Emilio Soria-Olivas
Automated Machine Learning in Radiomics: A Comparative Evaluation of Performance, Efficiency and Accessibility
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Automated machine learning (AutoML) frameworks can lower technical barriers for predictive and prognostic model development in radiomics by enabling researchers without programming expertise to build models. However, their effectiveness in addressing radiomics-specific challenges remains unclear. This study evaluates the performance, efficiency, and accessibility of general-purpose and radiomics-specific AutoML frameworks on diverse radiomics classification tasks, thereby highlighting development needs for radiomics. Ten public/private radiomics datasets with varied imaging modalities (CT/MRI), sizes, anatomies and endpoints were used. Six general-purpose and five radiomics-specific frameworks were tested with predefined parameters using standardized cross-validation. Evaluation metrics included AUC, runtime, together with qualitative aspects related to software status, accessibility, and interpretability. Simplatab, a radiomics-specific tool with a no-code interface, achieved the highest average test AUC (81.81%) with a moderate runtime (~1 hour). LightAutoML, a general-purpose framework, showed the fastest execution with competitive performance (78.74% mean AUC in six minutes). Most radiomics-specific frameworks were excluded from the performance analysis due to obsolescence, extensive programming requirements, or computational inefficiency. Conversely, general-purpose frameworks demonstrated higher accessibility and ease of implementation. Simplatab provides an effective balance of performance, efficiency, and accessibility for radiomics classification problems. However, significant gaps remain, including the lack of accessible survival analysis support and the limited integration of feature reproducibility and harmonization within current AutoML frameworks. Future research should focus on adapting AutoML solutions to better address these radiomics-specific challenges.
Empirical study of the modulus as activation function in computer vision applications
Jan 15, 2023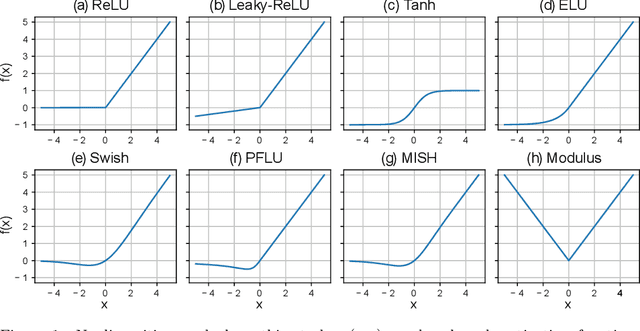



Abstract:In this work we propose a new non-monotonic activation function: the modulus. The majority of the reported research on nonlinearities is focused on monotonic functions. We empirically demonstrate how by using the modulus activation function on computer vision tasks the models generalize better than with other nonlinearities - up to a 15% accuracy increase in CIFAR100 and 4% in CIFAR10, relative to the best of the benchmark activations tested. With the proposed activation function the vanishing gradient and dying neurons problems disappear, because the derivative of the activation function is always 1 or -1. The simplicity of the proposed function and its derivative make this solution specially suitable for TinyML and hardware applications.
Approaching sales forecasting using recurrent neural networks and transformers
Apr 16, 2022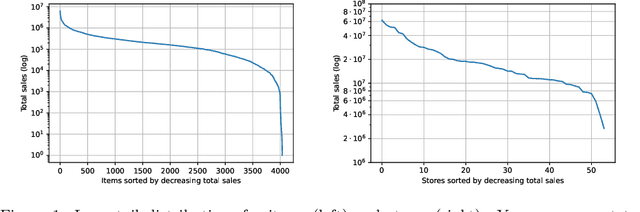
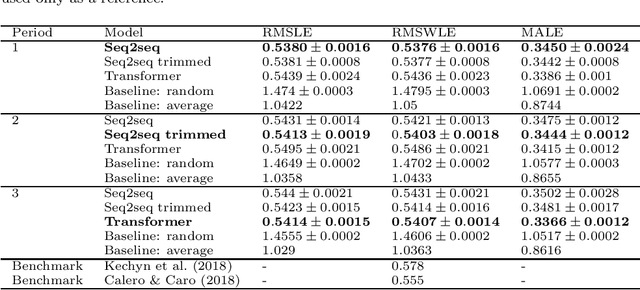
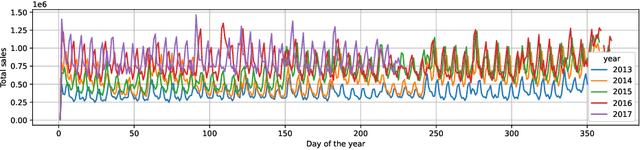
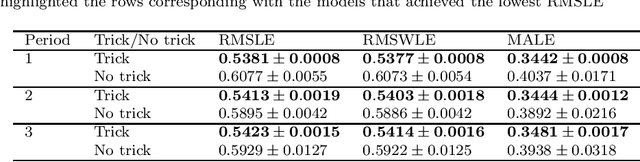
Abstract:Accurate and fast demand forecast is one of the hot topics in supply chain for enabling the precise execution of the corresponding downstream processes (inbound and outbound planning, inventory placement, network planning, etc). We develop three alternatives to tackle the problem of forecasting the customer sales at day/store/item level using deep learning techniques and the Corporaci\'on Favorita data set, published as part of a Kaggle competition. Our empirical results show how good performance can be achieved by using a simple sequence to sequence architecture with minimal data preprocessing effort. Additionally, we describe a training trick for making the model more time independent and hence improving generalization over time. The proposed solution achieves a RMSLE of around 0.54, which is competitive with other more specific solutions to the problem proposed in the Kaggle competition.
End-to-end Keyword Spotting using Xception-1d
Oct 09, 2021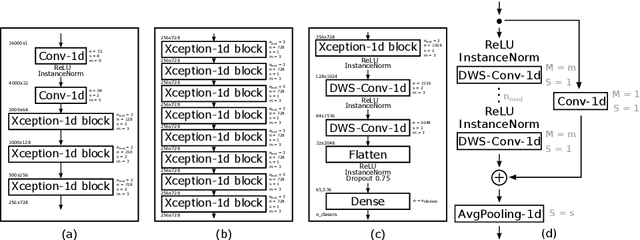
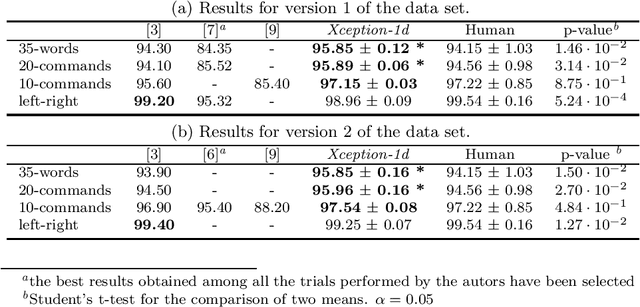
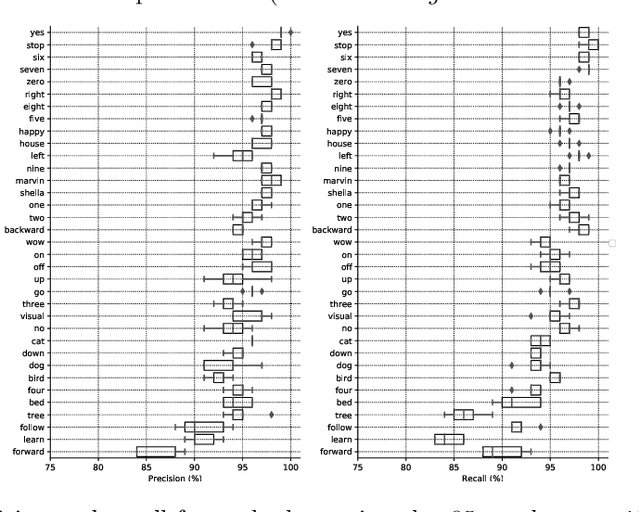
Abstract:The field of conversational agents is growing fast and there is an increasing need for algorithms that enhance natural interaction. In this work we show how we achieved state of the art results in the Keyword Spotting field by adapting and tweaking the Xception algorithm, which achieved outstanding results in several computer vision tasks. We obtained about 96\% accuracy when classifying audio clips belonging to 35 different categories, beating human annotation at the most complex tasks proposed.
Optimization of anemia treatment in hemodialysis patients via reinforcement learning
Sep 14, 2015



Abstract:Objective: Anemia is a frequent comorbidity in hemodialysis patients that can be successfully treated by administering erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs). ESAs dosing is currently based on clinical protocols that often do not account for the high inter- and intra-individual variability in the patient's response. As a result, the hemoglobin level of some patients oscillates around the target range, which is associated with multiple risks and side-effects. This work proposes a methodology based on reinforcement learning (RL) to optimize ESA therapy. Methods: RL is a data-driven approach for solving sequential decision-making problems that are formulated as Markov decision processes (MDPs). Computing optimal drug administration strategies for chronic diseases is a sequential decision-making problem in which the goal is to find the best sequence of drug doses. MDPs are particularly suitable for modeling these problems due to their ability to capture the uncertainty associated with the outcome of the treatment and the stochastic nature of the underlying process. The RL algorithm employed in the proposed methodology is fitted Q iteration, which stands out for its ability to make an efficient use of data. Results: The experiments reported here are based on a computational model that describes the effect of ESAs on the hemoglobin level. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated and compared with the well-known Q-learning algorithm and with a standard protocol. Simulation results show that the performance of Q-learning is substantially lower than FQI and the protocol. Conclusion: Although prospective validation is required, promising results demonstrate the potential of RL to become an alternative to current protocols.
* 17 pages, 10 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge