Emanuele Crisostomi
Department of Energy, Systems, Territory and Constructions Engineering, University of Pisa and
Condition monitoring and early diagnostics methodologies for hydropower plants
Nov 13, 2019



Abstract:Hydropower plants are one of the most convenient option for power generation, as they generate energy exploiting a renewable source, they have relatively low operating and maintenance costs, and they may be used to provide ancillary services, exploiting the large reservoirs of available water. The recent advances in Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) and in machine learning methodologies are seen as fundamental enablers to upgrade and modernize the current operation of most hydropower plants, in terms of condition monitoring, early diagnostics and eventually predictive maintenance. While very few works, or running technologies, have been documented so far for the hydro case, in this paper we propose a novel Key Performance Indicator (KPI) that we have recently developed and tested on operating hydropower plants. In particular, we show that after more than one year of operation it has been able to identify several faults, and to support the operation and maintenance tasks of plant operators. Also, we show that the proposed KPI outperforms conventional multivariable process control charts, like the Hotelling $t_2$ index.
A Scalable Predictive Maintenance Model for Detecting Wind Turbine Component Failures Based on SCADA Data
Oct 22, 2019
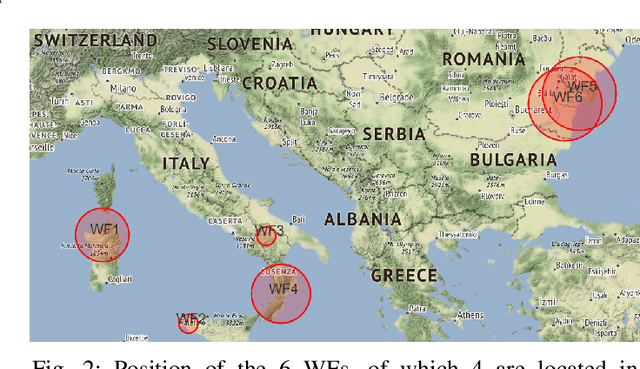


Abstract:In this work, a novel predictive maintenance system is presented and applied to the main components of wind turbines. The proposed model is based on machine learning and statistical process control tools applied to SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) data of critical components. The test campaign was divided into two stages: a first two years long offline test, and a second one year long real-time test. The offline test used historical faults from six wind farms located in Italy and Romania, corresponding to a total of 150 wind turbines and an overall installed nominal power of 283 MW. The results demonstrate outstanding capabilities of anomaly prediction up to 2 months before device unscheduled downtime. Furthermore, the real-time 12-months test confirms the ability of the proposed system to detect several anomalies, therefore allowing the operators to identify the root causes, and to schedule maintenance actions before reaching a catastrophic stage.
A Machine Learning Model for Long-Term Power Generation Forecasting at Bidding Zone Level
Oct 08, 2019
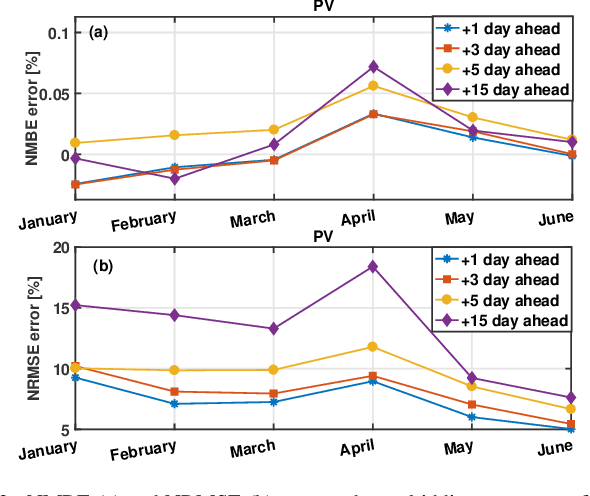
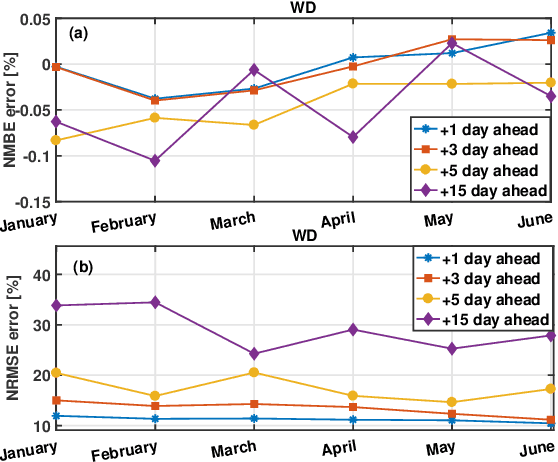
Abstract:The increasing penetration level of energy generation from renewable sources is demanding for more accurate and reliable forecasting tools to support classic power grid operations (e.g., unit commitment, electricity market clearing or maintenance planning). For this purpose, many physical models have been employed, and more recently many statistical or machine learning algorithms, and data-driven methods in general, are becoming subject of intense research. While generally the power research community focuses on power forecasting at the level of single plants, in a short future horizon of time, in this time we are interested in aggregated macro-area power generation (i.e., in a territory of size greater than 100000 km^2) with a future horizon of interest up to 15 days ahead. Real data are used to validate the proposed forecasting methodology on a test set of several months.
Day-Ahead Hourly Forecasting of Power Generation from Photovoltaic Plants
Feb 26, 2019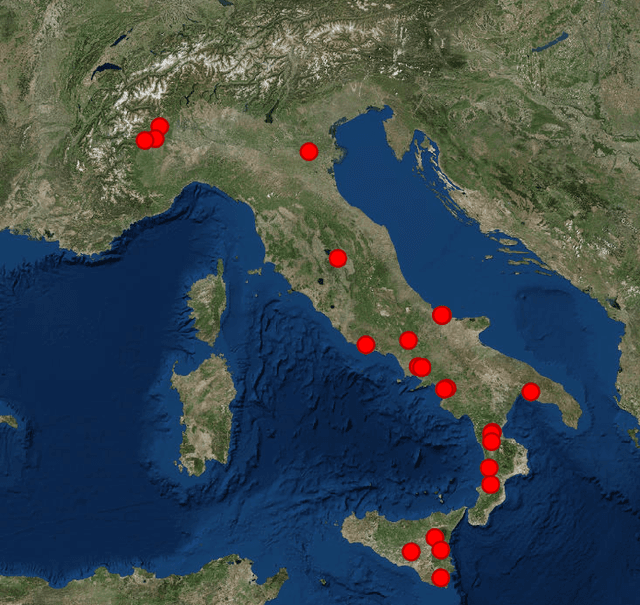
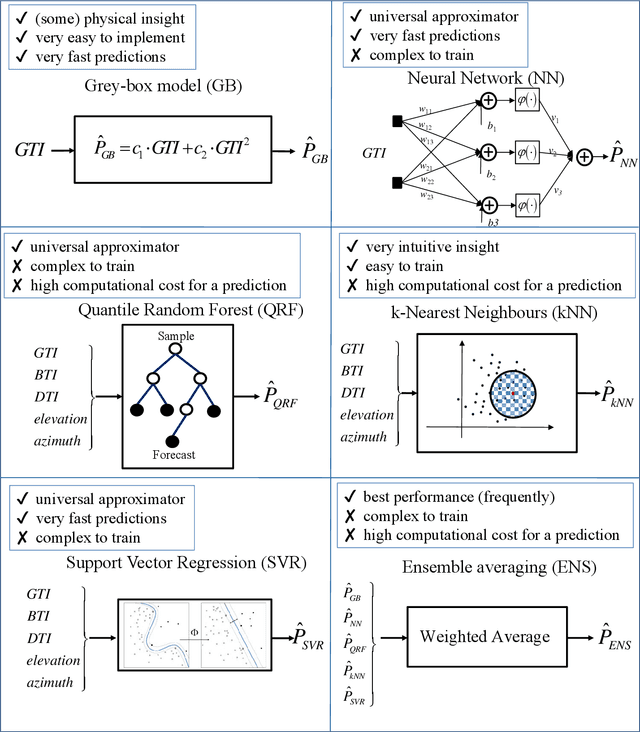
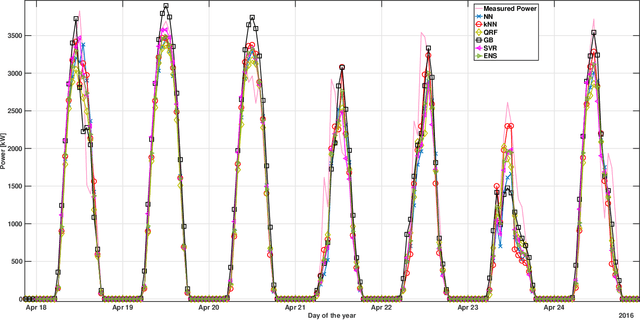
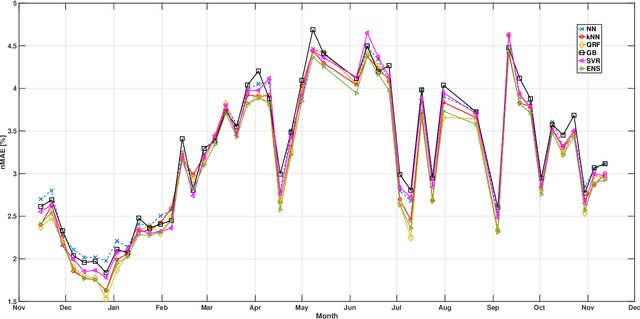
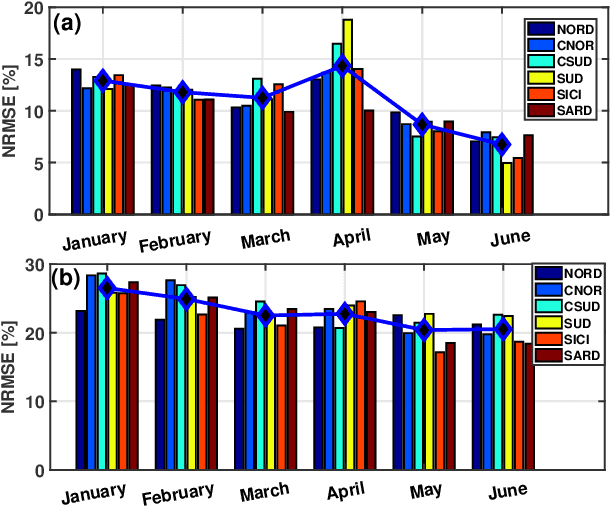
Abstract:The ability to accurately forecast power generation from renewable sources is nowadays recognised as a fundamental skill to improve the operation of power systems. Despite the general interest of the power community in this topic, it is not always simple to compare different forecasting methodologies, and infer the impact of single components in providing accurate predictions. In this paper we extensively compare simple forecasting methodologies with more sophisticated ones over 32 photovoltaic plants of different size and technology over a whole year. Also, we try to evaluate the impact of weather conditions and weather forecasts on the prediction of PV power generation.
* Preprint of IEEE Transactions of Sustainable Energy, Vol. 9, Issue 2, pp. 831 - 842 (2018)
An Assessment on the Use of Stationary Vehicles as a Support to Cooperative Positioning
Feb 26, 2015
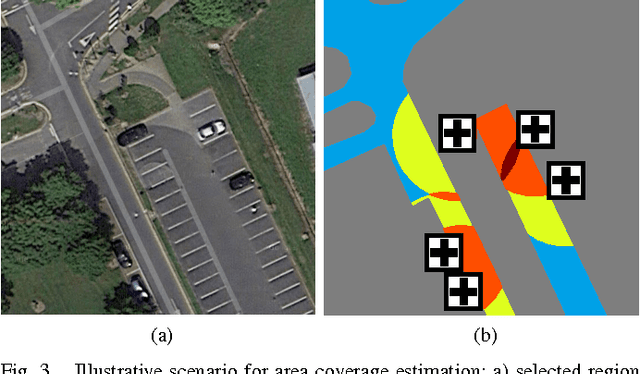
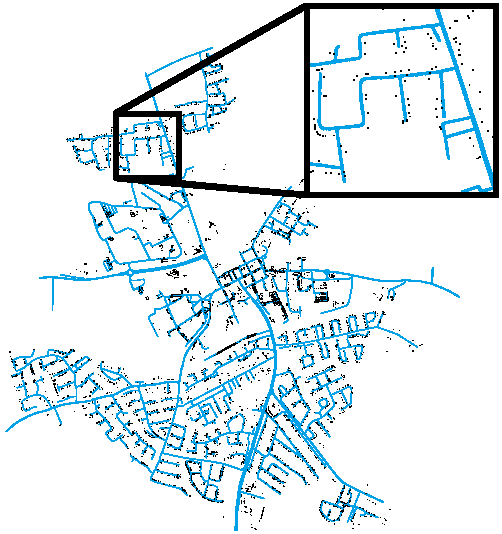
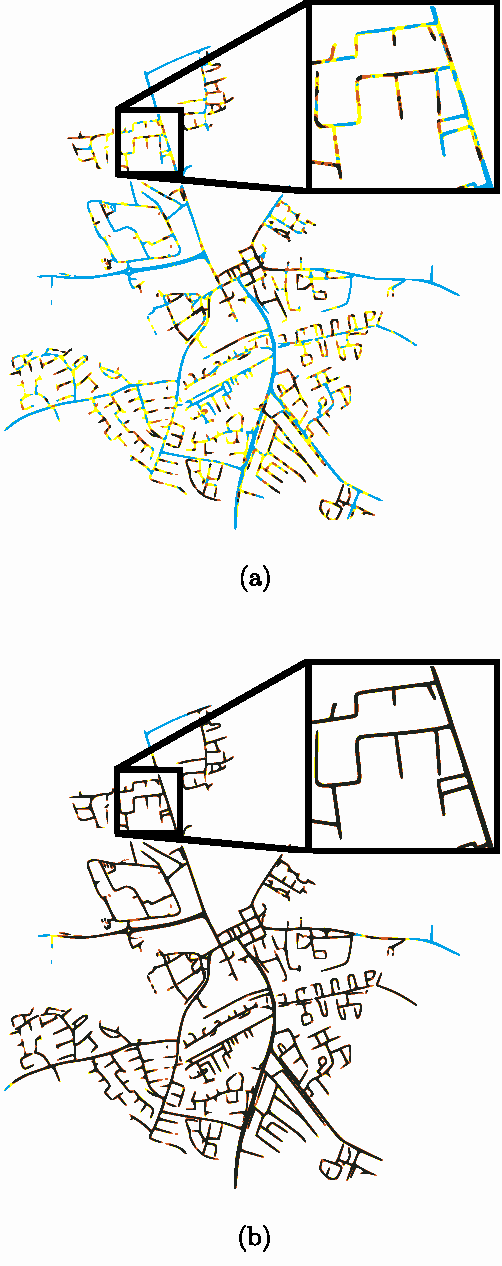
Abstract:In this paper, we consider the use of stationary vehicles as tools to enhance the localisation capabilities of moving vehicles in a VANET. We examine the idea in terms of its potential benefits, technical requirements, algorithmic design and experimental evaluation. Simulation results are given to illustrate the efficacy of the technique.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge