Emilios Cambouropoulos
Pay (Cross) Attention to the Melody: Curriculum Masking for Single-Encoder Melodic Harmonization
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Melodic harmonization, the task of generating harmonic accompaniments for a given melody, remains a central challenge in computational music generation. Recent single encoder transformer approaches have framed harmonization as a masked sequence modeling problem, but existing training curricula inspired by discrete diffusion often result in weak (cross) attention between melody and harmony. This leads to limited exploitation of melodic cues, particularly in out-of-domain contexts. In this work, we introduce a training curriculum, FF (full-to-full), which keeps all harmony tokens masked for several training steps before progressively unmasking entire sequences during training to strengthen melody-harmony interactions. We systematically evaluate this approach against prior curricula across multiple experimental axes, including temporal quantization (quarter vs. sixteenth note), bar-level vs. time-signature conditioning, melody representation (full range vs. pitch class), and inference-time unmasking strategies. Models are trained on the HookTheory dataset and evaluated both in-domain and on a curated collection of jazz standards, using a comprehensive set of metrics that assess chord progression structure, harmony-melody alignment, and rhythmic coherence. Results demonstrate that the proposed FF curriculum consistently outperforms baselines in nearly all metrics, with particularly strong gains in out-of-domain evaluations where harmonic adaptability to novel melodic queues is crucial. We further find that quarter-note quantization, intertwining of bar tokens, and pitch-class melody representations are advantageous in the FF setting. Our findings highlight the importance of training curricula in enabling effective melody conditioning and suggest that full-to-full unmasking offers a robust strategy for single encoder harmonization.
Incorporating Structure and Chord Constraints in Symbolic Transformer-based Melodic Harmonization
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Transformer architectures offer significant advantages regarding the generation of symbolic music; their capabilities for incorporating user preferences toward what they generate is being studied under many aspects. This paper studies the inclusion of predefined chord constraints in melodic harmonization, i.e., where a desired chord at a specific location is provided along with the melody as inputs and the autoregressive transformer model needs to incorporate the chord in the harmonization that it generates. The peculiarities of involving such constraints is discussed and an algorithm is proposed for tackling this task. This algorithm is called B* and it combines aspects of beam search and A* along with backtracking to force pretrained transformers to satisfy the chord constraints, at the correct onset position within the correct bar. The algorithm is brute-force and has exponential complexity in the worst case; however, this paper is a first attempt to highlight the difficulties of the problem and proposes an algorithm that offers many possibilities for improvements since it accommodates the involvement of heuristics.
An Argument-based Creative Assistant for Harmonic Blending
Mar 06, 2016

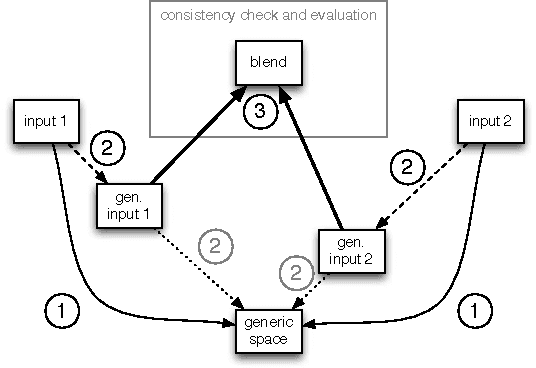
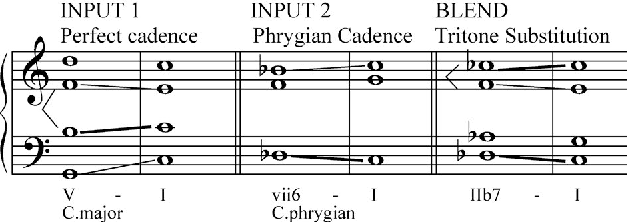
Abstract:Conceptual blending is a powerful tool for computational creativity where, for example, the properties of two harmonic spaces may be combined in a consistent manner to produce a novel harmonic space. However, deciding about the importance of property features in the input spaces and evaluating the results of conceptual blending is a nontrivial task. In the specific case of musical harmony, defining the salient features of chord transitions and evaluating invented harmonic spaces requires deep musicological background knowledge. In this paper, we propose a creative tool that helps musicologists to evaluate and to enhance harmonic innovation. This tool allows a music expert to specify arguments over given transition properties. These arguments are then considered by the system when defining combinations of features in an idiom-blending process. A music expert can assess whether the new harmonic idiom makes musicological sense and re-adjust the arguments (selection of features) to explore alternative blends that can potentially produce better harmonic spaces. We conclude with a discussion of future work that would further automate the harmonisation process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge