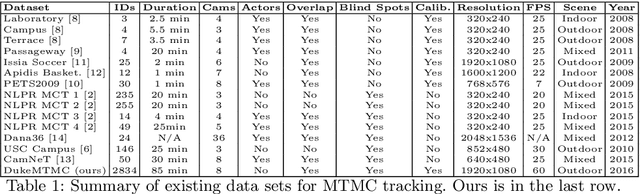
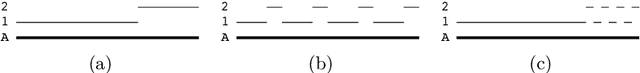
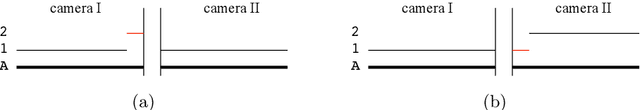
Abstract:To help accelerate progress in multi-target, multi-camera tracking systems, we present (i) a new pair of precision-recall measures of performance that treats errors of all types uniformly and emphasizes correct identification over sources of error; (ii) the largest fully-annotated and calibrated data set to date with more than 2 million frames of 1080p, 60fps video taken by 8 cameras observing more than 2,700 identities over 85 minutes; and (iii) a reference software system as a comparison baseline. We show that (i) our measures properly account for bottom-line identity match performance in the multi-camera setting; (ii) our data set poses realistic challenges to current trackers; and (iii) the performance of our system is comparable to the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge