Entao Yang
Is Grokking a Computational Glass Relaxation?
May 16, 2025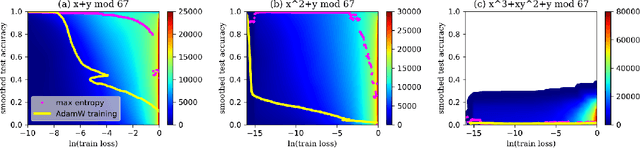
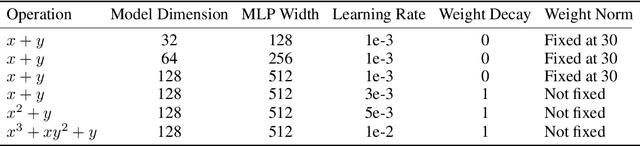
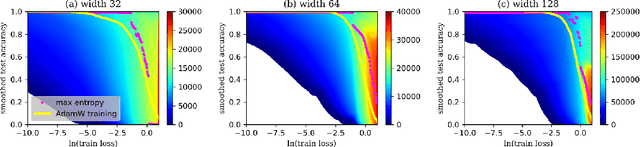
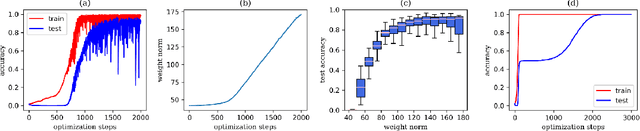
Abstract:Understanding neural network's (NN) generalizability remains a central question in deep learning research. The special phenomenon of grokking, where NNs abruptly generalize long after the training performance reaches a near-perfect level, offers a unique window to investigate the underlying mechanisms of NNs' generalizability. Here we propose an interpretation for grokking by framing it as a computational glass relaxation: viewing NNs as a physical system where parameters are the degrees of freedom and train loss is the system energy, we find memorization process resembles a rapid cooling of liquid into non-equilibrium glassy state at low temperature and the later generalization is like a slow relaxation towards a more stable configuration. This mapping enables us to sample NNs' Boltzmann entropy (states of density) landscape as a function of training loss and test accuracy. Our experiments in transformers on arithmetic tasks suggests that there is NO entropy barrier in the memorization-to-generalization transition of grokking, challenging previous theory that defines grokking as a first-order phase transition. We identify a high-entropy advantage under grokking, an extension of prior work linking entropy to generalizability but much more significant. Inspired by grokking's far-from-equilibrium nature, we develop a toy optimizer WanD based on Wang-landau molecular dynamics, which can eliminate grokking without any constraints and find high-norm generalizing solutions. This provides strictly-defined counterexamples to theory attributing grokking solely to weight norm evolution towards the Goldilocks zone and also suggests new potential ways for optimizer design.
High-entropy Advantage in Neural Networks' Generalizability
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:While the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics ignites a worldwide discussion on the origins of neural networks and their foundational links to physics, modern machine learning research predominantly focuses on computational and algorithmic advancements, overlooking a picture of physics. Here we introduce the concept of entropy into neural networks by reconceptualizing them as hypothetical physical systems where each parameter is a non-interacting 'particle' within a one-dimensional space. By employing a Wang-Landau algorithms, we construct the neural networks' (with up to 1 million parameters) entropy landscapes as functions of training loss and test accuracy (or loss) across four distinct machine learning tasks, including arithmetic question, real-world tabular data, image recognition, and language modeling. Our results reveal the existence of \textit{entropy advantage}, where the high-entropy states generally outperform the states reached via classical training optimizer like stochastic gradient descent. We also find this advantage is more pronounced in narrower networks, indicating a need of different training optimizers tailored to different sizes of neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge